
Silicon Forest is a Washington County cluster of high-tech companies located in the Portland metropolitan area in the U.S. state of Oregon. The term most frequently refers to the industrial corridor between Beaverton and Hillsboro in northwest Oregon. The high-technology industry accounted for 19 percent of Oregon's economy in 2005, and the Silicon Forest name has been applied to the industry throughout the state in such places as Corvallis, Bend, and White City. Nevertheless, the name refers primarily to the Portland metropolitan area, where about 1,500 high-tech firms were located as of 2006.

Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI), also known simply as Analog, is an American multinational semiconductor company specializing in data conversion, signal processing, and power management technology, headquartered in Wilmington, Massachusetts.
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation is an American semiconductor company specializing in the design and manufacturing of low power field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). Headquartered in the Silicon Forest area of Hillsboro, Oregon, the company also has operations in San Jose, Calif., Shanghai, Manila, Penang, and Singapore. Lattice Semiconductor has more than 1000 employees and an annual revenue of more than $660 million as of 2022. The company was founded in 1983 and went public in 1989. It is traded on the Nasdaq stock exchange under the symbol LSCC.

Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a Japanese manufacturer of electronic components, based in Nagaokakyo, Kyoto. It produces ceramic passive electronic components, primarily capacitors, and has a majority marketshare worldwide in ceramic filters, high-frequency parts, and sensors. As of March 31, 2013 Murata Manufacturing has 24 subsidiaries in Japan and 52 overseas in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Germany, France, Italy, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, the Netherlands, Spain, Hungary, Finland, China, Taiwan, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, Hong Kong, Vietnam and India.
A thin-film bulk acoustic resonator is a device consisting of a piezoelectric material manufactured by thin film methods between two conductive – typically metallic – electrodes and acoustically isolated from the surrounding medium. The operation is based on the piezoelectricity of the piezolayer between the electrodes.
Soitec is an international company based in France, that manufactures substrates used in the creation of semiconductors.
RF Micro Devices, was an American company that designed and manufactured high-performance radio frequency systems for applications that drive wireless and broadband communications. Headquartered in Greensboro, North Carolina, RFMD traded on the NASDAQ under the symbol RFMD. The Company was founded in Greensboro, North Carolina, in 1991. RF Micro had 3500 employees, 1500 of them in Guilford County, North Carolina.
ON Semiconductor Corporation is an American semiconductor supplier company, based in Scottsdale, Arizona. Products include power and signal management, logic, discrete, and custom devices for automotive, communications, computing, consumer, industrial, LED lighting, medical, military/aerospace and power applications. onsemi runs a network of manufacturing facilities, sales offices and design centers in North America, Europe, and the Asia Pacific regions. Based on its 2016 revenues of $3.907 billion, onsemi ranked among the worldwide top 20 semiconductor sales leaders, and was ranked No. 483 on the 2022 Fortune 500 based on its 2021 sales.
Elemental was an American software company based in Portland, Oregon, and active from 2006 to 2015. It was founded by three engineers formerly of the semiconductor company Pixel works: Sam Blackman (CEO), Jesse Rosenzweig (CTO), and Brian Lewis. In 2015, it was acquired by Amazon.

Veeco Instruments Inc. is a global capital equipment supplier, headquartered in the U.S., that designs and builds processing systems used in semiconductor and compound semiconductor manufacturing, data storage and scientific markets for applications such as advanced packaging, photonics, power electronics and display technologies.

MACOM Technology Solutions, Inc. is a developer and producer of radio, microwave, and millimeter wave semiconductor devices and components. The company is headquartered in Lowell, Massachusetts, and in 2005 was Lowell's largest private employer. MACOM is certified to the ISO 9001 international quality standard and ISO 14001 environmental standard. The company has design centers and sales offices in North America, Europe, Asia and Australia.
Electro Scientific Industries, Inc. (ESI) is an American high technology company headquartered in the Portland, Oregon, metropolitan area, specifically in Beaverton, Oregon, since 2021, but from 1963–2021, it was based in the unincorporated Cedar Mill area just north of Beaverton. ESI is a developer and supplier of photonic and laser systems for microelectronics manufacturers. Founded in 1944, it is the oldest high-tech company in Oregon. Along with Tektronix, and later Intel, it has spawned numerous technology-based companies in the Portland area, an area known as the Silicon Forest. From 1983 to 2019, shares in the company were publicly traded on NASDAQ, under the ticker symbol ESIO.
Cascade Microtech is a semiconductor test equipment manufacturer based in Beaverton in the Portland metropolitan area of the United States. Founded in 1983, the Oregon-based company employs nearly 400 people. Formerly publicly traded company as CSCD on the NASDAQ, the company is now fully merged with FormFactor, Inc.

GreenPeak Technologies was an Utrecht, Netherlands-based fabless company developing semiconductor products and software for the IEEE 802.15.4 and Zigbee wireless market segment. Zigbee technology is used for Smart Home data communications and to facilitate the Internet of Things, the term used to refer to devices designed to be operated and managed by internet-enabled controllers and management systems.

Qorvo, Inc. is an American multinational company specializing in products for wireless, wired, and power markets. The company was created by the merger of TriQuint Semiconductor and RF Micro Devices, which was announced in 2014 and completed on January 1, 2015. It trades on Nasdaq under the ticker symbol QRVO. The headquarters for the company originally were in both Hillsboro, Oregon, and Greensboro, North Carolina, but in mid-2016 the company began referring to its North Carolina site as its exclusive headquarters.

Walden C. "Wally" Rhines is an American engineer and businessman. Rhines is President and CEO of Cornami, Inc., a fabless semiconductor company focused on fully homomorphic encryption. Previously, he was President and CEO of Mentor Graphics, a Siemens Business for 23 years and Executive VP of the Semiconductor Group of Texas Instruments for 21 years. Rhines was named overall CEO of the Year by Portland Business Journal in 2012 and Oregon Technology Executive of the Year by the Technology Association of Oregon in 2003. He was named an IEEE Fellow in 2017.
Ampleon is a global semiconductor manufacturer headquartered in Nijmegen (Gelderland), Netherlands and the former RF Power business division of NXP Semiconductors.
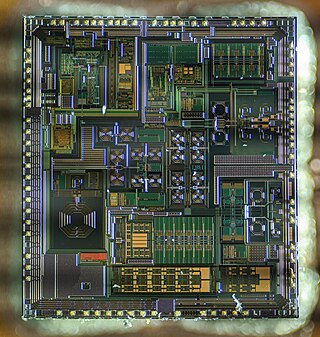
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wireless telecommunications, such as cellular networks, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS receivers, broadcasting, vehicular communication systems, and the radio transceivers in all modern mobile phones and wireless networking devices. RF CMOS technology was pioneered by Pakistani engineer Asad Ali Abidi at UCLA during the late 1980s to early 1990s, and helped bring about the wireless revolution with the introduction of digital signal processing in wireless communications. The development and design of RF CMOS devices was enabled by van der Ziel's FET RF noise model, which was published in the early 1960s and remained largely forgotten until the 1990s.
Filtronic is a UK public limited company (PLC) that is AIM-listed on the London Stock Exchange (FTC.L). It is a designer and manufacturer of RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave (mmWave) components and subsystems for applications in telecommunications, defence, space and transport. It is headquartered at NETPark in County Durham with other facilities in Leeds and Manchester and a US manufacturing site in Salisbury, MD.








