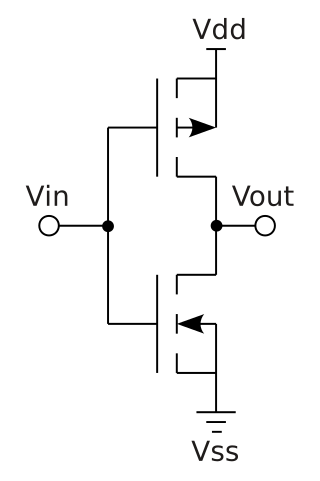
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, RF circuits, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.

Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI), also known simply as Analog, is an American multinational semiconductor company specializing in data conversion, signal processing, and power management technology, headquartered in Wilmington, Massachusetts.
Silicon on sapphire (SOS) is a hetero-epitaxial process for metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) manufacturing that consists of a thin layer of silicon grown on a sapphire wafer. SOS is part of the silicon-on-insulator (SOI) family of CMOS technologies.

A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die. Their usage has grown dramatically with the increased use of cell phones, telecommunications, portable electronics, and automobiles with electronics and digital sensors.

A mobile phone feature is a capability, service, or application that a mobile phone offers to its users. Mobile phones are often referred to as feature phones, and offer basic telephony. Handsets with more advanced computing ability through the use of native code try to differentiate their own products by implementing additional functions to make them more attractive to consumers. This has led to great innovation in mobile phone development over the past 20 years.
Maxim Integrated Products, Inc., a subsidiary of Analog Devices, designs, manufactures, and sells analog and mixed-signal integrated circuits for the automotive, industrial, communications, consumer, and computing markets. Maxim's product portfolio includes power and battery management ICs, sensors, analog ICs, interface ICs, communications solutions, digital ICs, embedded security, and microcontrollers. The company is headquartered in San Jose, California, and has design centers, manufacturing facilities, and sales offices worldwide.
A thin-film bulk acoustic resonator is a device consisting of a piezoelectric material manufactured by thin film methods between two conductive – typically metallic – electrodes and acoustically isolated from the surrounding medium. The operation is based on the piezoelectricity of the piezolayer between the electrodes.
Edholm's law, proposed by and named after Phil Edholm, refers to the observation that the three categories of telecommunication, namely wireless (mobile), nomadic and wired networks (fixed), are in lockstep and gradually converging. Edholm's law also holds that data rates for these telecommunications categories increase on similar exponential curves, with the slower rates trailing the faster ones by a predictable time lag. Edholm's law predicts that the bandwidth and data rates double every 18 months, which has proven to be true since the 1970s. The trend is evident in the cases of Internet, cellular (mobile), wireless LAN and wireless personal area networks.

TriQuint Semiconductor was a semiconductor company that designed, manufactured, and supplied high-performance RF modules, components and foundry services. The company was founded in 1985 in Beaverton, Oregon before moving to neighboring Hillsboro, Oregon. In February 2014, Greensboro, North Carolina-based RF Micro Devices and TriQuint announced a merger in which the new company would be Qorvo, Inc., with the merger completed on January 1, 2015.

Asad Ali Abidi is a Pakistani-American electrical engineer. He serves as a tenured professor at University of California, Los Angeles, and is the inaugural holder of the Abdus Salam Chair at the Lahore University of Management Sciences (LUMS). He is best known for pioneering RF CMOS technology during the late 1980s to early 1990s. As of 2008, the radio transceivers in all wireless networking devices and modern mobile phones are mass-produced as RF CMOS devices.
LDMOS is a planar double-diffused MOSFET used in amplifiers, including microwave power amplifiers, RF power amplifiers and audio power amplifiers. These transistors are often fabricated on p/p+ silicon epitaxial layers. The fabrication of LDMOS devices mostly involves various ion-implantation and subsequent annealing cycles. As an example, the drift region of this power MOSFET is fabricated using up to three ion implantation sequences in order to achieve the appropriate doping profile needed to withstand high electric fields.
A radio-frequency integrated circuit, or RFIC, is an electrical integrated circuit operating in a frequency range suitable for wireless transmission. Applications for RFICs include radar and communications.

pSemi, is a San Diego–based manufacturer of high-performance RF CMOS integrated circuits. A Murata Manufacturing company since December 2014, the company's products are used in aerospace and defense, broadband, industrial, mobile wireless device, test and measurement equipment and wireless infrastructure markets. Their UltraCMOS technology is a proprietary implementation of silicon on sapphire (SOS) and silicon on insulator (SOI) substrates that enables high levels of monolithic integration.
IQE PLC is a British semiconductor company founded 1988 in Cardiff, Wales, which manufactures advanced epitaxial wafers.
Ronald Reedy is an American businessman, scientist and researcher. In the semiconductor industry, he advanced silicon on sapphire (SOS) and CMOS technology.

Qorvo, Inc. is an American multinational company specializing in products for wireless, wired, and power markets. The company was created by the merger of TriQuint Semiconductor and RF Micro Devices, which was announced in 2014 and completed on January 1, 2015. It trades on Nasdaq under the ticker symbol QRVO. The headquarters for the company originally were in both Hillsboro, Oregon, and Greensboro, North Carolina, but in mid-2016 the company began referring to its North Carolina site as its exclusive headquarters.
Natalino Camilleri from the Nitero, Inc., Austin, TX was named Fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in 2015 for leadership in radio frequency integrated circuits and systems.
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wireless telecommunications, such as cellular networks, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS receivers, broadcasting, vehicular communication systems, and the radio transceivers in all modern mobile phones and wireless networking devices. RF CMOS technology was pioneered by Pakistani engineer Asad Ali Abidi at UCLA during the late 1980s to early 1990s, and helped bring about the wireless revolution with the introduction of digital signal processing in wireless communications. The development and design of RF CMOS devices was enabled by van der Ziel's FET RF noise model, which was published in the early 1960s and remained largely forgotten until the 1990s.
Filtronic is a UK public limited company (PLC) that is AIM-listed on the London Stock Exchange (FTC.L). It is a designer and manufacturer of RF, microwave, and millimeter-wave (mmWave) components and subsystems for applications in telecommunications, defence, space and transport. It is headquartered at NETPark in County Durham with other facilities in Leeds and Manchester and a US manufacturing site in Salisbury, MD.









