
The 2003 Atlantic hurricane season was a very active season with tropical cyclogenesis occurring before and after the official bounds of the season—the first such occurrence since the 1970 season. The season produced 21 tropical cyclones, of which 16 developed into named storms; seven of those attained hurricane status, of which three reached major hurricane status. The strongest hurricane of the season was Hurricane Isabel, which reached Category 5 status on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale northeast of the Lesser Antilles; Isabel later struck North Carolina as a Category 2 hurricane, causing $3.6 billion in damage and a total of 51 deaths across the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States.

The 2002 Atlantic hurricane season was a near-average Atlantic hurricane season. It officially started on June 1, 2002, and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally limit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones develop in the Atlantic Ocean. The season produced fourteen tropical cyclones, of which twelve developed into named storms; four became hurricanes, and two attained major hurricane status. While the season's first cyclone did not develop until July 14, activity quickly picked up: eight storms developed in the month of September. It ended early however, with no tropical storms forming after October 6—a rare occurrence caused partly by El Niño conditions. The most intense hurricane of the season was Hurricane Isidore with a minimum central pressure of 934 mbar, although Hurricane Lili attained higher winds and peaked at Category 4 whereas Isidore only reached Category 3. However, Lili had a minimum central pressure of 938 mbar.

The 2001 Atlantic hurricane season was a fairly active Atlantic hurricane season that produced 17 tropical cyclones, 15 named storms, nine hurricanes, and four major hurricanes. The season officially lasted from June 1, 2001, to November 30, 2001, dates which by convention limit the period of each year when tropical cyclones tend to form in the Atlantic Ocean basin. The season began with Tropical Storm Allison on June 4, and ended with Hurricane Olga, which dissipated on December 6.
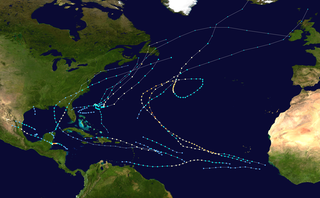
The 2000 Atlantic hurricane season was a fairly active hurricane season, but featured the latest first named storm in a hurricane season since 1992. The hurricane season officially began on June 1, and ended on November 30. It was slightly above average due to a La Niña weather pattern although most of the storms were weak. It was also the only season to have two of the storms affect Ireland. The first cyclone, Tropical Depression One, developed in the southern Gulf of Mexico on June 7 and dissipated after an uneventful duration. However, it would be almost two months before the first named storm, Alberto, formed near Cape Verde; Alberto also dissipated with no effects on land. Several other tropical cyclones—Tropical Depression Two, Tropical Depression Four, Chris, Ernesto, Nadine, and an unnamed subtropical storm—did not impact land. Five additional storms—Tropical Depression Nine, Florence, Isaac, Joyce, and Leslie—minimally affected land areas.

Tropical Storm Odette was a rare off-season tropical cyclone that hit the island of Hispaniola in early December 2003. As the fifteenth named storm of the 2003 Atlantic hurricane season, Odette formed near the coast of Panama a few days after the official end of the Atlantic hurricane season ended on November 30, and ultimately made landfall on the Dominican Republic as a moderate tropical storm, before becoming extratropical on December 7, dissipating two days later.
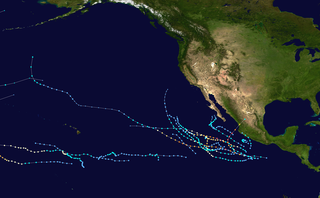
The 2002 Pacific hurricane season was a near–average season which produced fifteen named storms. Eight hurricanes formed, including a record-equaling three Category 5 hurricanes, a record it shares with the 1994 and 2018 seasons. It was also a near-average season in terms of accumulated cyclone energy (ACE), having an ACE of 125. The season officially began on May 15, 2002 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1, 2002 in the Central Pacific; both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclone formation occurs in these regions of the Pacific. The first system of the 2002 season, Hurricane Alma, formed on May 24, and the last, Tropical Depression Sixteen-E, dissipated on November 16.

The 2000 Pacific hurricane season was an above-average Pacific hurricane season, although most of the storms were weak and short-lived. There were few notable storms this year. Tropical storms Miriam, Norman, and Rosa all made landfall in Mexico with minimal impact. Hurricane Daniel briefly threatened the U.S. state of Hawaii while weakening. Hurricane Carlotta was the strongest storm of the year and the second-strongest June hurricane in recorded history. Carlotta killed 18 people when it sank a freighter. Overall, the season was significantly more active than the previous season, with 19 tropical storms. In addition, six hurricanes developed. Furthermore, there were total of two major hurricanes.

The 2007 Atlantic hurricane season was the first season since 2003 to feature tropical activity both before and after the official bounds of the season. There were an above-average number of named storms during the season – 15, however many storms were weak and short-lived. Despite the predominance of weak systems, this was the first season on record to feature more than one Category 5 landfalling hurricane. This would not happen again until 2017. It produced 17 tropical cyclones, 15 tropical storms, six hurricanes, and two major hurricanes. It officially started on June 1 and ended on November 30, dates which conventionally delimit the period during which most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic Ocean, although as shown by Subtropical Storm Andrea and Tropical Storm Olga in early May and early December, respectively, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. The first system, Subtropical Storm Andrea, developed on May 9, while the last storm, Tropical Storm Olga, dissipated on December 13. The most intense hurricane, Dean, was, at the time, the third most intense landfalling Atlantic storm on record. It was the second on record in which an Atlantic hurricane, Felix, and an eastern Pacific hurricane, Henriette, made landfall on the same day. September had a then record-tying eight storms, until it was surpassed in 2020. However, the strengths and durations of most of the storms were low.

Tropical Storm Chantal was a North Atlantic tropical cyclone that moved across the Caribbean Sea in August 2001. The fourth depression and third named storm of the 2001 Atlantic hurricane season, Chantal developed from a tropical wave on August 14 in the tropical Atlantic Ocean. It tracked rapidly westward for much of its duration, and after degenerating into a tropical wave, it passed through the Windward Islands. Chantal reached a peak intensity of 70 mph (110 km/h) twice in the Caribbean Sea, and each time it was anticipated to attain hurricane status; however, wind shear and later land interaction prevented strengthening to hurricane status. On August 21 Chantal, moved ashore near the border of Mexico and Belize, before dissipating on the next day.

Tropical Storm Helene was a long-lived tropical cyclone that oscillated for ten days between a tropical wave and a 70 mph (110 km/h) tropical storm. It was the twelfth tropical cyclone and eighth tropical storm of the 2000 Atlantic hurricane season, forming on September 15 east of the Windward Islands. After degenerating into a tropical wave, the system produced flooding and mudslides in Puerto Rico. It reformed into a tropical depression on September 19 south of Cuba, and crossed the western portion of the island the next day while on the verge of dissipation. However, it intensified into a tropical storm in the Gulf of Mexico, reaching its peak intensity while approaching the northern Gulf Coast.

The 2012 Pacific hurricane season was a moderately active Pacific hurricane season that saw an unusually high number of tropical cyclones pass west of the Baja California Peninsula. The season officially began on May 15 in the eastern Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the central Pacific (from 140°W to the International Date Line, north of the equator; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in these regions of the Pacific Ocean. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year. This season's first system, Tropical Storm Aletta, formed on May 14, and the last, Tropical Storm Rosa, dissipated on November 3.

The 2006 Pacific hurricane season was the first above-average season since 1997 which produced twenty-five tropical cyclones, with nineteen named storms, though most were rather weak and short-lived. There were eleven hurricanes, of which six became major hurricanes. Following the inactivity of the previous seasons, forecasters predicted that season would be only slightly above active. It was also the first time since 2003 in which one cyclone of at least tropical storm intensity made landfall. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year.

Hurricane Hernan was fourth and final tropical cyclone to strike Mexico at hurricane intensity during the 1996 Pacific hurricane season. The thirteenth tropical cyclone, eighth named storm, and fifth hurricane of the season, Hernan developed as a tropical depression from a tropical wave to the south of Mexico on September 30. The depression quickly strengthened, and became Tropical Storm Hernan later that day. Hernan curved north-northwestward the following day, before eventually turning north-northeastward. Still offshore of the Mexican coast on October 2, Hernan intensified into a hurricane. Six hours later, Hernan attained its peak as an 85 mph (140 km/h) Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale (SSHWS). After weakening somewhat, on 1000 UTC October 3, Hurricane Hernan made landfall near Barra de Navidad, Jalisco, with winds of 75 mph (120 km/h). Only two hours after landfall, Hernan weakened to a tropical storm. By October 4, Tropical Storm Hernan had weakened into a tropical depression, and dissipated over Nayarit on the following day.

Hurricane Virgil was a late season hurricane of the 1992 Pacific hurricane season that struck southwestern Mexico in October 1992. Forming from a tropical wave that left Africa on September 13, it slowly developed into a tropical depression. It soon strengthened into Tropical Storm Virgil, and rapidly intensified into a hurricane on October 2. Continuing to intensify, the hurricane attained major hurricane strength, and peaked as a Category 4 hurricane off the coast of Mexico. Shortly before landfall, it weakened to a Category 2 hurricane, and it dissipated on October 5. Damage was generally minimal, though one person was reported missing.

Tropical Storm Odile was a late season tropical storm that formed during the 2008 Pacific hurricane season and affected parts of southern Mexico. A tropical depression formed on October 8, and became Tropical Storm Odile 18 hours later. The storm paralleled the south coast of Mexico, with the center located only several miles offshore. After peaking in intensity, increasing southeasterly vertical wind shear induced a trend of rapid weakening on the storm. Correspondingly, Odile was downgraded to a tropical depression early on 12 October, subsequently degenerating into a remnant low about 55 mi (85 km) south of Manzanillo, Colima. From thereon, the low proceeded slowly south-southwestward before dissipating on October 13. Since Odile stayed at sea, its effects along coastlines were limited. The most notable damages were caused by flooding along the southern coast of Mexico, mostly in Chiapas, Oaxaca, Guerrero and Michoacán. The exact amount of damage, however, remains unknown, and no fatalities were reported as a result of the storm.

Tropical Storm Carlos was the first of five tropical cyclones to make landfall during the 2003 Pacific hurricane season. It formed on June 26 from a tropical wave to the south of Mexico. It quickly strengthened as it approached the coast, and early on June 27 Carlos moved ashore in Oaxaca with winds of 65 mph (105 km/h). The storm rapidly deteriorated to a remnant low, which persisted until dissipating on June 29. Carlos brought heavy rainfall to portions of southern Mexico, peaking at 337 mm (13.3 in) in two locations in Guerrero. Throughout its path, the storm damaged about 30,000 houses, with a monetary damage total of 86.7 million pesos. At least nine people were killed throughout the country, seven due to mudslides and two from river flooding; there was also a report of two missing fishermen.

The 2017 Pacific hurricane season was an above average Pacific hurricane season in terms of named storms, though less active than the previous three, featuring eighteen named storms, nine hurricanes, and four major hurricanes. Despite the considerable amount of activity, most of the storms were weak and short-lived. The season officially started on May 15 in the eastern Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the respective regions. However, the formation of tropical cyclones is possible at any time of the year, as illustrated in 2017 by the formation of the season's first named storm, Tropical Storm Adrian, on May 9. At the time, this was the earliest formation of a tropical storm on record in the eastern Pacific basin proper. The season saw near-average activity in terms of accumulated cyclone energy (ACE), in stark contrast to the extremely active seasons in 2014, 2015, and 2016; and for the first time since 2012, no tropical cyclones formed in the Central Pacific basin. However, for the third year in a row, the season featured above-average activity in July, with the ACE value being the fifth highest for the month. Damage across the basin reached $375.28 million (2017 USD), while 45 people were killed by the various storms.

Tropical Storm Matthew was a weak but deadly and destructive tropical cyclone which made landfall in Central America during the 2010 Atlantic hurricane season. The fifteenth tropical cyclone and thirteenth named storm of the year, Matthew formed on September 23 and lost its tropical characteristics in the morning of September 26. However, its remnants continued to produce life-threatening rain over parts of Central America as it dissipated.

Hurricane Ernesto was a Category 2 hurricane and a damaging tropical cyclone that affected several Caribbean Islands and areas of Central America during August 2012. The fifth named storm and second hurricane of the 2012 Atlantic hurricane season, Ernesto originated from a tropical wave that emerged off the west coast of Africa in late July. Moving westward, the system developed into a tropical depression in the central Atlantic, and further into a tropical storm prior to entering the Caribbean Sea. The system encountered high wind shear south of Jamaica but subsequently reached its peak intensity as a Category 2 hurricane as it made landfall on the Yucatán Peninsula. Ernesto briefly emerged in the Bay of Campeche as a strong tropical storm before dissipating over the mountainous terrain of Mexico. The remnant circulation emerged in the eastern Pacific basin, contributing to the formation of Tropical Storm Hector.

Hurricane Ingrid was one of two tropical cyclones, along with Hurricane Manuel, to strike Mexico within a 24-hour period, the first such occurrence since 1958. Ingrid was the ninth named storm and second hurricane of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season. It formed on September 12 in the Gulf of Mexico from a broad disturbance that also spawned Manuel in the eastern Pacific. After initially moving westward toward Veracruz, Ingrid turned northeastward away from the coast. Favorable conditions allowed it to attain hurricane status on September 14, and the next day Ingrid attained peak winds of 140 km/h (85 mph). Subsequently, increased wind shear weakened the convection as the storm turned more to the northwest and west. On September 16, Ingrid made landfall just south of La Pesca, Tamaulipas in northeastern Mexico as a strong tropical storm, and dissipated the next day. The hurricane was also the last one to form in the Gulf of Mexico until Hurricane Hermine in 2016.























