
The 2003 Pacific typhoon season was a slightly below average yearlong period of tropical cyclogenesis exhibiting the development of 45 tropical depressions, of which 21 became named storms; of those, 14 became typhoons. Though every month with the exception of February and March featured tropical activity, most storms developed from May through October. During the season, tropical cyclones affected the Philippines, Japan, China, the Korean Peninsula, Indochina, and various islands in the western Pacific.

Typhoon Longwang, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Maring, was the deadliest tropical cyclone to impact China during the 2005 Pacific typhoon season. Longwang was first identified as a tropical depression on September 25 north of the Mariana Islands. Moving along a general westward track, the system quickly intensified and reached typhoon status on September 27. After reaching Category 4-equivalent intensity on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, adverse atmospheric conditions along with internal structural changes resulted in temporary weakening. The structural change culminated in Longwang becoming an annular typhoon and prompted re-intensification. The storm attained peak strength with winds of 175 km/h (109 mph) and a pressure of 930 mbar on October 1 as it approached Taiwan. Interaction with the mountainous terrain of the island and further structural changes caused some weakening before the typhoon made landfall near Hualien City early on October 2. Crossing the island in six hours, Longwang emerged over the Taiwan Strait before moving onshore again later that day, this time in Fujian Province, China as a minimal typhoon. Once over mainland China, the storm quickly weakened and ultimately dissipated late on October 3.

The 1990 Pacific typhoon season was another active season. It has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1990, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean.

The 1989 Pacific typhoon season was the first of six consecutive years of above-average activity in the Western Pacific. It was an extremely active season spawning 32 tropical storms, 20 typhoons and five super typhoons. It has no official bounds; it ran year-round in 1989, but most tropical cyclones tend to form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean between May and November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. The first storm, Winona, formed on January 15, while the final storm, Jack, dissipated on December 27. This season was also quite a deadly season that were caused by a few notable storms such as Tropical Storm Cecil, which was the worst storm to impact Vietnam in over 50 years, and Typhoon Gay, which directly impacted the Malay Peninsula as the worst typhoon in 35 years. Both of these storms make up around half of the total fatalities of the entire season alone.

Typhoon Ike, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Nitang, was the second deadliest tropical cyclone in the 20th century in the Philippines. Ike originated from an area of disturbed weather southeast of Guam on August 21, 1984, and five days later, developed into a tropical depression. Following an increase in organization, the depression attained tropical storm intensity on August 27. Initially tracking west-southwest, the storm gradually gained strength as wind shear resulted relaxed and Ike became a typhoon on August 30. Continuing to rapidly intensity, Ike turned west and attained peak intensity on September 1, with the Japan Meteorological Agency estimating winds of 170 km/h (105 mph). At around 14:00 UTC that day, Ike made landfall on the northeastern tip of Mindanao. The cyclone emerged into the South China Sea on September 3 as a tropical storm before re-intensifying into a typhoon and moving onshore Hainan. Ike then struck the Chinese mainland as a tropical storm in Guangxi and dissipated on September 6.

Typhoon Alex, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Etang, affected the Taiwan, China, and South Korea during July 1987. Typhoon Alex developed from the monsoon trough that spawned a tropical disturbance late on July 21 southwest of Guam which organized into a tropical depression shortly thereafter. The system steadily became better organized, and the next day, a tropical depression had developed. Satellite intensity estimates gradually increased, and on July 23, the depression intensified into Tropical Storm Alex. After initially tracking west-northwest, Tropical Storm Alex started tracking northwest. An eye developed on July 24, and on the next day, Alex was classified as a typhoon, when Alex attained its peak intensity of 120 km/h (75 mph) and a minimum barometric pressure of 970 mbar (29 inHg). Alex weakened while tracking more northward, though interaction with Taiwan resulted in a more westward track starting on July 27. The storm struck near Shanghai as a tropical storm, and weakened over land, although it remained identifiable through August 2.

Typhoon Amy, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Gening, was the second typhoon to strike China in a week during mid-July 1991. An area of convection was first observed on July 13 within the vicinity of Yap. A tropical depression developed the next day. While initially tracking westward, the system slowly deepened, becoming Tropical Storm Amy on July 16. After briefly turning northwestward, Amy intensified into a typhoon on July 17. Continuing to intensify as it tracked through the Luzon Strait, Amy reached its peak intensity of 175 km/h (110 mph) on July 18. That evening, the typhoon began to show signs of weakening, although it was still believed to have been a typhoon when it made landfall in the province of Guangdong on July 19, becoming the strongest tropical cyclone to hit the province in 22 years. Once inland, the storm rapidly weakened, and by late on July 20, had dissipated completely.

Typhoon Clara, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Rubing, left flooding in the northern Philippines and southern China during September 1981. An area of disturbed weather was first detected on September 11 near Ponape. After moving westward, the system gradually became better organized and thunderstorm activity increased. On September 16, the system attained tropical storm status. Two days later, Clara attained typhoon intensity and subsequently began to deepen at a faster rate. On September 19, Clara reached maximum intensity, before making landfall along the northern tip of Luzon. Clara steadily weakened after interacting with land, but by late on September 20, Clara leveled off in intensity over the South China Sea. The next day, Clara moved ashore to the east-northeast of Hong Kong while still at typhoon intensity before rapidly dissipating over land.

Typhoon Sarah, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Openg, was a powerful typhoon that caused extensive damage along an erratic path across the Western Pacific in September 1989. Originating from a disturbance within a monsoon trough in early September, Sarah was first classified as a tropical depression near the Mariana Islands on September 5. Moving quickly westward, the depression soon strengthened into Tropical Storm Sarah. On September 8, the storm abruptly turned southward and temporarily attained typhoon status. Following a series of interactions with secondary areas of low pressure, the storm turned northward the following day. By September 11, Sarah entered a region favoring development and underwent a period of explosive intensification. At the end of this phase, the storm attained its peak intensity as a Category 4–equivalent typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale. The typhoon subsequently weakened rapidly and made two landfalls in Taiwan by September 12. After moving over the Taiwan Strait, Sarah made its final landfall in Eastern China on September 13 before dissipating the following day.

Typhoon Sinlaku was a damaging typhoon that affected Okinawa, Taiwan, and eastern China in September 2002. The 16th named storm of the 2002 Pacific typhoon season, Sinlaku formed on August 27 northeast of the Northern Marianas Islands. After initially moving to the north, it began a generally westward motion that it maintained for the rest of its duration. Sinlaku strengthened into a typhoon and attained its peak winds on August 31. Over the next few days, it fluctuated slightly in intensity while moving over or near the Ryukyu Islands. On September 4, the typhoon's eye crossed over Okinawa. It dropped heavy rainfall and produced strong winds that left over 100,000 people without power. Damage on the island was estimated at $14.3 million.

Typhoon Rammasun, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Florita, was the first of four typhoons to contribute to heavy rainfall and deadly flooding in the Philippines in July 2002. The fifth tropical cyclone of the 2002 Pacific typhoon season, Rammasun developed around the same time as Typhoon Chataan, only further to the west. The storm tracked northwestward toward Taiwan, and on July 2 it attained its peak intensity with winds of 155 km/h (96 mph). Rammasun turned northward, passing east of Taiwan and China. In Taiwan, the outer rainbands dropped rainfall that alleviated drought conditions. In China, the rainfall occurred after previously wet conditions, resulting in additional flooding, although damage was less than expected; there was about $85 million in crop and fishery damage in one province.

Tropical Storm Vongfong affected China after a deadly flood season. The 14th named storm of the 2002 Pacific typhoon season, Vongfong developed as a tropical depression on August 10. Initially it was disorganized due to hostile conditions, and it failed to intensify significantly before crossing the Philippine island of Luzon. There, flooding forced 3,500 people to evacuate their homes. In the Philippines, the storm killed 35 people and caused $3.3 million in damage.

Typhoon Wayne, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Katring, was an intense tropical cyclone that brought significant flooding to the Philippines in July 1983. The typhoon originated from an area of disturbed weather that formed far from land towards the end of July. Late on July 22, Wayne developed gale-force winds while moving west. The next day, it was estimated to have become a typhoon, and Wayne subsequently entered a period of rapid deepening. During the morning hours of July 24, the typhoon was estimated to have reached its peak intensity of 205 km/h (125 mph), but soon began to weaken due to interaction with land. By the time it moved ashore in southern China on July 25, Wayne had weakened considerably. After moving inland, Wayne weakened rapidly. The following day, Wayne was no longer a tropical cyclone.

Typhoon Fitow, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Quedan, was the strongest typhoon to make landfall in Mainland China during October since 1949. The 21st named storm of the 2013 Pacific typhoon season, Fitow developed on September 29 to the east of the Philippines. It initially tracked north-northwestward, gradually intensifying into a tropical storm and later to typhoon status, or with winds of at least 120 km/h (75 mph). Fitow later turned more to the west-northwest due to an intensifying ridge to the east, bringing the typhoon over the Ryukyu Islands with peak winds of 140 km/h (87 mph) on October 5. The next day, the typhoon struck China at Fuding in Fujian province. Fitow quickly weakened over land, dissipating on October 7.

Typhoon Gerald, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Neneng, affected the Philippines, Taiwan, and China during September 1987. A tropical depression developed on September 4, and within 24 hours, intensified into a tropical storm. After initially moving erratically within the Philippine Sea, Gerald moved west-northwest and then northwest while steadily deepening. Gerald obtained typhoon intensity on September 8, and the following day, attained maximum intensity. Shortly thereafter, the typhoon skirted southwestern Taiwan, which resulted in a steady weakening trend. On September 10, Gerald moved ashore north of Hong Kong near Amoy. Gerald dissipated the next day.
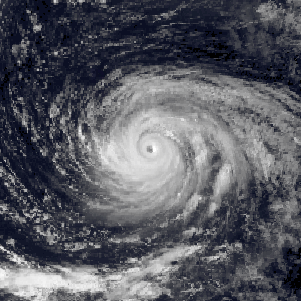
Typhoon Vera, known as Typhoon Loleng in the Philippines, affected Okinawa, China, and South Korea during August 1986. A tropical depression formed on August 13 and attained tropical storm intensity later that day. Initially, Vera meandered in the monsoon trough. On August 17, however, the system abruptly re-formed to east-northeast, and subsequently began to move east and then north. Vera became a typhoon on August 20, and peaked in intensity two days later. Typhoon Vera then turned west-northwest and slowly weakened as it approached Okinawa. After passing near the island, Vera turned north as it tracked east of China. The typhoon made landfall on South Korea on August 28 as a tropical storm, and the next day, transitioned into an extratropical cyclone.

Typhoon Joe, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Nitang, affected the Philippines, China, and Vietnam during July 1980. An area of disturbed weather formed near the Caroline Islands on July 14. Shower activity gradually became better organized, and two days later, the system was upgraded into a tropical depression. On July 18, the depression was classified as Tropical Storm Joe. Initially, Joe moved northwest, but began to turn to the west-northwest, anchored by a subtropical ridge to its north. Joe started to deepen at a faster clip, and attained typhoon intensity on July 19. The eye began to clear out, and the next day, Joe reached its highest intensity. Shortly thereafter, Joe moved ashore the Philippines. There, 31 people were killed and 300,000 others were directly affected. Around 5,000 homes were destroyed, resulting in an additional 29,000 homeless. Damage in the nation was estimated at $14.5 million (1980 USD).
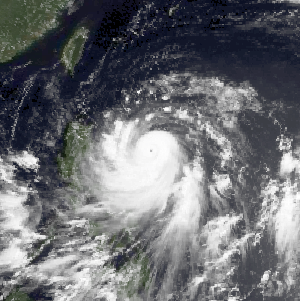
Typhoon Warren, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Huaning, struck the Philippines and China during July 1988. An area of disturbed weather developed within the vicinity of the Caroline Islands during the second week of July. A tropical depression developed southeast of Guam on July 12, and on the next day, intensified into a tropical storm. Tracking generally west-northwest, Warren deepened into a typhoon on July 14. The storm subsequently entered a period of rapid intensification, commencing with Warren reaching its highest intensity on July 16. The following evening, the typhoon brushed Luzon, resulting in a weakening trend, although Warren was still a typhoon when it made landfall near Shantou. Warren rapidly dissipated inland.

Typhoon Ofelia, known as Typhoon Bising in the Philippines, was the first of two typhoons in 1990 to directly affect the Philippines within a week. Typhoon Ofelia originated from an area of disturbed weather embedded in the monsoon trough situated near the Caroline Islands. Slowly organizing, the disturbance tracked westward, and was designated a tropical depression on June 15. After an increase in convection, the depression was upgraded into a tropical storm on June 17. On June 19, Ofelia turned northwest and after development of a central dense overcast, Ofelia was upgraded into a typhoon late on June 20. After turning north, Ofelia obtained its maximum intensity following the development of an eye. The typhoon skirted past the northeastern tip of Luzon and near the east coast of Taiwan, commencing a rapid weakening trend. On the evening on June 23, Ofelia struck the southern portion of Zhejiang. The storm then began to track north, recurving towards the Korean Peninsula. The storm tracked through the province of Jiangsu, and at 00:00 UTC on June 24, transitioned into an extratropical cyclone, only to merge with a frontal zone on June 25.

Typhoon Zeke, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Etang, was the first of two typhoons to make landfall in China within a week during mid-July 1991. An area of disturbed weather developed east of the Philippines towards the end of the first week of July. Tracking west-northwestward, the disturbance organized into a tropical depression on July 9. After tracking across the Philippines, where it left two people missing and injured three others, the depression intensified into a tropical storm on July 10. The storm steadily deepened as it moved across the South China Sea, and on July 12 it strengthened into a typhoon. While at its peak intensity of 120 km/h (75 mph), Zeke moved onshore at Hainan, where it began to weaken. The system tracked across Vietnam on July 13, and dissipated within two days after moving inland.





















