
Mycology is the branch of biology concerned with the study of fungi, including their taxonomy, genetics, biochemical properties, and use by humans. Fungi can be a source of tinder, food, traditional medicine, as well as entheogens, poison, and infection.

Edible mushrooms are the fleshy fruit bodies of several species of macrofungi. Edibility may be defined by criteria including the absence of poisonous effects on humans and desirable taste and aroma. Edible mushrooms are consumed for their nutritional and culinary value. Mushrooms, especially dried shiitake, are sources of umami flavor.

A truffle is the fruiting body of a subterranean ascomycete fungus, predominantly one of the many species of the genus Tuber. In addition to Tuber, over one hundred other genera of fungi are classified as truffles including Geopora, Peziza, Choiromyces, and Leucangium. These genera belong to the class Pezizomycetes and the Pezizales order. Several truffle-like basidiomycetes are excluded from Pezizales, including Rhizopogon and Glomus. Truffles are ectomycorrhizal fungi, so they are usually found in close association with tree roots. Spore dispersal is accomplished through fungivores, animals that eat fungi. These fungi have significant ecological roles in nutrient cycling and drought tolerance.
Fungiculture is the cultivation of fungi such as mushrooms. Cultivating fungi can yield foods, medicine, construction materials and other products. A mushroom farm is involved in the business of growing fungi.

The eastern bettong, also known as the southern or Tasmanian bettong, is a small, hopping, rat-like mammal native to grassy forests of southeastern Australia and Tasmania. A member of the rat-kangaroo family (Potoroidae), it is active at night and feeds on fungi and plant roots. Like most marsupials, it carries its young in a pouch. The eastern bettong is under pressure by introduced predators and habitat loss. The subspecies on mainland Australia is extinct, but populations of the Tasmanian subspecies have been reintroduced there.

The Terfeziaceae, or desert truffles, is a family of truffles endemic to arid and semi-arid areas of the Mediterranean Region, North Africa, and the Middle East, where they live in ectomycorrhizal association with Helianthemum species and other ectomycorrhizal plants. This group consists of three genera: Terfezia, Tirmania, and Mattirolomyces. They are a few centimetres across and weigh from 30 to 300 grams (1–10 oz). Desert truffles are often used as a culinary ingredient.

Tuber magnatum, the white truffle, is a species of truffle in the order Pezizales and family Tuberaceae. It is found in southern Europe.
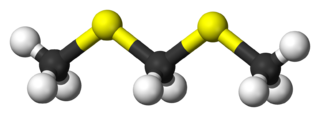
2,4-Dithiapentane is an organosulfur compound. It is a colorless liquid with a strong odor.

Carlo Vittadini was an Italian doctor and mycologist.

A false truffle or a hymenogastrale is any species of fungus that has underground fruiting bodies that produce basidiocarps resembling the true truffles of genus Tuber. While rodents such as squirrels eat a wide variety of false truffle species, many are considered toxic or otherwise unpalatable and only a few are sought after as food for humans.

The summer truffle or burgundy truffle is a species of truffle, found in almost all European countries.

Octaviania is a genus of truffle-like fungi in the family Boletaceae. The widespread genus is estimated to contain 15 species.

Tuber oregonense, commonly known as the Oregon white truffle, is a species of edible truffle in the genus Tuber. Described as new to science in 2010, the North American species is found on the western coast of the United States, from northern California to southern British Columbia west of the Cascade Range. A mycorrhizal fungus, it grows in a symbiotic association with Douglas fir. It overlaps in distribution with the closely related T. gibbosum, but they have different growing seasons: T. oregonense typically appears from October through March, while T. gibbosum grows from January to June. The fruit bodies of the fungus are roughly spherical to irregular in shape, and resemble small potatoes up to 5 cm (2 in) in diameter. Inside the truffle is the gleba, which is initially white before it becomes a marbled tan color. The large, often thick-walled, and strongly ornamented spores are produced in large spherical asci. The truffle is highly prized for its taste and aroma. Some individuals have claimed success in cultivating the truffles in Christmas tree farms.

Tuber is a genus in the fungal family Tuberaceae, with estimated molecular dating to the end of the Jurassic period. It includes several species of truffles that are highly valued as delicacies.

Choiromyces is a genus of truffle-like fungi in the Tuberaceae family. The widespread genus contains five species.

Kalapuya brunnea is a species of truffle in the monotypic fungal genus Kalapuya. The truffle occurs only in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States, in western Oregon and northern California. Known locally as the Oregon brown truffle, it was formerly thought to be an undescribed species of Leucangium until molecular analysis demonstrated that it was distinct from that genus. The truffle is reddish brown with a rough and warty outer skin, while the interior spore-producing gleba is initially whitish before developing greyish-brown mottling as it matures. Mature truffles have an odor resembling garlicky cheese, similar to mature Camembert. The species has been harvested for culinary purposes in Oregon.

Tuber sinoexcavatum is a species of truffle in the family Tuberaceae. Described as a new species in 2011, it is found in China. The pale yellowish-brown to brown truffles measure up to 3 cm (1.2 in) in diameter. The species is named for its close resemblance to the common European truffle T. excavatum.
Tuber anniae is a species of truffle in the genus Tuber. The truffle is purported to be uncommon, but is primarily found in the United States Pacific Northwest. Recently the fruiting of closely related taxa have been found in the Baltic Rim countries, primarily forests dominated by Scots pine in eastern Finland.

Tuber melanosporum, called the black truffle,Périgord truffle or French black truffle, is a species of truffle native to Southern Europe. It is one of the most expensive edible fungi in the world. In 2013, the truffle cost between 1,000 and 2,000 euros per kilogram.

Tuber canaliculatum, commonly called Michigan truffle and Appalachian truffle, is a fungus that grows in eastern North America including the Midwest. It is brick red in color. It is foraged and used in Appalachian cuisine.


















