
Pygidicranidae is a family of earwigs in the suborder Neodermaptera. The family currently contains twelve subfamilies and twenty six genera. Eight of the subfamilies are monotypic, each containing a single genus. Of the subfamilies, both Astreptolabidinae and Burmapygiinae are extinct and known solely from fossils found in Burmese amber. Similarly Archaeosoma, Gallinympha, and Geosoma, which have not been placed into any of the subfamilies, are also known only from fossils. Living members of the family are found in Australia, South Africa, North America, and Asia. The monotypic genus Anataelia, described by Ignacio Bolivar in 1899, is found only on the Canary Islands. As with all members of Neodermaptera, pygidicranids do not have any ocelli. The typical pygidicranid bodyplan includes a small, flattened-looking body, which has a dense covering of bristly hairs (setae). The pair of cerci at the end of the abdomen are symmetrical in structure. The head is broad, with the fourth, fifth and sixth antenna segments (antennomeres) that are not transverse. In general Pygidicranids also have equally sized ventral cervical sclerites, and in having the rearmost sclerite separated from, or only touching the center of the prosternum. Cannibalism of young has been observed in at least one species in the family, Challia hongkongensis, in which an adult female was found eating a still-living nymph of the same species. The same species in a different area has been observed possibly eating fruits or seeds, making the species an omnivore.

Arixeniidae is a family of earwigs in the suborder Neodermaptera. Arixeniidae was formerly considered a suborder, Arixeniina, but was reduced in rank to family and included in the new suborder Neodermaptera.
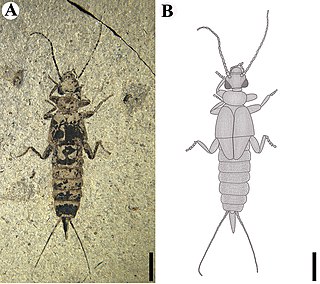
Protodiplatyidae is an extinct family of earwigs. It is one of three families in the suborder Archidermaptera, alongside Dermapteridae and Turanovia. Species are known from Jurassic and Early Cretaceous fossils and have unsegmented cerci and tarsi with four to five segments.
Microdiplatys is an extinct genus of earwigs, in the family Protodiplatyidae. It is one of only six genera in the family, its family being the only one in the suborder.
Protodiplatys is an extinct genus of earwigs, in the family Protodiplatyidae, the suborder Archidermaptera, and the order Dermaptera. It is known from three species, P. fortis and P. gracilis, which are known from the Middle-Late Jurassic Karabastau Formation in Kazakhstan, and P. mongoliensis from the Aptian aged Gurvan-Eren Formation of Mongolia.
Archidermapteron martynovi is an extinct species of earwig, in the genus Archidermapteron, family Protodiplatyidae, the suborder Archidermaptera, the order Dermaptera, and is the only species in the genus Archidermapteron, which simply means "ancient member of the Dermaptera". It had long, segmented cerci unlike modern species of Dermaptera, but tegmina and hind wings that folded up into a "wing package" that are like modern earwigs. The only clear fossil of the species was found in Russia.
Asiodiplatys is a monotypic genus containing the single species Asiodiplatys speciousus, an extinct species of earwig in the family Protodiplatyidae. It had long and thin cerci that were very different from modern species of Dermaptera, but tegmina and hind wings that folded up into a "wing package" that are like modern earwigs. Like Archidermapteron martynovi, the only clear fossil of the species was found in Russia.
Microdiplatys campodeiformis is an extinct species of earwig in the family Protodiplatyidae. It is one of only two species in the genus Microdiplatys, the other being Microdiplatys oculatus.
Microdiplatys oculatus is an extinct species of earwig in the family Protodiplatyidae. It is one of only two species in the genus Microdiplatys, the other being Microdiplatys campodeiformis.

Anisolabididae is a family of earwigs, in the suborder Neodermaptera and the order Dermaptera.

The cohort Polyneoptera is one of the major groups of winged insects, comprising the Orthoptera and all other neopteran insects believed to be more closely related to Orthoptera than to any other insect orders. They were formerly grouped together with the Palaeoptera and Paraneoptera as the Hemimetabola or Exopterygota on the grounds that they have no metamorphosis, the wings gradually developing externally throughout the nymphal stages. Many members of the group have leathery forewings (tegmina) and hindwings with an enlarged anal field (vannus).
Elipsocus is a genus of damp barklice in the family Elipsocidae. There are more than 20 described species in Elipsocus.

Apalacris is a genus of grasshoppers in the family Acrididae and subfamily Coptacrinae. The recorded distribution of species includes: India, Indo-China and Malesia.

Neodermaptera, sometimes called Catadermaptera, is a suborder of earwigs in the order Dermaptera. There are more than 2,000 described species in Neodermaptera.

Diaperasticus is a genus of earwigs in the family Forficulidae. There are about six described species in Diaperasticus.
Semenoviolidae is an extinct family of earwigs in the order Dermaptera. There are at least two genera and two described species in Semenoviolidae.

Dermapteridae is an extinct family of earwigs known from the Late Triassic to Mid Cretaceous, it is part of the extinct suborder Archidermaptera, alongside Protodiplatyidae and Turanovia. It was first named as a subfamily by Vishniakova in 1980, and elevated to family status by Engel in 2003 without discussion.
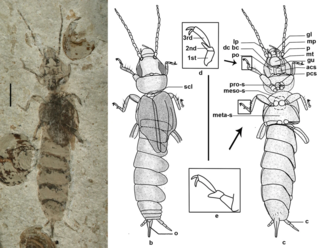
Eodermaptera is an extinct suborder of earwigs known from the Middle Jurassic to Mid Cretaceous. Defining characteristics include "tarsi three-segmented, tegmina retain venation, 8th and 9th abdominal tergite in females are narrowed, but separate from 10th tergite and not covered by 7th tergite and exposed ovipositor" They are considered to be more closely related to Neodermaptera than the more basal Archidermaptera.
Haplodiplatys is a genus of Asian earwigs erected by Walter Douglas Hincks in 1955. It is the only member of the monotypic family Haplodiplatyidae, with many species originally placed in the genus Diplatys; a key to them was prepared by Alan Brindle.

Chelidurella is a genus of European earwigs, in the family Forficulidae and subfamily Anechurinae, erected by Karl Wilhelm Verhoeff in 1902. The recorded distribution of species is mostly in northern Europe including Britain. The genus name was recently restored by Kirstová et al., who provide a key for identification of males.










