
Colbert County is a county located in the northwestern part of the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 census the county's population was 57,227. The county seat is Tuscumbia. The largest city is Muscle Shoals.

Tuscumbia is a city in and the county seat of Colbert County, Alabama, United States. As of the 2010 census, the population was 8,423. The city is part of The Shoals metropolitan area.

Courtland is a town in Lawrence County, Alabama, United States, and is included in the Decatur Metropolitan Area, as well as the Huntsville-Decatur Combined Statistical Area. The population was 609 at the 2010 census, down from 769 in 2000.

Decatur is the largest city and county seat of Morgan County in the U.S. state of Alabama. Nicknamed "The River City," it is located in northern Alabama on the banks of Wheeler Lake along the Tennessee River. The population was 57,938 at the 2020 census.

The Tennessee River is the largest tributary of the Ohio River. It is approximately 652 miles (1,049 km) long and is located in the southeastern United States in the Tennessee Valley. The river was once popularly known as the Cherokee River, among other names, as the Cherokee people had their homelands along its banks, especially in what are now East Tennessee and northern Alabama. Additionally, its tributary, the Little Tennessee River, flows into it from Western North Carolina and northeastern Georgia, where the river also was bordered by numerous Cherokee towns. Its current name is derived from the Cherokee town, Tanasi, which was located on the Tennessee side of the Appalachian Mountains.

The Tennessee Valley is the drainage basin of the Tennessee River and is largely within the U.S. state of Tennessee. It stretches from southwest Kentucky to north Alabama and from northeast Mississippi to the mountains of Virginia and North Carolina. The border of the valley is known as the Tennessee Valley Divide. The Tennessee Valley contributes greatly to the formation of Tennessee's three legally recognized sectors.

This is a list of the earliest railroads in North America, including various railroad-like precursors to the general modern form of a company or government agency operating locomotive-drawn trains on metal tracks.

Wheeler Dam is a hydroelectric dam on the Tennessee River between Lauderdale County and Lawrence County in Alabama. It is one of nine dams on the river owned and operated by the Tennessee Valley Authority, which built the dam in the mid-1930s as part of a New Deal-era initiative to improve navigation on the river and bring flood control and economic development to the region. The dam impounds the Wheeler Lake of 67,070 acres (27,140 ha) and its tailwaters feed into Wilson Lake.
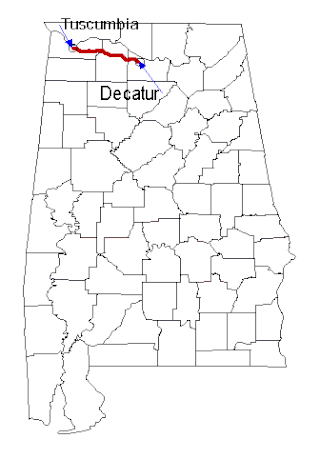
Incorporated on January 13, 1832, the Tuscumbia, Courtland and Decatur Railroad was a railroad in Alabama, the United States.

The Memphis and Charleston Railroad, completed in 1857, was the first railroad in the United States to link the Atlantic Ocean with the Mississippi River. Chartered in 1846, the 311 miles (501 km) 5 ft gauge railroad ran from Memphis, Tennessee to Stevenson, Alabama through the towns of Corinth, Mississippi and Huntsville, Alabama. The portion between Memphis and LaGrange, Tennessee was originally to be part of the LaGrange and Memphis Railroad, chartered in 1838. From Stevenson, the road was connected to Chattanooga, Tennessee via the Nashville and Chattanooga Railroad. In Alabama, the railroad followed the route of the Tuscumbia, Courtland and Decatur Railroad between Tuscumbia and Decatur, the first railroad to be built west of the Appalachian Mountains.

Newbern Depot, also known as Newbern Illinois Central Depot or as the Newbern–Dyersburg station, is an Amtrak station and museum in Newbern, Tennessee. It is an unstaffed flag stop on the City of New Orleans route, which serves Newbern and nearby Dyersburg when passengers have tickets to and from the station. The building was constructed by Illinois Central Railroad in 1920 and was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1993.
The Tuscumbia Railway was chartered on January 16, 1830, and a 2.1 mile railroad was built from downtown Tuscumbia, Alabama to the docks on the Tennessee River west of Sheffield. This was the first railroad chartered or constructed west of the Appalachian Mountains. The purpose of this railroad was to allow transport of cotton bales to a new wharf on the Tennessee River. Also the name of a tourist railroad constructed in city-owned Spring Park.

Yuma Quartermaster Depot State Historic Park, formerly Yuma Crossing State Historic Park, and now one of the Yuma Crossing and Associated Sites on the National Register of Historic Places in the Yuma Crossing National Heritage Area. It is an Arizona state park in the city of Yuma, Arizona, US.

The Coudersport and Port Allegany Railroad Station is a railroad station in Coudersport, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It was built by the Coudersport and Port Allegany Railroad in 1899 and opened in January 1900 during the lumber industry boom in Potter County. When the lumber ran out, the railroad's business decreased and in 1964 the line and station were purchased by the Wellsville, Addison and Galeton Railroad. The station was abandoned in 1970 and was unoccupied until 1975, when the borough of Coudersport purchased it. The borough restored it and put a new roof on, then used the building for office space. The station was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on November 21, 1976.

The Blair's Ferry Storehouse is a historic brick structure in the U.S. city of Loudon, Tennessee. Originally built as a storehouse for the burgeoning riverboat trade in the community of Blair's Ferry in the 1830s, the structure was eventually renovated and used for a variety of functions throughout the 19th and 20th centuries. The building is one of the region's earliest surviving examples of a structure designed specifically as a warehouse. In 1977, the building was placed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Southern Railway Depot is a historic building in Decatur, Alabama. The depot was built in 1904–05 along the Southern Railway line. Decatur had become a transportation hub of North Alabama by the 1870s, with its connections to the Tennessee River, the east–west Tuscumbia, Courtland and Decatur Railroad, and the north–south Louisville and Nashville Railroad.

The Courtland Historic District is a historic district in Courtland, Alabama. Courtland was founded in 1818 and incorporated the following year. Its location was chosen to be close to the Tennessee River to facilitate transportation, but also close to cotton plantations to the south. The town's founders envisioned becoming the county seat of the newly formed Lawrence County, but the title instead went to Moulton. Many of the earliest structures in Courtland were built of logs, and were later replaced with frame and brick buildings. Development plateaued by 1830, but received a slight bump from the Tuscumbia, Courtland and Decatur Railroad beginning in 1834. The oldest houses in the district date from this era, including the 1828 Federal-style John McMahon House and several I-houses.

The Colbert County Courthouse Square Historic District is a historic district in Tuscumbia, Alabama. It contains 22 buildings and residences centered on the Colbert County Courthouse.

The Dry Creek explosives depot was a secure storage facility at Dry Creek, near Port Adelaide, from 1904 to 1995, serving the construction, mining and quarrying industries of South Australia and the mines of Broken Hill in New South Wales.

The Third Street Railroad Trestle is a historic wooden railroad trestle bridge crossing Shoal Creek in downtown Austin, Texas. Built around 1922 by the International–Great Northern Railroad, it replaced an earlier bridge in the same place. The bridge was used by the I–GN Railroad, the Missouri Pacific Railroad, and the Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad until 1964, when commercial rail traffic stopped; after 1991 the bridge was abandoned. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2021.





















