
Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Skinks are characterized by their smaller legs in comparison to typical lizards and are found in different habitats except arctic and subarctic regions.

The bronze grass skink, bronze mabuya or speckled forest skink, is a species of skink found in South and Southeast Asia. It is a common, but shy, ground-dwelling species that is active both day and night.
Anomalopus mackayi, commonly known as the five-clawed worm skink, long-legged worm skink, and MacKay's burrowing skink, is a species of smooth-scaled burrowing skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to eastern Australia.

The Italian three-toed skink or the cylindrical skink is a species of lizard found from Italy, to northern Algeria, Libya, Morocco and Tunisia and in india. It is common in some locations and is usually found in sunny areas with dense vegetation but can also be found in arid areas. They reach about 48 cm (19 in) in length, out of which the tail constitutes more than half. Its body is long and snake-like, coloured usually between brown and olive and may have dark stripes on the back. Each of the highly reduced legs has three fingers. These skinks are active during daytime and prey mainly on insects. Females of the species give birth to live young. The population of this skink is slowly declining, but it has some tolerance to habitat modification.

The Algerian three-toed skink is a species of "grass-swimming" skink with an elongated serpentine shape and reduced limbs. It is endemic to north-western Africa.

The western three-toed skink is a species of lizard with tiny legs in the family Scincidae. It is found in the Iberian Peninsula, southern France and parts of northwestern Italy. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, temperate shrubland, Mediterranean-type shrubby vegetation, temperate grassland, sandy shores, arable land, pastureland, and rural gardens. It was first described 1829 by the French naturalist Georges Cuvier. The generic name comes from the Greek "chalcides" meaning 'copper' and the specific name is derived from the Latin "striatus" meaning 'streak'.
The Lord Howe Island skink is a part of the native Australian reptiles’ classification. The Lord Howe Island Skink is a species of skink in the family Scincidae, located on Australia's Norfolk Island and Lord Howe Island. The Lord Howe Island skink population is uncommon to be found on Lord Howe island, however the majority of their population is located on the Norfolk Island complex.This skink is metallic bronze in colour and has flecks for defining features. It can grow up to 8cm in length, making them medium in size. Its taxonomy is diverse, the skink is a part of the Scincidae family, Oligosoma genus. This skink population is protected and considered vulnerable under the Environment Protection and biodiversity conservation act 1999.

The Blue Mountains water skink or Blue Mountains swamp-skink is a species of skink in the family Scincidae. An endangered species, it is found only in restricted parts of the mountains of southeastern Australia.

Morethia boulengeri is a species of lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia.

The four-toed earless skink, also known commonly as Péron's earless skink, the lowlands earless skink, or the four-toed mulch skink, is a viviparous earless skink endemic to southern Australia.

Cryptoblepharus australis, commonly called the inland snake-eyed skink, is a species of skink in the genus Cryptoblepharus.

The desert egernia, unadorned desert-skink or desert skink is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The desert egernia is endemic to the continent of Australia, and is widespread, with populations recorded in all mainland states and territories except the Australian Capital Territory. The desert egernia is found in dry, desert areas with deep, uncompacted sandy/loamy soils and little significant vegetation cover.

The saltbush Morethia skink, or more commonly referred to as saltbush skink, is a species of skink found in Australia. They are part of an 8 species genus of Morethia, which are all endemic to Australia. Akin to other members of the Morethia genus, saltbush skinks feature transparent disks as eye covers and eyelids which are stationary, along with specialised limbs which enable quick traversal of sand dunes. Taxonomically, the species was first classified by German explorer Wilhelm Karl Hartwig in 1871.
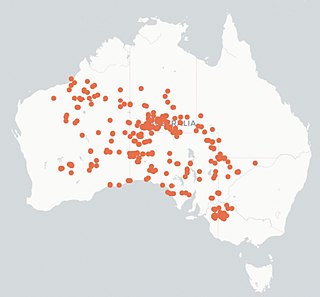
Ctenotus brooksi, also known commonly as Brooks' wedge-snouted ctenotus, the wedgesnout ctenotus, and the sandhill ctenotus, is a species of skink, a lizard in the family Scincidae. The species is endemic to Australia and found in semi-arid regions.
The south-western mulch-skink is a species of skink found in Western Australia.
The southwestern earless skink is a species of skink found in South Australia and Western Australia.

The Hemiergis millewae, commonly known as the Millewa skink or Triodia earless skink, is a species of hemiergis lizards that is endemic to Australia. It is a specialist species, highly dependent on Spinifex for food and shelter, and has only been observed in semi-arid Mallee woodlands of southern and eastern Australia. It is considered endangered throughout parts of its range.
The Victoria three-toed earless skink is a species of skink found in New South Wales and Victoria in Australia.
The eastern robust slider is a nocturnal, burrowing species of skink found in continental Australia. Other common names are 'spotted lerista', and 'common burrowing skink'. The earliest written description of the species was provided by Albert Günther in 1867, based on a specimen caught in Queensland.

Lerista timida, the dwarf three-toed slider or wood mulch-slider, is a species of skink found in Australia. Other common names for the species include timid slider and dwarf burrowing skink. The skink is a member of the Lerista genus which are confined to continental Australia and are mostly a burrowing species of skink. The genus consists of consists elongated, smooth-scaled, Fossorial lizards that are specialized for life in the upper soils and dry leaf litter through which they slide using Lateral undulation as a form of locomotive action, giving rise to their nickname as sliders. They normally emerge of a night-time to hunt for small Invertebrates such as ants, termites and insects. If disturbed, they dive immediately into any loose substrate to avoid predation, this behavior leaves behind a distinctive disrupted wavy track that often found on sandy flats or dunes, roads and tracks.















