
Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against gram-positive bacilli and anaerobic gram-negative bacilli. Neomycin comes in oral and topical formulations, including creams, ointments, and eyedrops. Neomycin belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics that contain two or more amino sugars connected by glycosidic bonds.

Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin.
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity.

In biochemistry, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) is a redox-active coenzyme associated with various proteins, which is involved with several enzymatic reactions in metabolism. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group, which may be in the form of FAD or flavin mononucleotide (FMN). Many flavoproteins are known: components of the succinate dehydrogenase complex, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, and a component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
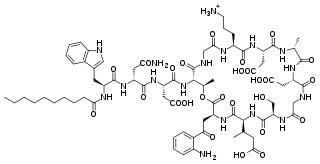
Daptomycin, sold under the brand name Cubicin among others, is a lipopeptide antibiotic used in the treatment of systemic and life-threatening infections caused by Gram-positive organisms.
Methylotrophs are a diverse group of microorganisms that can use reduced one-carbon compounds, such as methanol or methane, as the carbon source for their growth; and multi-carbon compounds that contain no carbon-carbon bonds, such as dimethyl ether and dimethylamine. This group of microorganisms also includes those capable of assimilating reduced one-carbon compounds by way of carbon dioxide using the ribulose bisphosphate pathway. These organisms should not be confused with methanogens which on the contrary produce methane as a by-product from various one-carbon compounds such as carbon dioxide. Some methylotrophs can degrade the greenhouse gas methane, and in this case they are called methanotrophs. The abundance, purity, and low price of methanol compared to commonly used sugars make methylotrophs competent organisms for production of amino acids, vitamins, recombinant proteins, single-cell proteins, co-enzymes and cytochromes.

Viomycin is a member of the tuberactinomycin family, a group of nonribosomal peptide antibiotics exhibiting anti-tuberculosis activity. The tuberactinomycin family is an essential component in the drug cocktail currently used to fight infections of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Viomycin was the first member of the tuberactinomycins to be isolated and identified, and was used to treat TB until it was replaced by the less toxic, but structurally related compound, capreomycin. The tuberactinomycins target bacterial ribosomes, binding RNA and disrupting bacterial protein synthesis and certain forms of RNA splicing. Viomycin is produced by the actinomycete Streptomyces puniceus.

Platensimycin, a metabolite of Streptomyces platensis, is an antibiotic, which act by blocking enzymes.

Prodigiosin is the red dyestuff produced by many strains of the bacterium Serratia marcescens, as well as other Gram-negative, gamma proteobacteria such as Vibrio psychroerythrus and Hahella chejuensis. It is responsible for the pink tint occasionally found in grime that accumulates on porcelain surfaces such as bathtubs, sinks, and toilet bowls. It is in the prodiginines family of compounds which are produced in some Gram-negative gamma proteobacteria, as well as select Gram-positive Actinobacteria. The name prodigiosin is derived from prodigious.

Roseophilin is an antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces griscovirides shown to have antitumor activity. The chemical structure can be considered in terms of two components, a macrotricyclic segment and a heterocyclic side-chain. Several laboratory syntheses of roseophilin are based upon the Paal-Knorr synthesis, and two others are based on the Nazarov cyclization reaction. The compound is related to the prodiginines.
Streptomyces spectabilis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces spectabilis produces hangtaimycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, neomycin B, sisomycin, tobramycin, paromomycin, spectinabilin, spectinomycin, aminocyclitol, actinospectacin, prodigiosine and the streptovaricin complex.

Indolocarbazoles (ICZs) are a class of compounds that are under current study due to their potential as anti-cancer drugs and the prospective number of derivatives and uses found from the basic backbone alone. First isolated in 1977, a wide range of structures and derivatives have been found or developed throughout the world. Due to the extensive number of structures available, this review will focus on the more important groups here while covering their occurrence, biological activity, biosynthesis, and laboratory synthesis.
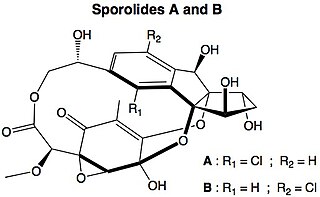
Sporolides A and B are polycyclic macrolides extracted from the obligate marine bacterium Salinispora tropica, which is found in ocean sediment. They are composed of a chlorinated cyclopenta[a]indene ring and a cyclohexenone moiety. They were the second group of compounds isolated from Salinispora, and were said to indicate the potential of marine actinomycetes as a source of novel secondary metabolites. The structures and absolute stereochemistries of both metabolites were elucidated using a combination of NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography.

Germicidins are a groups of natural products arising from Streptomyces species that acts as autoregulatory inhibitor of spore germination. In Streptomyces viriochromogenes, low concentrations inhibit germination of its own arthrospores, and higher concentrations inhibit porcine Na+/K+ -activated ATPase. Inhibitory effects on germination are also observed when germicidin from Streptomyces is applied to Lepidium sativum. Germicidins and other natural products present potential use as pharmaceuticals, and in this case, those with possible antibiotic or antifungal activity.
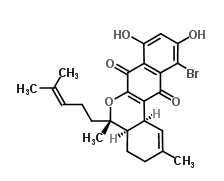
Marinone is an antibiotic made by marine actinomycetes.
Curcumin synthase categorizes three enzyme isoforms, type III polyketide synthases (PKSs) present in the leaves and rhizome of the turmeric plant that synthesize curcumin. CURS1-3 are responsible for the hydrolysis of feruloyldiketide-CoA, previously produced in the curcuminoid pathway, and a decarboxylative condensation reaction that together comprise one of the final steps in the synthesis pathway for curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin, the compounds that give turmeric both its distinctive yellow color, and traditional medical benefits. CURS should not be confused with Curcuminoid Synthase (CUS), which catalyzes the one-pot synthesis of bisdemethoxycurcumin in Oryza sativa.
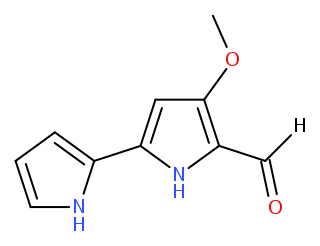
Tambjamines are a group of natural products that are structurally related to the prodiginines. They are enamine derivatives of 4-methoxy-2,2'-bipyrrole-5-carboxaldehyde (MBC).
Streptomyces albidoflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Poland. Streptomyces albidoflavus produces dibutyl phthalate and streptothricins.
Streptomyces violaceoruber is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces. Streptomyces violaceoruber produces protoactinorhodin, kendomycin, phospholipase A2, granaticin and methylenomycin A.

The prodiginines are a family of red tripyrrole dyestuffs produced by Gammaproteobacteria as well as some Actinomycetota. The group is named after prodigiosin (prodiginine) and is biosynthesized through a common set of enzymes. They are interesting due to their history and their varied biological activity.















