
Joseph Sill Clark Jr. was an American author, lawyer and politician. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as the 116th Mayor of Philadelphia from 1952 to 1956 and as a United States Senator from Pennsylvania from 1957 to 1969. Clark was the only Unitarian Universalist elected to a major office in Pennsylvania in the modern era.

The 1994 United States Senate elections were elections held November 8, 1994, in which the Republican Party was able to take control of the Senate from the Democrats. In a midterm election, the opposition Republicans held the traditional advantage. Congressional Republicans campaigned against the early presidency of Bill Clinton, including his unsuccessful health care plan.

The 1998 United States Senate elections were held on November 3 and seen as an even contest between the Republican Party and Democratic Party. While the Democrats had to defend more seats up for election, Republican attacks on the morality of President Bill Clinton failed to connect with voters and anticipated Republican gains did not materialize. The Republicans picked up open seats in Ohio and Kentucky and narrowly defeated Democratic incumbent Carol Moseley Braun (Illinois), but these were cancelled out by the Democrats' gain of an open seat in Indiana and defeats of Republican Senators Al D'Amato and Lauch Faircloth. The balance of the Senate remained unchanged at 55–45 in favor of the Republicans. With Democrats gaining five seats in the House of Representatives, this marked the first time since 1934 that the out-of-presidency party failed to gain congressional seats in a mid-term election, and the first time since 1822 that the party not in control of the White House failed to gain seats in the mid-term election of a President's second term. These are the last senate elections that resulted in no net change in the balance of power.

The 1988 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate in which, in spite of the Republican victory by George H. W. Bush in the presidential election, the Democrats gained a net of one seat in the Senate. Seven seats changed parties, with four incumbents being defeated. The Democratic majority in the Senate increased by one from 54/46 to 55/45.

The 1986 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate in the middle of Ronald Reagan's second presidential term. The Republicans had to defend an unusually large number of freshman Senate incumbents who had been elected on President Ronald Reagan's coattails in 1980. Democrats won a net of eight seats, defeating seven freshman incumbents and regaining control of the Senate for the first time since January 1981. The party not controlling the presidency gained seats, as usually occurs in mid-term elections.

The 1982 United States Senate elections were held on November 2, 1982. They were elections for the United States Senate following Republican gains in 1980. A total of four seats changed hands between parties, and the lone independent, Senator Harry Byrd Jr., retired. Democrats made a net gain of one seat in the elections. A special election in 1983 was then held after the winner of Washington's 1982 election died at the beginning of the term.

The 1980 United States Senate elections coincided with Ronald Reagan's victory in the presidential election. Reagan's large margin of victory over incumbent Jimmy Carter pulled in many Democratic voters and gave a huge boost to Republican Senate candidates.

The 1978 United States Senate elections in the middle of Democratic President Jimmy Carter's term. Thirteen seats changed hands between parties. The Democrats at first lost a net of two seats to the Republicans, and then one more in a special election. Democrats nevertheless retained a 58-41 majority.

The 1976 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate that coincided with Democratic Jimmy Carter's presidential election and the United States Bicentennial celebration. Although almost half of the seats decided in this election changed parties, Carter's narrow victory did not provide coattails for the Democrats, and the balance of the chamber remained the same.

The 1970 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate, taking place in the middle of Richard Nixon's first term as President. The Democrats lost a net of three seats, while the Republicans and the Conservative Party of New York picked up one net seat each, and former Democrat Harry F. Byrd Jr. was re-elected as an independent.

The 1966 United States Senate elections was an election on November 8, 1966 for the United States Senate which occurred midway through the second term of President Lyndon B. Johnson. With divisions in the Democratic base over the Vietnam War, and with the traditional mid-term advantage of the party not holding the presidency, the Republicans took three Democratic seats. Despite Republican gains, the balance remained overwhelmingly in favor of the Democrats, who retained a 64–36 majority. This was also the first election that occurred after the Voting Rights Act of 1965 became law.

The 1964 United States Senate elections coincided with the election of President Lyndon B. Johnson by an overwhelming majority, to a full term. His Democratic Party picked up a net two seats from the Republicans. As of 2019, this is the last time either party has had a two-thirds majority in the Senate, which would have hypothetically allowed the Senate Democrats to override a veto, convict and expel certain officials, or invoke cloture without any votes from Republicans. The Senate election coincided with Democratic gains in the House in the same year.

The 1956 United States Senate elections were elections for the United States Senate that coincided with the re-election of President Dwight D. Eisenhower. Although the Democrats gained two seats in regular elections, the Republicans gained back two seats in special elections, leaving the party balance of the chamber remained unchanged.
The Republican Party of Pennsylvania, commonly known as the PA GOP, is based in Harrisburg in the United States state of Pennsylvania. It is affiliated with the Republican Party of the United States.

The 1952 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held on November 4, 1952. Incumbent Republican Henry Cabot Lodge Jr. lost to John F. Kennedy, the Democratic Party nominee. This election marked the end of the Lodge family dynasty and the beginning of the Kennedy family dynasty.
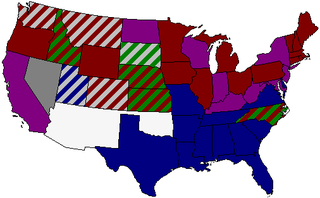
The United States Senate elections of 1896 and 1897 were elections in which the Democratic Party lost seven seats in the United States Senate, mostly to smaller third parties.

The 1980 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 4, 1980. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator Richard Schweiker decided to retire, instead of seeking a third term. Republican nominee Arlen Specter won the open seat, defeating Democratic nominee Peter F. Flaherty.

The 2012 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 6, 2012, alongside a presidential election, other elections to the United States Senate in other states, as well as elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator Bob Casey, Jr. ran for and won re-election to a second term, defeating Republican nominee Tom Smith, and Libertarian nominee Rayburn Smith.

The 1956 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 6, 1956. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator James H. Duff sought re-election to another term, but was defeated by the Democratic nominee, Joseph S. Clark, Jr.

The 1988 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania was held on November 8, 1988. Incumbent Republican U.S. Senator H. John Heinz III successfully sought re-election to another term, defeating Democratic nominee Joe Vignola.




















