The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad built in the Northeastern United States to haul anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Pennsylvania. The railroad was authorized on April 21, 1846, for freight and transportation of passengers, goods, wares, merchandise, and minerals in Pennsylvania and the railroad was incorporated and established on September 20, 1847, as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad Company.

NJ Transit Rail Operations is the rail division of NJ Transit. It operates commuter rail service in New Jersey, with most service centered on transportation to and from New York City, Hoboken, and Newark. NJ Transit also operates rail service in Orange and Rockland counties in New York under contract to Metro-North Railroad. The commuter rail lines saw 45,838,200 riders in 2022, making it the third-busiest commuter railroad in North America and the longest commuter rail system in North America by route length.

The Central Railroad of New Jersey, also known as the Jersey Central, Jersey Central Lines or New Jersey Central, was a Class I railroad with origins in the 1830s. It was absorbed into Conrail in April 1976 along with several other prominent bankrupt railroads of the Northeastern United States.
Conrail Shared Assets Operations (CSAO) is the commonly used name for modern-day Conrail, an American railroad company. It operates three networks, the North Jersey, South Jersey/Philadelphia, and Detroit Shared Assets Areas, where it serves as a contract local carrier and switching company for its owners, CSX Transportation and the Norfolk Southern Railway. When most of the former Conrail's track was split between these two railroads, the three shared assets areas were kept separate to avoid giving one railroad an advantage in those areas. The company operates using its own employees and infrastructure but owns no equipment outside MOW equipment.

For the purposes of this article, the Jersey City area extends North to Edgewater, South to Bayonne and includes Kearny Junction and Harrison but not Newark. Many routes east of Newark are listed here.

The Passaic and Harsimus Line, part of Conrail Shared Assets Operations, serves freight in northeastern New Jersey. It takes trains from the Northeast Corridor and Lehigh Line near Newark Liberty International Airport northeast and east into Jersey City. It is part of CSX's main corridor from upstate New York to the rest of the east coast.

The Raritan Valley Line is a commuter rail service operated by New Jersey Transit (NJT) which serves passengers in municipalities in Union, Somerset, Middlesex and Hunterdon counties in the Raritan Valley region in central New Jersey, United States. The line's most frequent western terminus is Raritan station in Raritan. Some weekday trains continue farther west and terminate at the High Bridge station, located in High Bridge. Most eastbound trains terminate in Newark; passengers bound for New York make a cross-platform transfer. A limited number of weekday trains continue directly to New York.

New York New Jersey Rail, LLC is a switching and terminal railroad that operates the only car float operation across Upper New York Bay between Jersey City, New Jersey and Brooklyn, New York. Since mid-November 2008, it has been owned by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, which acquired it for about $16 million as a step in a process that might see a Cross-Harbor Rail Tunnel completed.

The Conrail Lehigh Line is a railroad line in New Jersey that is part of Conrail Shared Assets Operations under the North Jersey Shared Assets Area division. The line runs from CP Port Reading Junction in Manville to Oak Island Yard in Newark. The line is double-track and signaled through its entire length. The line began operations in 1999 using former existing tracks from Manville to Newark that was once part of the original Lehigh Line which is still in existence and is owned and operated by Norfolk Southern Railway.

The Pennsylvania Railroad Station was the intermodal passenger terminal for the Pennsylvania Railroad's (PRR) vast holdings on the Hudson River and Upper New York Bay in Jersey City, New Jersey. By the 1920s the station was called Exchange Place. The rail terminal and its ferry slips were the main New York City station for the railroad until the opening in 1910 of New York Pennsylvania Station, made possible by the construction of the North River Tunnels. It was one of the busiest stations in the world for much of the 19th century.

Roselle Park is a New Jersey Transit railroad station in Roselle Park, New Jersey. Located on the Conrail Lehigh Line which is owned by Conrail Shared Assets Operations on West Lincoln Avenue between Chestnut Street and Locust Street, it is served by Raritan Valley Line trains that travel between Newark Penn Station and Raritan. There is also limited service between High Bridge and New York Penn Station and one weekday morning train to Hoboken Terminal.

Union is a NJ Transit railroad station in Union, New Jersey. Located on the Conrail Lehigh Line, Union is served by Raritan Valley Line trains that travel between Newark Penn Station and Raritan. There is also limited service to and from High Bridge and New York Penn Station and one morning train to Hoboken Terminal. The physical structures of the station are owned by NJ Transit; however, the land remains the property of Conrail Shared Assets Operations, which is in turn owned by Norfolk Southern Railway and CSX Corporation.

Bergen Hill refers to the lower Hudson Palisades in New Jersey, where they emerge on Bergen Neck, which in turn is the peninsula between the Hackensack and Hudson Rivers, and their bays. In Hudson County, it reaches a height of 260 feet.
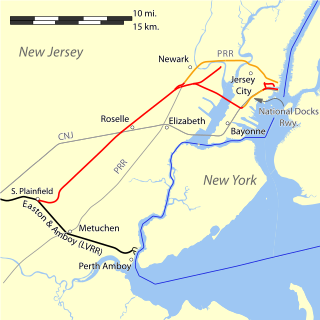
The Lehigh Valley Terminal Railway was a Lehigh Valley Railroad company organized in 1891 through the consolidation of the companies that formed the Lehigh Valley's route from South Plainfield through Newark to Jersey City via its bridge across Newark Bay. Until 1895, when the Greenville and Hudson Railway was constructed, the Lehigh Valley depended on the National Docks Railway to reach the Hudson River terminal.
Greenville Yard is a freight rail yard in the Port of New York and New Jersey. It is located on Upper New York Bay in Jersey City, New Jersey, adjacent and north of Port Jersey. Originally developed in 1904 by the Pennsylvania Railroad, it was later taken over by Conrail. It has been owned by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey since 2010. It takes its name from the former municipality of Greenville, now part of the city.

Oak Island Yard is a freight rail yard located north of Port Newark-Elizabeth Marine Terminal and Newark International Airport in an industrial area of Ironbound, Newark, New Jersey at 91 Bay Ave., United States. The sprawling complex includes engine house, classification yard, auto unloading terminal, and maintenance facilities. It has ten reception tracks, an automated hump, 30 relatively short classification tracks, and nine departure tracks. In 1999, it classified 800 to 1000 cars per day.
National Docks Secondary is a freight rail line within Conrail's North Jersey Shared Assets Area in Hudson County, New Jersey, used by CSX Transportation. It provides access for the national rail network to maritime, industrial, and distribution facilities at Port Jersey, the Military Ocean Terminal at Bayonne (MOTBY), and Constable Hook as well as carfloat operations at Greenville Yard. The line is an important component in the planned expansion of facilities in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The single track right of way comprises rail beds, viaducts, bridges, and tunnels originally developed at the end of the 19th century by competing railroads.

Point-No-Point Bridge is a railroad bridge crossing the Passaic River between Newark and Kearny, New Jersey, United States, in the New Jersey Meadowlands. The swing bridge is the fourth from the river's mouth at Newark Bay and is 2.6 miles (4.2 km) upstream from it. A camelback through truss bridge, it is owned by Conrail as part of its North Jersey Shared Assets and carries the Passaic and Harsimus Line used by CSX Transportation and Norfolk Southern. River Subdivision accesses the line via Marion Junction. Conrail is replacing the bridge, which was opened in 1901. Work began in November 2022.

The Lehigh Line is a railroad line in Central New Jersey, Northeastern Pennsylvania, and the Lehigh Valley region of eastern Pennsylvania. It is owned and operated by the Norfolk Southern Railway. The line runs west from the vicinity of the Port of New York and New Jersey in Manville, New Jersey via Conrail's Lehigh Line to the southern end of Wyoming Valley's Coal Region in Lehigh Township, Pennsylvania.

ExpressRail is a network of on- or near-dock rail yards supporting intermodal freight transport at the major container terminals of the Port of New York and New Jersey. The development of dockside trackage and rail yards for transloading has been overseen by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, which works in partnership with other public and private stakeholders. As of 2019, four ExpressRail facilities were in operation, with a total built capacity of 1.5 million lifts.



















