| Upper Tabuating Dam | |
|---|---|
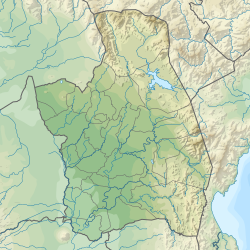
 View of the dam towards the south | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Location | Barangay Nazareth, General Tinio, Nueva Ecija [1] |
| Coordinates | 15°23′35″N121°07′01″E / 15.393153°N 121.117017°E |
| Purpose | Multi-purpose [2] |
| Status | Operational |
| Construction began | 2010 (Irrigation component) [3] February 2015 (Dam component) [4] |
| Opening date | December 2020 [1] |
| Construction cost | PhP 878 Million [1] |
| Owner | National Irrigation Administration |
| Dam and spillways | |
| Type of dam | Earth fill dam |
| Impounds | Tabuating River |
| Height | 25.56 metres (83.9 ft) |
| Length | 760 metres (2,490 ft) |
| Reservoir | |
| Total capacity | 4,960,000 cubic metres (4,020 acre⋅ft) |
The Upper Tabuating Dam is a multi-purpose earth-fill dam located at Barangay Nazareth, General Tinio, Nueva Ecija in the Philippines. It is located at the upstream of Tabuating River near the border of General Tinio with Fort Magsaysay in Palayan.
Contents
Inaugurated in May 2021, it is part of the Upper Tabuating Small Reservoir Irrigation Project (UT-SRIP) of the National Irrigation Administration (NIA) of the Philippines which was designed for tourism, aquaculture, cash crops and power generation. [1] [2]