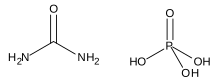
Urea, also called carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two amino groups joined by a carbonyl functional group. It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.

A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment or hand-tool methods.
Ureases, functionally, belong to the superfamily of amidohydrolases and phosphotriesterases. Ureases are found in numerous bacteria, fungi, algae, plants, and some invertebrates, as well as in soils, as a soil enzyme. They are nickel-containing metalloenzymes of high molecular weight.

Phosphoric acid is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula H3PO4. It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solution, which is a colourless, odourless, and non-volatile syrupy liquid. It is a major industrial chemical, being a component of many fertilizers.
The nitrophosphate process is a method for the industrial production of nitrogen fertilizers invented by Erling Johnson in the municipality of Odda, Norway around 1927.

3,3′-Diaminobenzidine (DAB) is an organic compound with the formula (C6H3(NH2)2)2. This derivative of benzidine is a precursor to polybenzimidazole, which forms fibers that are renowned for their chemical and thermal stability. As its water-soluble tetrahydrochloride, DAB has been used in immunohistochemical staining of nucleic acids and proteins.

Sulfamic acid, also known as amidosulfonic acid, amidosulfuric acid, aminosulfonic acid, sulphamic acid and sulfamidic acid, is a molecular compound with the formula H3NSO3. This colourless, water-soluble compound finds many applications. Sulfamic acid melts at 205 °C before decomposing at higher temperatures to water, sulfur trioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen.
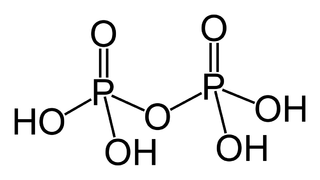
In chemistry, a phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus (P) atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is bonded to four oxygen (O) atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. Two or more of these PO4 tetrahedra may be connected by shared single-bonded oxygens, forming linear or branched chains, cycles, or more complex structures. The single-bonded oxygen atoms that are not shared are completed with acidic hydrogen atoms. The general formula of a phosphoric acid is Hn+2−2xPnO3n+1−x, where n is the number of phosphorus atoms and x is the number of fundamental cycles in the molecule's structure, between 0 and n + 2/2.

Ammonium phosphate is the inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)3PO4. It is the ammonium salt of orthophosphoric acid. A related "double salt", (NH4)3PO4.(NH4)2HPO4 is also recognized but is impractical to use. Both triammonium salts evolve ammonia. In contrast to the unstable nature of the triammonium salts, the diammonium phosphate (NH4)2HPO4 and monoammonium salt (NH4)H2PO4 are stable materials that are commonly used as fertilizers to provide plants with fixed nitrogen and phosphorus.

Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydrating agent.

Arsenic acid or arsoric acid is the chemical compound with the formula H3AsO4. More descriptively written as AsO(OH)3, this colorless acid is the arsenic analogue of phosphoric acid. Arsenate and phosphate salts behave very similarly. Arsenic acid as such has not been isolated, but is only found in solution, where it is largely ionized. Its hemihydrate form (2H3AsO4·H2O) does form stable crystals. Crystalline samples dehydrate with condensation at 100 °C.

Biuret is a chemical compound with the chemical formula HN(CONH2)2. It is a white solid that is soluble in hot water. A variety of organic derivatives are known. The term "biuret" also describes a family of organic compounds with the chemical formula R1R2N−C(=O)−N(R3)−C(=O)−NR4R5, where R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are hydrogen, organyl or other groups. Also known as carbamylurea, it results from the condensation of two equivalents of urea. It is a common undesirable impurity in urea-based fertilizers, as biuret is toxic to plants.

Dipotassium phosphate (K2HPO4) (also dipotassium hydrogen orthophosphate; potassium phosphate dibasic) is the inorganic compound with the formula K2HPO4.(H2O)x (x = 0, 3, 6). Together with monopotassium phosphate (KH2PO4.(H2O)x), it is often used as a fertilizer, food additive, and buffering agent. It is a white or colorless solid that is soluble in water.

Fertigation is the injection of fertilizers, used for soil amendments, water amendments and other water-soluble products into an irrigation system.

Urea nitrate is a fertilizer-based high explosive that has been used in improvised explosive devices in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iraq, and various terrorist acts elsewhere in the world such as in the 1993 World Trade Center bombings. It has a destructive power similar to better-known ammonium nitrate explosives, with a velocity of detonation between 3,400 m/s (11,155 ft/s) and 4,700 m/s (15,420 ft/s). It has chemical formula of CH5N3O4 or (NH2)2COHNO3.

Copper(II) phosphate are inorganic compounds with the formula Cu3(PO4)2. They can be regarded as the cupric salts of phosphoric acid. Anhydrous copper(II) phosphate and a trihydrate are blue solids.
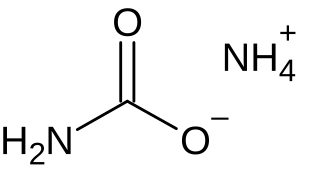
Ammonium carbamate is a chemical compound with the formula [NH4][H2NCO2] consisting of ammonium cation NH+4 and carbamate anion NH2COO−. It is a white solid that is extremely soluble in water, less so in alcohol. Ammonium carbamate can be formed by the reaction of ammonia NH3 with carbon dioxide CO2, and will slowly decompose to those gases at ordinary temperatures and pressures. It is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of urea (NH2)2CO, an important fertilizer.

Triuret is an organic compound with the formula (H2NC(O)NH)2CO. It is a product from the pyrolysis of urea. Triuret is a colorless, crystalline, hygroscopic solid, slightly soluble in cold water or ether, and more soluble in hot water. It is a planar molecule. The central carbonyl is hydrogen-bonded to both terminal amino groups.

Thorium(IV) nitrate is a chemical compound, a salt of thorium and nitric acid with the formula Th(NO3)4. A white solid in its anhydrous form, it can form tetra- and pentahydrates. As a salt of thorium it is weakly radioactive.
Protactinium compounds are compounds containing the element protactinium. These compounds usually have protactinium in the +5 oxidation state, although these compounds can also exist in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states.