
Soul food is an ethnic cuisine originating in the Southern United States historically pertaining to African-Americans. It originated from the cuisines of enslaved Africans trafficked to the North American colonies through the Atlantic slave trade during the Antebellum period and is closely associated with the cuisine of the American South. The expression "soul food" originated in the mid-1960s, when "soul" was a common word used to describe African-American culture. Soul food uses cooking techniques and ingredients from West African, Central African, Western European, and Indigenous cuisine of the Americas. Soul food came from the blending of what African Americans ate in their native countries in Africa and what was available to them as slaves. The cuisine had its share of negativity initially. Soul food was initially seen as low class food, and Northern African Americans looked down on their Black Southern counterparts who preferred soul food. The term evolved from being the diet of a slave in the South to being a primary pride in the African American community in the North such as New York City.

Julie Ethel Dash is an American filmmaker, music video and commercial director, author, and website producer. Dash received her MFA in 1985 at the UCLA Film School and is one of the graduates and filmmakers known as the L.A. Rebellion. The L.A. Rebellion refers to the first African and African-American students who studied film at UCLA. Through their collective efforts, they sought to put an end to the prejudices of Hollywood by creating experimental and unconventional films. The main goal of these films was to create original Black stories and bring them to the main screens. After Dash had written and directed several shorts, her 1991 feature Daughters of the Dust became the first full-length film directed by an African-American woman to obtain general theatrical release in the United States. In 2004, Daughters of the Dust was named to the National Film Registry by the Library of Congress. Stemming from the film's success, Dash also released novels of the same title in 1992 and 1999. This film even inspired Beyoncé, arguably the music industry's most influential artist, with her 2016 album titled Lemonade.

Gullah is a creole language spoken by the Gullah people, an African-American population living in coastal regions of South Carolina and Georgia as well as extreme northeastern Florida and the extreme southeast of North Carolina.

The Gullah are an African American ethnic group who predominantly live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of South Carolina, North Carolina, Georgia, and Florida within the coastal plain and the Sea Islands. Their language and culture have preserved a significant influence of Africanisms as a result of their historical geographic isolation and the community's relation to their shared history and identity.

Daufuskie Island, located between Hilton Head Island and Savannah, is the southernmost inhabited sea island in South Carolina. It is 5 miles (8 km) long by almost 2.5 miles (4.0 km) wide – approximate surface area of 8 square miles (21 km2). With over 3 miles (5 km) of beachfront, Daufuskie is surrounded by the waters of Calibogue Sound, the Intracoastal Waterway and the Atlantic Ocean. It was listed as a census-designated place in the 2020 census with a population of 557.

The Lowcountry is a geographic and cultural region along South Carolina's coast, including the Sea Islands. The region includes significant salt marshes and other coastal waterways, making it an important source of biodiversity in South Carolina.

Daughters of the Dust is a 1991 independent film written, directed and produced by Julie Dash and is the first feature film directed by an African-American woman distributed theatrically in the United States. Set in 1902, it tells the story of three generations of Gullah women in the Peazant family on Saint Helena Island as they prepare to migrate off the island, out of the Southern United States, and into the North.
Vertamae Smart-Grosvenor was an American culinary anthropologist, griot, poet, food writer, and broadcaster on public media. Born into a Gullah family in the Low Country of South Carolina, she moved with them as a child to Philadelphia during the Great Migration. Later she lived in Paris before settling in New York City. She was active in the Black Arts Movement and performed on Broadway.

Jeffrey Adam "Duff" Goldman is an American pastry chef, television personality, and cookbook author. He is the executive chef of the Baltimore-based Charm City Cakes shop, which was featured in the Food Network reality television show Ace of Cakes, and his second, Los Angeles–based, shop Charm City Cakes West, which is featured in Food Network's Duff Till Dawn and "Cake Masters" series. His work has also been featured on the Food Network Challenge, Iron Chef America, Oprah, The Tonight Show with Jay Leno, Man v. Food, Buddy vs. Duff, Duff Takes the Cake, and Duff's Happy Fun Bake Time.

Atlantic Creole is a cultural identifier of those with origins in the transatlantic settlement of the Americas via Europe and Africa.

Julie & Julia is a 2009 American biographical comedy-drama film written and directed by Nora Ephron starring Meryl Streep and Amy Adams in the title roles with Stanley Tucci, Chris Messina and Linda Emond in supporting roles. The film contrasts the life of chef Julia Child in the early years of her culinary career with the life of young New Yorker Julie Powell, who aspires to cook all 524 recipes in Child's cookbook in 365 days, a challenge she described on her popular blog, which made her a published author.
Barbara O. Jones, also known as Barbarao, Barbara-O, and Barbara O., is an American actor from Ohio best known for her work in the films of the L.A. Rebellion movement of 1970s black filmmakers, starring in films by Haile Gerima and Julie Dash. She also appeared on television alongside Muhammad Ali in Freedom Road and had smaller roles in other films including Demon Seed and on television.

James West Fraser is an American artist. One of the leading artists in the representational/En Plein Air tradition, Fraser has built his career on richly painted, atmospheric vistas of cities, coasts, and landscapes.

John Martin Taylor, also known as Hoppin' John, is an American food writer and culinary historian, known for his writing on the cooking of the American South, and, in particular, the foods of the lowcountry, the coastal plain of South Carolina and Georgia. He has played a role in reintroducing many traditional southern dishes, and has advocated the return to stone-ground, whole-grain, heirloom grits and cornmeal production.

Igbo Landing is a historic site at Dunbar Creek on St. Simons Island, Glynn County, Georgia. It was the setting of a mass suicide in 1803 by captive Igbo people who had taken control of their slave ship and refused to submit to slavery in the United States. The event's moral value as a story of resistance towards slavery has symbolic importance in African American folklore as the flying Africans legend, and in literary history.
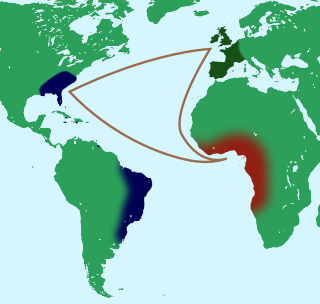
Flying Africans are figures of African diaspora legend who escape enslavement by a magical passage back over the ocean. Most noted in Gullah culture, they also occur in wider African-American folklore, and in that of some Afro-Caribbean peoples.

The Gullah are African Americans who live in the Lowcountry region of the U.S. states of Georgia, Florida, South Carolina, and North Carolina, in both the coastal plain and the Sea Islands. They developed a creole language, also called Gullah, and a culture with some African influence.
Emily Meggett was an American Geechee-Gullah community leader, chef, and author who co-wrote Gullah Geechee Home Cooking: Recipes from the Matriarch of Edisto Island in 2022. She lived on Edisto Island, near Charleston, South Carolina.
Benjamin "BJ" Dennis IV is an American chef known for his focus on Gullah Geechee cuisine.
Benjamin "BJ" Dennis IV is an American Gullah Geechee chef and caterer from Charleston, South Carolina who is known for preserving Gullah Geechee cooking and culture. Additionally, he is also notable for his discovery of hill rice in December 2016 in Trinidad, which was thought to have been extinct.

















