Related Research Articles
A mojo, in the African-American spiritual practice called Hoodoo, is an amulet consisting of a flannel bag containing one or more magical items. It is a "prayer in a bag", or a spell that can be carried with or on the host's body. Alternative American names for the mojo bag include gris-gris bag, hand, mojo hand, toby, nation sack,conjure hand, lucky hand, conjure bag, juju bag, trick bag, tricken bag, root bag, and jomo. The word mojo also refers to magic and charms. Mojo containers are bags, gourds, bottles, shells, and other containers. The making of mojo bags in Hoodoo is a system of African-American occult magic. The creation of mojo bags is an esoteric system that involves sometimes housing spirits inside of bags for either protection, healing, or harm and to consult with spirits. Other times mojo bags are created to manifest results in a person's life such as good-luck, money or love.

Zora Neale Hurston was an American author, anthropologist, and filmmaker. She portrayed racial struggles in the early-1900s American South and published research on hoodoo. The most popular of her four novels is Their Eyes Were Watching God, published in 1937. She also wrote more than 50 short stories, plays, and essays.

Necromancy is the practice of magical sorcery involving communication with the dead by summoning their spirits as apparitions or visions for the purpose of divination; imparting the means to foretell future events; and discovery of hidden knowledge. Sometimes categorized under death magic, the term is occasionally also used in a more general sense to refer to black magic or witchcraft as a whole. In fictional settings such as Dungeons & Dragons, or fantasy video games, it is associated with the reanimation of corpses often meant to be used as weapons.

Hoodoo is a set of spiritual practices, traditions, and beliefs that were created by enslaved African Americans in the Southern United States from various traditional African spiritualities, Christianity and elements of indigenous botanical knowledge. Practitioners of Hoodoo are called rootworkers, conjure doctors, conjure man or conjure woman, root doctors, Hoodoo doctors, and swampers. Regional synonyms for Hoodoo include conjure or rootwork. As a syncretic spiritual system, it also incorporates Islam brought over by enslaved West African Muslims and Spiritualism. Scholars define Hoodoo as a folk religion. Folk religions are syncretic traditions between two or more cultural religions, in this case African indigenous spirituality and Abrahamic religion.
Powwow, also called Brauche or Braucherei in the Pennsylvania Dutch language, is a vernacular system of North American traditional medicine and folk magic originating in the culture of the Pennsylvania Dutch. Blending aspects of folk religion with healing charms, "powwowing" includes a wide range of healing rituals used primarily for treating ailments in humans and livestock, as well as securing physical and spiritual protection, and good luck in everyday affairs. Although the word "powwow" is Native American, these ritual traditions are of European origin and were brought to colonial Pennsylvania in the transatlantic migrations of German-speaking people from Central Europe in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. A practitioner is sometimes referred to as a "Powwower" or Braucher, but terminology varies by region. These folk traditions continue to the present day in both rural and urban settings, and have spread across North America.

Nigromancy, meaning black magic together with six associated practices of black divination, has traditionally referred to the use of supernatural powers or magic for evil and selfish purposes, specifically the seven magical arts prohibited by canon law, as expounded by Johannes Hartlieb in 1456.
Their Eyes Were Watching God is a 1937 novel by American writer Zora Neale Hurston. It is considered a classic of the Harlem Renaissance, and Hurston's best known work. The novel explores protagonist Janie Crawford's "ripening from a vibrant, but voiceless, teenage girl into a woman with her finger on the trigger of her own destiny".

John the Conqueror, also known as High John de Conqueror, John, Jack, and many other folk variants, is a folk hero from African-American folklore. He is associated with the roots of Ipomoea purga, the John the Conqueror root or John the Conqueroo, to which magical powers are ascribed in African-American folklore, especially among the Hoodoo tradition of folk magic. Muddy Waters mentions him as Johnny Cocheroo in the songs "Mannish Boy" and "I'm Your Hoochie Coochie Man". In "Mannish Boy", the line is "I think I'll go down/To old Kansas too/I'm gonna bring back my second cousin/That little Johnny Conqueroo" and in "I'm Your Hoochie Coochie Man", it is called "John De Conquer Blue".

Catherine Anna Yronwode is an American writer, editor, graphic designer, typesetter, and publisher with an extensive career in the comic book industry. She is also a practitioner of folk magic.

In some cultures, a rabbit's foot is carried as an amulet believed to bring good luck. This belief is held by individuals in a great number of places around the world, including Europe, China, Africa, and North and South America. In variations of this superstition, the rabbit it came from must possess certain attributes, such as having been killed in a particular place, using a particular method, or by a person possessing particular attributes.
African-American folktales are the storytelling and oral history of enslaved African Americans during the 1700-1900s. These stories reveal life lessons, spiritual teachings, and cultural knowledge and wisdom for the African-American community which became part of their cultural heritage. During slavery, African-Americans created folk stories that spoke about the hardships of slavery and created folk spirits and heroes that were able to outwit and outsmart their slaveholders and defeat their enemies. These folk stories gave hope to enslaved people that folk spirits will liberate them from slavery. Many folktales are unique to African-American culture, while others are influenced by African, European, and Native American tales.

Gris-gris is a Voodoo amulet originating in Africa which is believed to protect the wearer from evil or bring luck, and in some West African countries is used as a supposed method of birth control. It consists of a small cloth bag, usually inscribed with verses from an ancestor and a ritual number of small objects, worn on the person.

Louisiana Voodoo, also known as New Orleans Voodoo, is an African diasporic religion that originated in Louisiana, now in the southern United States. It arose through a process of syncretism between the traditional religions of West Africa, the Roman Catholic form of Christianity, and Haitian Vodou. No central authority is in control of Louisiana Voodoo, which is organized through autonomous groups.

Mule Bone: A Comedy of Negro Life is a 1930 play by American authors Langston Hughes and Zora Neale Hurston. The process of writing the play led Hughes and Hurston, who had been close friends, to sever their relationship. Mule Bone was not staged until 1991, when it was produced in New York City by the Lincoln Center Theater.
White magic has traditionally referred to the use of supernatural powers or magic for selfless purposes. Practitioners of white magic have been given titles such as wise men or women, healers, white witches or wizards. Many of these people claimed to have the ability to do such things because of knowledge or power that was passed on to them through hereditary lines, or by some event later in their lives. White magic was practiced through healing, blessing, charms, incantations, prayers, and songs. White magic is the benevolent counterpart of malicious black magic.
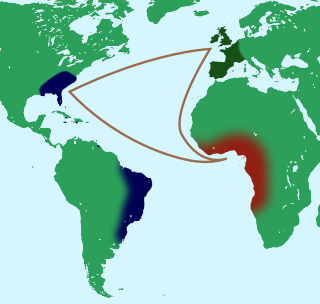
Flying Africans are figures of African diaspora legend who escape enslavement by a magical passage back over the ocean. Most noted in Gullah culture, they also occur in wider African-American folklore, and in that of some Afro-Caribbean peoples.

Mules and Men is a 1935 autoethnographical collection of African-American folklore collected and written by anthropologist Zora Neale Hurston. The book explores stories she collected in two trips: one in Eatonville and Polk County, Florida, and one in New Orleans. Hurston's decision to focus her research on Florida came from a desire to record the cross-section of black traditions in the state. In her introduction to Mules and Men, she wrote, "Florida is a place that draws people—white people from all over the world, and Negroes from every Southern state surely and some from the North and West". Hurston documented 70 folktales during the Florida trip, while the New Orleans trip yielded a number of stories about Marie Laveau, voodoo and Hoodoo traditions. Many of the folktales are told in vernacular; recording the dialect and diction of the Black communities Hurston studied.
Jonah's Gourd Vine is Zora Neale Hurston's 1934 debut novel. The novel is a semi-autobiographical novel following John Buddy Pearson and his wife, Lucy. The characters share the same first names as Hurston's parents and make a similar migration from Notasulga, Alabama to Hurston's childhood home, Eatonville, Florida.

Pustaha is the magic book of the Batak people of North Sumatra, Indonesia. The book contains magical formulas, divinations, recipes, and laws. The pustaha is written and compiled by a Batak magician-priest (datu).

Caroline Dye also known as Aunt Caroline, was a renowned African American Hoodoo woman, rental property investor, soothsayer, rootworker and conjuror based in Newport, Arkansas.
References
- ↑ Anderson, Jeffrey E. (December 2005). Conjure In African American Society . Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0-8071-3092-3.
- 1 2 3 Newbell Niles PH. D. Puckett (January 2003). Folk Beliefs of the Southern Negro. Kessinger Publishing, LLC. ISBN 0-7661-2778-8.
- 1 2 Long, Carolyn Morrow (April 2001). Spiritual Merchants: Religion, Magic, and Commerce. The University of Tennessee Press. ISBN 1-57233-110-0.
- 1 2 Catherine Yronwode. "Black Cat Spiritual Supplies" . Retrieved August 25, 2018.
- ↑ Hurston, Zora Neale (January 1990). Mules and Men. Harper Perennial. ISBN 0-06-091648-6.


