
The unified modeling language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
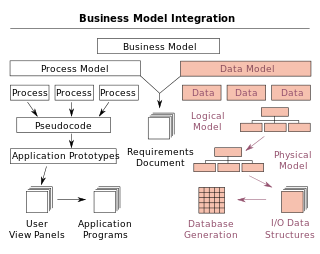
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner. The corresponding professional activity is called generally data modeling or, more specifically, database design.
The XML Metadata Interchange (XMI) is an Object Management Group (OMG) standard for exchanging metadata information via Extensible Markup Language (XML).

An entity–relationship model describes interrelated things of interest in a specific domain of knowledge. A basic ER model is composed of entity types and specifies relationships that can exist between entities.

Objecteering is a UML and MDA CASE tool edited by Objecteering Software, a subsidiary of Softeam.

Business process modeling (BPM) in business process management and systems engineering is the activity of representing processes of an enterprise, so that the current business processes may be analyzed, improved, and automated. BPM is typically performed by business analysts, who provide expertise in the modeling discipline; by subject matter experts, who have specialized knowledge of the processes being modeled; or more commonly by a team comprising both. Alternatively, the process model can be derived directly from events' logs using process mining tools.

Object process methodology (OPM) is a conceptual modeling language and methodology for capturing knowledge and designing systems, specified as ISO/PAS 19450. Based on a minimal universal ontology of stateful objects and processes that transform them, OPM can be used to formally specify the function, structure, and behavior of artificial and natural systems in a large variety of domains.

An information model in software engineering is a representation of concepts and the relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data semantics for a chosen domain of discourse. Typically it specifies relations between kinds of things, but may also include relations with individual things. It can provide sharable, stable, and organized structure of information requirements or knowledge for the domain context.

Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model.

StarUML is a software engineering tool for system modeling using the Unified Modeling Language, as well as Systems Modeling Language, and classical modeling notations. It is published by MKLabs and is available on Windows, Linux and MacOS.

Unicom System Architect is an enterprise architecture tool that is used by the business and technology departments of corporations and government agencies to model their business operations and the systems, applications, and databases that support them. System Architect is used to build architectures using various frameworks including TOGAF, ArchiMate, DoDAF, MODAF, NAF and standard method notations such as sysML, UML, BPMN, and relational data modeling. System Architect is developed by UNICOM Systems, a division of UNICOM Global, a United States-based company.
WebML is a visual notation and a methodology for designing complex data-intensive Web applications. It provides graphical, yet formal, specifications, embodied in a complete design process, which can be assisted by visual design tools.
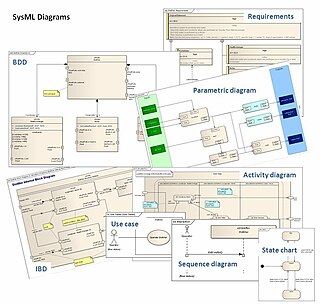
The systems modeling language (SysML) is a general-purpose modeling language for systems engineering applications. It supports the specification, analysis, design, verification and validation of a broad range of systems and systems-of-systems.
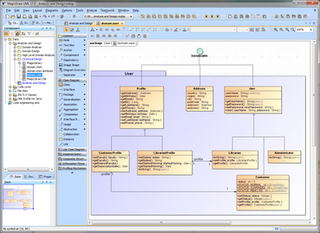
MagicDraw is a proprietary visual UML, SysML, BPMN, and UPDM modeling tool with team collaboration support.
Within data modelling, cardinality is the numerical relationship between rows of one table and rows in another. Common cardinalities include one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many. Cardinality can be used to define data models as well as analyze entities within datasets.

UModel is a UML software modeling tool from Altova, the creator of XMLSpy. UModel supports all 14 UML 2 diagram types and adds a unique diagram for modeling XML Schemas in UML. UModel also supports SysML for embedded system developers, and business process modeling for enterprise analysts. UModel includes code engineering functionality including code generation in Java, C#, and Visual Basic, reverse engineering of existing applications, and round-trip engineering.
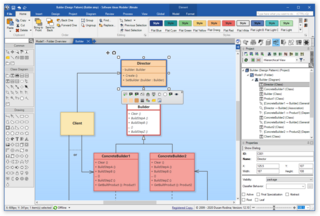
Software Ideas Modeler is a CASE and an UML tool. The modeler supports all 14 diagram types specified in UML 2.5. It also supports among others the following diagrams and standards:

Modelio is an open-source UML tool developed by Modeliosoft, based in Paris, France. It supports the UML2 and BPMN standards.
The Lifecycle Modeling Language (LML) is an open-standard modeling language designed for systems engineering. It supports the full lifecycle: conceptual, utilization, support and retirement stages. Along with the integration of all lifecycle disciplines including, program management, systems and design engineering, verification and validation, deployment and maintenance into one framework. LML was originally designed by the LML steering committee. The specification was published October 17, 2013.

Sparx Systems Enterprise Architect is a visual modeling and design tool based on the OMG UML. The platform supports: the design and construction of software systems; modeling business processes; and modeling industry based domains. It is used by businesses and organizations to not only model the architecture of their systems, but to process the implementation of these models across the full application development life-cycle.
















