| UML diagram types |
|---|
| Structural UML diagrams |
| Behavioral UML diagrams |
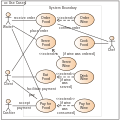
Interaction Overview Diagram [1] is one of the fourteen "nominative" types of diagrams [2] of the Unified Modeling Language (UML), which can picture a control flow with nodes that can contain interaction diagrams.
The interaction overview diagram is similar to the activity diagram, in that both visualize a sequence of activities. The difference is that, for an interaction overview, each individual activity is pictured as a frame which can contain a nested interaction diagram. This makes the interaction overview diagram useful to "deconstruct a complex scenario that would otherwise require multiple if-then-else paths to be illustrated as a single sequence diagram". [3]
The other notation elements for interaction overview diagrams are the same as for activity diagrams. These include initial, final, decision, merge, fork and join nodes. The two new elements in the interaction overview diagrams are the "interaction occurrences" and "interaction elements." [4]