In object-oriented programming, a class is an extensible program-code-template for creating objects, providing initial values for state and implementations of behavior.

The unified modeling language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a software design approach for the development of software systems. It provides a set of guidelines for the structuring of specifications, which are expressed as models. Model Driven Architecture is a kind of domain engineering, and supports model-driven engineering of software systems. It was launched by the Object Management Group (OMG) in 2001.
A stereotype is one of three types of extensibility mechanisms in the Unified Modeling Language (UML), the other two being tags and constraints. They allow designers to extend the vocabulary of UML in order to create new model elements, derived from existing ones, but that have specific properties that are suitable for a particular domain or otherwise specialized usage. The nomenclature is derived from the original meaning of stereotype, used in printing. For example, when modeling a network you might need to have symbols for representing routers and hubs. By using stereotyped nodes you can make these things appear as primitive building blocks.

In software engineering, a sequence diagram shows process interactions arranged in time sequence. This diagram depicts the processes and objects involved and the sequence of messages exchanged as needed to carry out the functionality. Sequence diagrams are typically associated with use case realizations in the 4+1 architectural view model of the system under development. Sequence diagrams are sometimes called event diagrams or event scenarios.

In software engineering, a class diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, operations, and the relationships among objects.
Component-based software engineering (CBSE), also called component-based development (CBD), is a style of software engineering that aims to construct a software system from components that are loosely-coupled and reusable. This emphasizes the separation of concerns among components.

Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a business process model.

A package diagram in the Unified Modeling Language depicts "specializations for Models and for Profiles that organize extensions to UML."
In Unified Modeling Language (UML), a component diagram depicts how components are wired together to form larger components or software systems. They are used to illustrate the structure of arbitrarily complex systems.
Glossary of Unified Modeling Language (UML) terms provides a compilation of terminology used in all versions of UML, along with their definitions. Any notable distinctions that may exist between versions are noted with the individual entry it applies to.
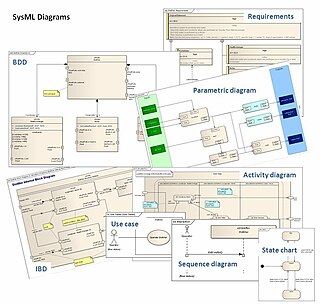
The systems modeling language (SysML) is a general-purpose modeling language for systems engineering applications. It supports the specification, analysis, design, verification and validation of a broad range of systems and systems-of-systems.
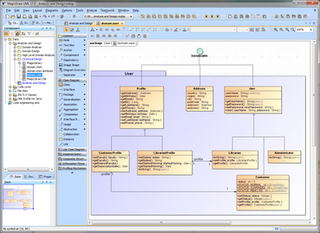
MagicDraw is a proprietary visual UML, SysML, BPMN, and UPDM modeling tool with team collaboration support.
Object-oriented design (OOD) is the process of planning a system of interacting objects to solve a software problem. It is a method for software design. By defining classes and their functionality for their children, each object can run the same implementation of the class with its state.

In object-oriented programming, an object diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a diagram that shows a complete or partial view of the structure of a modeled system at a specific time.
Composite structure diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static structure diagram, that shows the internal structure of a class and the collaborations that this structure makes possible.
In the Unified Modeling Language (UML), a Dependency is "a Relationship that signifies that a single model Element or a set of model Elements requires other model Elements for their specification or implementation." "This means that the complete semantics of the client Element(s) are either semantically or structurally dependent on the definition of the supplier Element(s)." Two or more elements in this relationship are called tuples.
UML state machine, formerly known as UML statechart, is an extension of the mathematical concept of a finite automaton in computer science applications as expressed in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) notation.
UML is a modeling language used by software developers. UML can be used to develop diagrams and provide users (programmers) with ready-to-use, expressive modeling examples. Some UML tools generate program language code from UML. UML can be used for modeling a system independent of a platform language. UML is a graphical language for visualizing, specifying, constructing, and documenting information about software-intensive systems. UML gives a standard way to write a system model, covering conceptual ideas. With an understanding of modeling, the use and application of UML can make the software development process more efficient.

The Interaction Flow Modeling Language (IFML) is a standardized modeling language in the field of software engineering. IFML includes a set of graphic notations to create visual models of user interactions and front-end behavior in software systems.