
Volvariella is a genus of mushrooms with deep salmon pink gills and spore prints.

Psilocybe azurescens is a species of psychedelic mushroom whose main active compounds are psilocybin and psilocin. It is among the most potent of the tryptamine-bearing mushrooms, containing up to 1.8% psilocybin, 0.5% psilocin, and 0.4% baeocystin by dry weight, averaging to about 1.1% psilocybin and 0.15% psilocin. It belongs to the family Hymenogastraceae in the order Agaricales.

Macrolepiota procera, the parasol mushroom, is a basidiomycete fungus with a large, prominent fruiting body resembling a parasol. It is a fairly common species on well-drained soils. It is found solitary or in groups and fairy rings in pastures and occasionally in woodland. It is widespread in temperate regions of Eurasia and possibly North America. Further research is needed to confirm whether specimens found in North America are the same species.

Inocybe is a large genus of mushroom-forming fungi with over 1400 species, including all forms and variations. Members of Inocybe are mycorrhizal, and some evidence shows that the high degree of speciation in the genus is due to adaptation to different trees and perhaps even local environments.

Candy cap or curry milkcap is the English-language common name for two closely related edible species of Lactarius; Lactarius camphoratus, and Lactarius rubidus. These mushrooms are valued for their highly aromatic qualities and are used culinarily as a flavoring rather than as a constituent of a full meal.

Amanita brunnescens, also known as the brown American star-footed amanita or cleft-footed amanita is a native North American mushroom of the large genus Amanita. It differs from A. phalloides by its fragile volva and tendency to bruise brown.

Clitocybe nebularis or Lepista nebularis, commonly known as the clouded agaric, cloudy clitocybe, or cloud funnel, is an abundant gilled fungus which appears both in conifer-dominated forests and broad-leaved woodland in Europe and North America. Appearing in Britain from mid to late autumn, it is edible, but may cause gastrointestinal issues.

The European white egg, bearded amanita or European egg amidella, is a species of fungus of the genus Amanita in the family Amanitaceae. It is a large, white-colored fungus, often tinged with cream. Native to Europe, it is found on plains as well as mountains in the Mediterranean region. It is similar to some deadly poisonous species.

Amanita persicina, commonly known as the peach-colored fly agaric, is a basidiomycete fungus of the genus Amanita with a peach-colored center. Until c. 2015, the fungus was believed to be a variety of A. muscaria.

Hebeloma cavipes is a species of mushroom in the family Hymenogastraceae.

Volvopluteus is a genus of small to medium-sized or big saprotrophic mushrooms growing worldwide. The genus has been segregated from Volvariella with which it shares some morphological characteristics such as the presence of a volva and a pink to pink-brown spore print. Phylogenetic analyses of DNA data have shown that Volvopluteus is closely related to Pluteus and both genera currently are classified in the family Pluteaceae, while Volvariella is not closely related to either genus and its position in the Agaricales is still uncertain.

Volvopluteus gloiocephalus, commonly known as the big sheath mushroom, rose-gilled grisette, or stubble rosegill, is a species of mushroom in the family Pluteaceae. For most of the 20th century it has been known under the names Volvariella gloiocephala or Volvariella speciosa, but recent molecular studies have placed it as the type species of the genus Volvopluteus, newly created in 2011. The cap of this mushroom is about 5–15 cm (2–6 in) in diameter, varies from white to grey or grey-brown, and is markedly sticky when fresh. The gills start out as white but they soon turn pink. The stipe is white and has a sack-like volva at the base. Microscopical features and DNA sequence data are of great importance for separating V. gloiocephalus from related species. V. gloiocephalus is a saprotrophic fungus that grows on grassy fields and accumulations of organic matter like compost or woodchips piles. It has been reported from all continents except Antarctica.

Amanita parcivolvata also known as ringless false fly amanita, is a fungus that produces fruit bodies ranging from 3–12 centimetres in width and height.

Cuphophyllus virgineus is a species of agaric in the family Hygrophoraceae. Its recommended English common name is snowy waxcap in the UK. The species has a largely north temperate distribution, occurring in grassland in Europe and in woodland in North America and northern Asia, but is also known from Australia. It typically produces basidiocarps in the autumn.

Volvariella surrecta, commonly known as the piggyback rosegill, is an agaric fungus in the family Pluteaceae. Although rare, the species is widely distributed, having been reported from Asia, North America, Northern Africa, Europe, and New Zealand. The fungus grows as a parasite on the fruit bodies of other gilled mushrooms, usually Clitocybe nebularis. V. surrecta mushrooms have white or greyish silky-hairy caps up to 8 cm (3.1 in) in diameter, and white gills that turns pink in maturity. The stipe, also white, is up to 9 cm (3.5 in) long, and has a sack-like volva at its base.

Volvariella bombycina, commonly known as the silky volvariella, silky sheath, silky rosegill, silver-silk straw mushroom, or tree mushroom, is a species of edible mushroom in the family Pluteaceae. It is an uncommon but widespread species, having been reported from Asia, Australia, the Caribbean, Europe, and North America. The fruit body (mushroom) begins developing in a thin, egg-like sac. This ruptures and the stem expands quickly, leaving the sac at the base of the stem as a volva. The cap, which can attain a diameter of up to 20 centimetres, is white to slightly yellowish and covered with silky hairs. On the underside of the cap are closely spaced gills, free from attachment to the stem, and initially white before turning pink as the spores mature. The mushroom grows singly or in clusters, often appearing in old knotholes and wounds in elms and maples. V. bombycina contains compounds with antibacterial properties.

Picipes badius, commonly known as the black-footed polypore or black-leg, is a species of fungus in the family Polyporaceae. It causes a white rot of hardwoods and conifers. The species is found in temperate areas of Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America. It has a dark brown or reddish-brown cap that reaches a diameter of 25 cm (9.8 in), and a stipe that is often completely black or brown at the top and black at the base.

Psilocybe allenii is a species of agaric fungus in the family Hymenogastraceae. Described as new to science in 2012, it is named after John W. Allen, who provided the type collection. It is found in the northwestern North America from British Columbia, Canada to Los Angeles, California, most commonly within 10 miles (16 km) of the Pacific coast.

Volvopluteus earlei is a species of mushroom in the family Pluteaceae. It was originally described in 1911 by American mycologist William Alphonso Murrill as Volvariopsis earlei, based on collections made in a Cuban banana field. The fungus was later shuffled to the genera Volvaria and Volvariella before molecular studies placed it in Volvopluteus, a genus newly described in 2011.
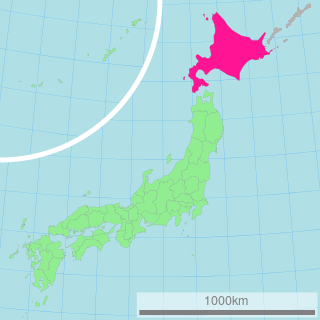
Volvopluteus asiaticus is a species of mushroom in the Pluteaceae family. The cap of this mushroom is about 70–90 mm (2.8–3.5 in) in diameter, greyish brown to brown. The gills start out white but they soon turn pink. The stipe is white and has a volva at the base. Microscopical features and DNA sequence data are of great importance for separating this taxon from related species. V. asiaticus is a saprotrophic fungus that was originally described as growing on the ground, in the humus layer. It is only known from Hokkaido (Japan).




















