Related Research Articles
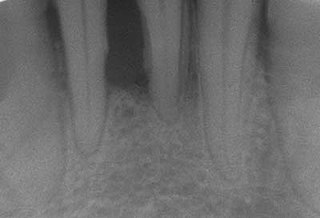
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cause of tooth loss for adults worldwide. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Bad breath may also occur.
Periodontology or periodontics is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants.

Occlusal trauma is the damage to teeth when an excessive force is acted upon them and they do not align properly.
Bleeding on probing (BoP) which is also known as bleeding gums or gingival bleeding is a term used by dentists and dental hygienists when referring to bleeding that is induced by gentle manipulation of the tissue at the depth of the gingival sulcus, or interface between the gingiva and a tooth. BoP is a sign of periodontal inflammation and indicates some sort of destruction and erosion to the lining of the sulcus or the ulceration of sulcular epithelium. The blood comes from lamina propria after the ulceration of the lining. BoP seems to be correlated with Periodontal Inflamed Surface Area (PISA).

Scaling and root planing, also known as conventional periodontal therapy, non-surgical periodontal therapy or deep cleaning, is a procedure involving removal of dental plaque and calculus and then smoothing, or planing, of the (exposed) surfaces of the roots, removing cementum or dentine that is impregnated with calculus, toxins, or microorganisms, the agents that cause inflammation. It is a part of non-surgical periodontal therapy. This helps to establish a periodontium that is in remission of periodontal disease. Periodontal scalers and periodontal curettes are some of the tools involved.

Gingival enlargement is an increase in the size of the gingiva (gums). It is a common feature of gingival disease. Gingival enlargement can be caused by a number of factors, including inflammatory conditions and the side effects of certain medications. The treatment is based on the cause. A closely related term is epulis, denoting a localized tumor on the gingiva.
The gingival fibers are the connective tissue fibers that inhabit the gingival tissue adjacent to teeth and help hold the tissue firmly against the teeth. They are primarily composed of type I collagen, although type III fibers are also involved.
Gingivectomy is a dental procedure in which a dentist or oral surgeon cuts away part of the gums in the mouth.

In dentistry, the subepithelial connective tissue graft is an oral and maxillofacial surgical procedure first described by Alan Edel in 1974. Currently, it is generally used to obtain root coverage following gingival recession, which was a later development by Burt Langer in the early 1980s.
Guided bone regeneration (GBR) and guided tissue regeneration (GTR) are dental surgical procedures that use barrier membranes to direct the growth of new bone and gingival tissue at sites with insufficient volumes or dimensions of bone or gingiva for proper function, esthetics or prosthetic restoration. Guided bone regeneration typically refers to ridge augmentation or bone regenerative procedures; guided tissue regeneration typically refers to regeneration of periodontal attachment.

Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms that is attached to tooth surfaces, termed plaque-induced gingivitis. Most forms of gingivitis are plaque-induced.

John Mankey Riggs was the leading authority on periodontal disease and its treatment in the United States, to the point that periodontal disease was known as "Riggs' disease."
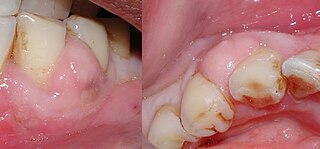
A periodontal abscess, is a localized collection of pus within the tissues of the periodontium. It is a type of dental abscess. A periodontal abscess occurs alongside a tooth, and is different from the more common periapical abscess, which represents the spread of infection from a dead tooth. To reflect this, sometimes the term "lateral (periodontal) abscess" is used. In contrast to a periapical abscess, periodontal abscesses are usually associated with a vital (living) tooth. Abscesses of the periodontium are acute bacterial infections classified primarily by location.
Aggressive periodontitis describes a type of periodontal disease and includes two of the seven classifications of periodontitis as defined by the 1999 classification system:
- Localized aggressive periodontitis (LAP)
- Generalized aggressive periodontitis (GAP)
In dentistry, numerous types of classification schemes have been developed to describe the teeth and gum tissue in a way that categorizes various defects. All of these classification schemes combine to provide the periodontal diagnosis of the aforementioned tissues in their various states of health and disease.
Clinical attachment loss (CAL) is the predominant clinical manifestation and determinant of periodontal disease.
Hereditary gingival fibromatosis (HGF), also known as idiopathic gingival hyperplasia, is a rare condition of gingival overgrowth. HGF is characterized as a benign, slowly progressive, nonhemorrhagic, fibrous enlargement of keratinized gingiva. It can cover teeth in various degrees, and can lead to aesthetic disfigurement. Fibrous enlargement is most common in areas of maxillary and mandibular tissues of both arches in the mouth. Phenotype and genotype frequency of HGF is 1:175,000 where males and females are equally affected but the cause is not entirely known. It mainly exists as an isolated abnormality but can also be associated with a multi-system syndrome.

Gingival grafting, also called gum grafting or periodontal plastic surgery, is a generic term for the performance of any of a number of periodontal surgical procedures in which the gum tissue is grafted. The aim may be to cover exposed root surfaces or merely to augment the band of keratinized tissue.
Periodontal surgery is a form of dental surgery that prevents or corrects anatomical, traumatic, developmental, or plaque-induced defects in the bone, gingiva, or alveolar mucosa. The objectives of this surgery include accessibility of instruments to root surface, elimination of inflammation, creation of an oral environment for plaque control, periodontal diseases control, oral hygiene maintenance, maintain proper embrasure space, address gingiva-alveolar mucosa problems, and esthetic improvement. The surgical procedures include crown lengthening, frenectomy, and mucogingival flap surgery.
References
- ↑ Shklar, G; Carranza, FA: The Historical Background of Periodontology. In Newman, MG; Takei, HH; Carrana FA, editors: Carranza’s Clinical Periodontology, 9th Edition. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2002. page 7.
- ↑ "Oral Surgery and Crown Lengthening". santaclaritacosmeticdentist.net. Retrieved April 17, 2014.
- ↑ American Dental Club of Paris: Meetings of December 1902 and January and March 1903. Dent Cosmos 1904; 46:39.
- ↑ The New York Times A SAN FRANCISCO DENTIST'S CHARGES, July 7, 1887