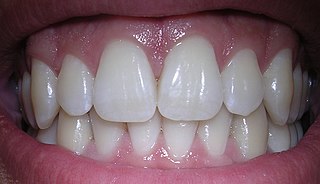
Human teeth function to mechanically break down items of food by cutting and crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digesting. As such, they are considered part of the human digestive system. Humans have four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, which each have a specific function. The incisors cut the food, the canines tear the food and the molars and premolars crush the food. The roots of teeth are embedded in the maxilla or the mandible and are covered by gums. Teeth are made of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness.
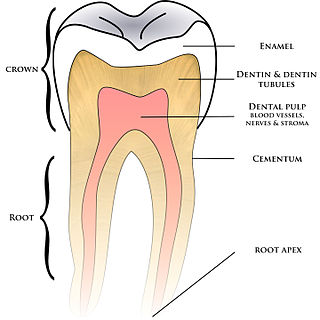
Cementum is a specialized calcified substance covering the root of a tooth. The cementum is the part of the periodontium that attaches the teeth to the alveolar bone by anchoring the periodontal ligament.

The gums or gingiva consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.

The periodontium is the specialized tissues that both surround and support the teeth, maintaining them in the maxillary and mandibular bones. Periodontics is the dental specialty that relates specifically to the care and maintenance of these tissues. It provides the support necessary to maintain teeth in function. It consists of four principal components, namely:

In dental anatomy, the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) is the location where the enamel, which covers the anatomical crown of a tooth, and the cementum, which covers the anatomical root of a tooth, meet. Informally it is known as the neck of the tooth. The border created by these two dental tissues has much significance as it is usually the location where the gingiva (gums) attaches to a healthy tooth by fibers called the gingival fibers.

The periodontal ligament, commonly abbreviated as the PDL, are a group of specialized connective tissue fibers that essentially attach a tooth to the alveolar bone within which they sit. It inserts into root cementum on one side and onto alveolar bone on the other.
Tooth development or odontogenesis is the complex process by which teeth form from embryonic cells, grow, and erupt into the mouth. For human teeth to have a healthy oral environment, all parts of the tooth must develop during appropriate stages of fetal development. Primary (baby) teeth start to form between the sixth and eighth week of prenatal development, and permanent teeth begin to form in the twentieth week. If teeth do not start to develop at or near these times, they will not develop at all, resulting in hypodontia or anodontia.
Periodontology or periodontics is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting tissues are known as the periodontium, which includes the gingiva (gums), alveolar bone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament. A periodontist is a dentist that specializes in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease and in the placement of dental implants.

The gingival sulcus is an area of potential space between a tooth and the surrounding gingival tissue and is lined by sulcular epithelium. The depth of the sulcus is bounded by two entities: apically by the gingival fibers of the connective tissue attachment and coronally by the free gingival margin. A healthy sulcular depth is three millimeters or less, which is readily self-cleansable with a properly used toothbrush or the supplemental use of other oral hygiene aids.
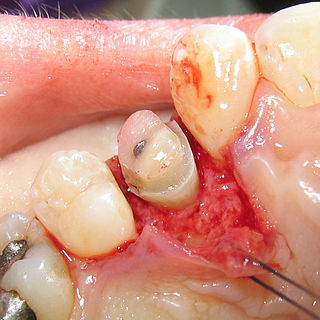
Crown lengthening is a surgical procedure performed by a dentist, or more frequently a periodontist, where more tooth is exposed by removing some of the gingival margin (gum) and supporting bone. Crown lengthening can also be achieved orthodontically by extruding the tooth.

Gingival and periodontal pockets are dental terms indicating the presence of an abnormal depth of the gingival sulcus near the point at which the gingival tissue contacts the tooth.

Crown-to-root-ratio is the ratio of the length of the part of a tooth that appears above the alveolar bone versus what lies below it. It is an important consideration in the diagnosis, treatment planning and restoration of teeth, one that hopefully guides the plan of treatment to the proper end result.
In dental anatomy, the junctional epithelium (JE) is that epithelium which lies at, and in health also defines, the base of the gingival sulcus. The probing depth of the gingival sulcus is measured by a calibrated periodontal probe. In a healthy-case scenario, the probe is gently inserted, slides by the sulcular epithelium (SE), and is stopped by the epithelial attachment (EA). However, the probing depth of the gingival sulcus may be considerably different from the true histological gingival sulcus depth.

The free gingival margin is the interface between the sulcular epithelium and the epithelium of the oral cavity. This interface exists at the most coronal point of the gingiva, otherwise known as the crest of the marginal gingiva.
A mucogingival junction is an anatomical feature found on the intraoral mucosa. The mucosa of the cheeks and floor of the mouth are freely moveable and fragile, whereas the mucosa around the teeth and on the palate are firm and keratinized. Where the two tissue types meet is known as a mucogingival junction.
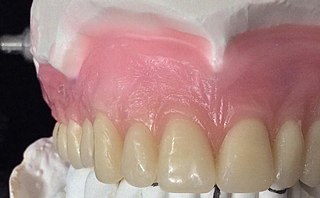
The gingiva often possess a textured surface that is referred to as being stippled. Stippling only presents on the attached gingiva bound to underlying alveolar bone, not the freely moveable alveolar mucosa or free gingiva. Stippling used to be thought to indicate health, but it has since been shown that smooth gingiva is not an indication of disease, unless it is smooth due to a loss of previously existing stippling.
The interdental papilla, also known as the interdental gingiva, is the part of the gums (gingiva) that exists coronal to the free gingival margin on the mesial and distal surfaces of the teeth. The interdental papillae fill in the area between the teeth apical to their contact areas to prevent food impaction; they assume a conical shape for the anterior teeth and a blunted shape buccolingually for the posterior teeth.

In dentistry, debridement refers to the removal by dental cleaning of accumulations of plaque and calculus (tartar) in order to maintain dental health. Debridement may be performed using ultrasonic instruments, which fracture the calculus, thereby facilitating its removal, as well as hand tools, including periodontal scaler and curettes, or through the use of chemicals such as hydrogen peroxide.
Clinical attachment loss (CAL) is the predominant clinical manifestation and determinant of periodontal disease.










