
Eosin is the name of several fluorescent acidic compounds which bind to and form salts with basic, or eosinophilic, compounds like proteins containing amino acid residues such as arginine and lysine, and stains them dark red or pink as a result of the actions of bromine on eosin. In addition to staining proteins in the cytoplasm, it can be used to stain collagen and muscle fibers for examination under the microscope. Structures that stain readily with eosin are termed eosinophilic. In the field of histology, Eosin Y is the form of eosin used most often as a histologic stain.
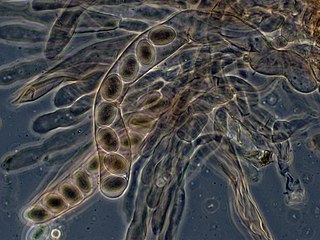
An ascus is the sexual spore-bearing cell produced in ascomycete fungi. Each ascus usually contains eight ascospores, produced by meiosis followed, in most species, by a mitotic cell division. However, asci in some genera or species can occur in numbers of one, two, four, or multiples of four. In a few cases, the ascospores can bud off conidia that may fill the asci with hundreds of conidia, or the ascospores may fragment, e.g. some Cordyceps, also filling the asci with smaller cells. Ascospores are nonmotile, usually single celled, but not infrequently may be coenocytic, and in some cases coenocytic in multiple planes. Mitotic divisions within the developing spores populate each resulting cell in septate ascospores with nuclei. The term ocular chamber, or oculus, refers to the epiplasm that is surrounded by the "bourrelet".

Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology, in cytology, and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues, cell populations, or organelles within individual cells.

The lateral lemniscus is a tract of axons in the brainstem that carries information about sound from the cochlear nucleus to various brainstem nuclei and ultimately the contralateral inferior colliculus of the midbrain. Three distinct, primarily inhibitory, cellular groups are located interspersed within these fibers, and are thus named the nuclei of the lateral lemniscus.

Histopathology is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments.

Elastic cartilage, fibroelastic cartilage or yellow fibrocartilage is a type of cartilage present in the pinnae (auricles) of the ear giving it shape, provides shape for the lateral region of the external auditory meatus, medial part of the auditory canal Eustachian tube, corniculate and cuneiform laryneal cartilages, and the epiglottis. It contains elastic fiber networks and collagen type II fibers. The principal protein is elastin.
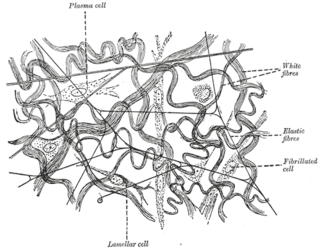
Elastic fibers are an essential component of the extracellular matrix composed of bundles of proteins (elastin) which are produced by a number of different cell types including fibroblasts, endothelial, smooth muscle, and airway epithelial cells. These fibers are able to stretch many times their length, and snap back to their original length when relaxed without loss of energy. Elastic fibers include elastin, elaunin and oxytalan.

Nile blue is a stain used in biology and histology. It may be used with live or fixed cells, and imparts a blue colour to cell nuclei.

An acid dye is a dye that is typically applied to a textile at low pH. They are mainly used to dye wool, not cotton fabrics. Some acid dyes are used as food colorants, and some can also be used to stain organelles in the medical field.

The tunica intima, or intima for short, is the innermost tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It is made up of one layer of endothelial cells, and is supported by an internal elastic lamina. The endothelial cells are in direct contact with the blood flow.

The tunica media, or media for short, is the middle tunica (layer) of an artery or vein. It lies between the tunica intima on the inside and the tunica externa on the outside.

Masson's trichrome is a three-colour staining procedure used in histology. The recipes emerged from Claude L. Pierre Masson's (1880–1959) original formulation have different specific applications, but all are suited for distinguishing cells from surrounding connective tissue.

Hematoxylin and eosin stain is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E.

Phosphotungstic acid haematoxylin (PTAH) is a mix of haematoxylin with phosphotungstic acid, used in histology for staining.

The emboliform nucleus is a deep cerebellar nucleus that lies immediately to the medial side of the dentate nucleus, partly covering its hilum. It is one of the four pairs of deep cerebellar nuclei, which are from lateral to medial: the dentate, emboliform, globose and fastigial. These nuclei can be seen using Weigert's elastic stain.
Lillie's trichrome is a combination of dyes used in histology.
Infantile digital fibromatosis (IDF), also termed inclusion body fibromatosis or Reye's tumor, usually occurs as a single, small, asymptomatic, nodule in the dermis on a finger or toe of infants and young children. IMF is a rare disorder with approximately 200 cases reported in the medical literature as of 2021. The World Health Organization in 2020 classified these nodules as a specific benign tumor type in the category of fibroblastic and myofibroblastic tumors. IDF was first described by the Australian pathologist Douglas Reye in 1965.
Movat's stain is a pentachrome stain originally developed by Henry Zoltan Movat (1923–1995), a Hungarian-Canadian Pathologist in Toronto in 1955 to highlight the various constituents of connective tissue, especially cardiovascular tissue, by five colors in a single stained slide. In 1972, H. K. Russell, Jr. modified the technique so as to reduce the time for staining and to increase the consistency and reliability of the staining, creating the Russell–Movat stain.

Luxol fast blue stain, abbreviated LFB stain or simply LFB, is a commonly used stain to observe myelin under light microscopy, created by Heinrich Klüver and Elizabeth Barrera in 1953. LFB is commonly used to detect demyelination in the central nervous system (CNS), but cannot discern myelination in the peripheral nervous system.
Verhoeff's stain, also known as Verhoeff's elastic stain (VEG) or Verhoeff–Van Gieson stain (VVG), is a staining protocol used in histology, developed by American ophthalmic surgeon and pathologist Frederick Herman Verhoeff (1874–1968) in 1908. The formulation is used to demonstrate normal or pathologic elastic fibers.















