
Electric power distribution is the final stage in the delivery of electricity. Electricity is carried from the transmission system to individual consumers. Distribution substations connect to the transmission system and lower the transmission voltage to medium voltage ranging between 2 kV and 33 kV with the use of transformers. Primary distribution lines carry this medium voltage power to distribution transformers located near the customer's premises. Distribution transformers again lower the voltage to the utilization voltage used by lighting, industrial equipment and household appliances. Often several customers are supplied from one transformer through secondary distribution lines. Commercial and residential customers are connected to the secondary distribution lines through service drops. Customers demanding a much larger amount of power may be connected directly to the primary distribution level or the subtransmission level.
Transpower New Zealand Limited (TPNZ) is the state-owned enterprise responsible for electric power transmission in New Zealand. It performs two major functions in the New Zealand electricity market. As the owner of the National Grid it provides the infrastructure of electric power transmission that allows consumers to have access to generation from a wide range of sources, and enables competition in the wholesale electricity market; as system operator it manages the real-time operation of the grid and the physical operation of the electricity market.

A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages. They are a common component of the infrastructure. There are 55,000 substations in the United States.
Power Grid Corporation of India Limited is an Indian central public sector undertaking under the ownership of the Ministry of Power, Government of India. It is engaged mainly in transmission of bulk power across different states of India. It is headquartered in Gurugram. Power Grid transmits about 50% of the total power generated in India on its transmission network.

National Grid, Malaysia is the high-voltage electric power transmission network in Peninsular Malaysia. It is operated and owned by Tenaga Nasional Berhad (TNB) by its Transmission Division. There are two other electrical grids in Sabah and Sarawak operated by Sabah Electricity Sdn Bhd (SESB) and Sarawak Energy Berhad (SEB) respectively.

West Bengal State Electricity Board (WBSEB) was a state government electricity regulation board in West Bengal in India. It was formed on 1 May 1955. In 2007, the Government of West Bengal unbundled the erstwhile WBSEB into two companies namely West Bengal State Electricity Distribution Company (WBSEDCL) and West Bengal State Electricity Transmission Company (WBSETCL). The two enterprises were formed on 1 April 2007 under the provisions of West Bengal Power Reform Scheme, 2007.

Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system is a traction power network for the southern portion of the Northeast Corridor (NEC), the Keystone Corridor, and several branch lines between New York City and Washington D.C. The system was constructed by the Pennsylvania Railroad between 1915 and 1938 before the North American power transmission grid was fully established. This is the reason the system uses 25 Hz, as opposed to 60 Hz, which is the standard frequency for power transmission in North America. The system is also known as the Southend Electrification, in contrast to Amtrak's 60 Hz traction power system that runs between Boston and New Haven, which is known as the Northend Electrification system.

An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power long distances, and lastly electric power distribution to individual customers, where voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage(s). Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. From small to large there are microgrids, wide area synchronous grids, and super grids.

Mahapareshan or Mahatransco is a wholly owned by government of Maharashtra and the major electricity transmission company in the state of Maharashtra, India.after 2003 it is converted to state-owned Electricity Companies.
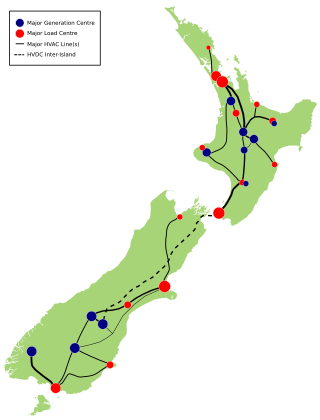
The National Grid is the nationwide system of electric power transmission in New Zealand. The grid is owned, operated and maintained by Transpower New Zealand, a state-owned enterprise, although some lines are owned by local distribution companies and leased to Transpower. In total, the national grid contains 11,803 kilometres (7,334 mi) of high-voltage lines and 178 substations.
Power Grid Company of Bangladesh Ltd. (PGCB) is the sole organization of Government of Bangladesh entrusted with transmission of power throughout the country. It is a government owned Public Limited Company which is listed at the Dhaka and Chittagong Stock Exchange.

The Whakamaru to Brownhill Road transmission line is a double-circuit 400 kV-capable transmission line constructed by Transpower to increase the capacity of the National Grid between the southern Waikato and the city of Auckland. The line runs from the Whakamaru sub-station near the Whakamaru Power Station, over a distance of 186 kilometres (116 mi) to the new Brownhill Road substation near Whitford in southeastern Auckland. The line will initially be operated at 220 kV. From Brownhill Road, 220 kV underground cables connect the line to the Pakuranga sub-station in eastern Auckland. The project was the subject of considerable controversy and protest during the planning and approval stages. Construction of the line started in February 2010, and the line was commissioned on 30 October 2012. The transmission line forms the major part of a wider North Island Grid Upgrade project with a forecast cost to completion of $894 million.
The North Auckland and Northland (NAaN) grid upgrade project reinforced transmission into the Auckland Region and across the harbour to North Auckland and the Northland Region. It added new 220 kV transmission capacity to the National Grid by providing 37 km of underground cable between the Pakuranga, Penrose, and Albany substations.

Electricity Ashburton Limited, trading as EA Networks is a co-operatively-owned electricity distribution company, based in Ashburton, New Zealand.

The electricity sector in Taiwan ranges from generation, transmission, distribution and sales of electricity, covering Taiwan island and its offshore islands.

Zaporozhtransformator (ZTR) is a Private Joint Stock Company, formerly - Zaporozhye Transformer Plant: a company specializing in the design and manufacturing of oil-filled power transformers, shunt reactors and magnetically controlled shunt reactors, with production facilities located in Zaporizhzhia, Ukraine.

The electricity sector in Macau ranges from generation, transmission, distribution and sales of electricity in Macau, China.

West Bengal State Electricity Distribution Company Limited (WBSEDCL) is a wholly owned enterprise of Government of West Bengal, established in 2007 as one of the two successors of West Bengal State Electricity Board, and is responsible for providing power to 96% of West Bengal with a customer base of more than 2.2 crore across the state. The company has achieved a profit of ₹95.13 crore (PAT) in the fiscal year 2010–11.

Dhaka Electric Supply Company Limited (DESCO) is a public limited company which distributes electricity at the Northern parts of Dhaka City and Tongi Town of Gazipur District. The company was created in November 1996 under the Companies Act 1994 as a Public Limited Company. The company is now under the Power Division of the Bangladesh Ministry of Power, Energy and Mineral Resources and serving a total number of 604,304 consumers as of 31 December 2013. Md. Selim Uddin, rank of additional secretary, is the chairperson of DESCO and Engr. Md. Kausar Ameer Ali is the managing director.
The high-voltage electricity substations in the United Kingdom are listed in the following tables. The substations provide entry points to, and exit points from, the National Grid (GB) or Northern Ireland Electricity Network. Entry points include power stations, major wind farms and inter-connectors from other countries and regions. Exit points are to lower voltage transmission and distribution substations which are also shown in the tables.















