
Shorea is a genus of about 196 species of mainly rainforest trees in the family Dipterocarpaceae. The genus is named after Sir John Shore, the governor-general of the British East India Company, 1793–1798. The timber of trees of the genus is sold under the common names lauan, luan, lawaan, meranti, seraya, balau, bangkirai, and Philippine mahogany.

Odoardo Beccari was an Italian botanist famous for his discoveries in Indonesia, New Guinea, and Australia. He has been called the greatest botanist to ever study Malesia. His author abbreviation is Becc. when citing a botanical name.

Hose's palm civet, also known as Hose's civet, is a viverrid species endemic to the island of Borneo. It is listed on the IUCN Red List as Vulnerable because of an ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 30% over the last three generations and suspected to be more than 30% in the next three generations due to declines in population inferred from habitat destruction and degradation.

Nepenthes lowii, or Low's pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is named after Hugh Low, who discovered it on Mount Kinabalu. This species is perhaps the most unusual in the genus, being characterised by its strongly constricted upper pitchers, which bear a greatly reduced peristome and a reflexed lid with numerous bristles on its lower surface.

Niah National Park, located within Miri Division, Sarawak, Malaysia, is the site of the Niah Caves which are an archeological site.

The black-capped fruit bat is a species of megabat in the monotypic genus Chironax.

The dayak fruit bat or dyak fruit bat is a relatively rare frugivorous megabat species found only on the Sunda Shelf of southeast Asia, specifically the Malay Peninsula south of the Isthmus of Kra, and the islands of Borneo and Sumatra. There are three species in the genus Dyacopterus: D. spadiceus, D. brooksi and D. rickarti. All are found in the forests of Malaysia, Thailand, and the Philippines. Few specimens of any of the three species exist, due not only to their rarity, but also because they rarely enter the sub-canopy of the forest where they can be caught in scientists' nets.

Nepenthes northiana, or Miss North's pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo, where it grows at elevations ranging from 0 to 500 m above sea level. The specific epithet northiana honours the English botanic illustrator Marianne North, who first depicted the species. Nepenthes northiana is one of the most famous Nepenthes, and its discovery in the latter half of the 19th century contributed to Sarawak's reputation as a land of spectacular exotic plants.

Nepenthes pilosa is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is characterised by a dense indumentum of long yellow-brown hairs. Pitchers have a distinctive hook-shaped appendage on the underside of the lid. The specific epithet derives from the Latin word pilosus, meaning "hairy".

Nepenthes murudensis, or the Murud pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Mount Murud in Borneo, after which it is named. It is of putative hybrid origin: its two original parent species are thought to be N. reinwardtiana and N. tentaculata.

Nepenthes faizaliana is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the limestone cliffs of Gunung Mulu National Park in Sarawak, Borneo. It is thought to be most closely related to N. boschiana.

Nepenthes muluensis, or the Mulu pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It grows in highland habitats at elevations of 1700 to 2400 m above sea level.

Nepenthes vogelii is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is thought to be most closely related to N. fusca.

Chionanthus, common name: fringetrees, is a genus of about 140 species of flowering plants in the family Oleaceae.

Jalan Arang National Secondary School is a public secondary school situated on Jalan Arang in Kuching, the capital of the East Malaysian state of Sarawak. The school was founded in January 2003. It offers classes from Transition up to Form 5.

Willughbeia is a genus of plant in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1820. It is native to Southeast Asia with a few species in the Indian Subcontinent. Several species have edible fruits enjoyed in many countries. Many species are vines with sticky latex.

Willughbeia edulis is a vine species bearing tropical fruit in the family Apocynaceae.
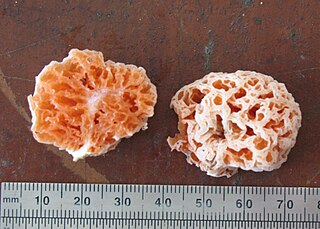
Spongiforma squarepantsii is a species of fungus in the family Boletaceae, genus Spongiforma. Found in Malaysia, it was described as new to science in 2011. It produces sponge-like, rubbery orange fruit bodies that have a fruity or musky odour. The fruit bodies reach dimensions of 10 cm (3.9 in) wide by 7 cm (2.8 in) tall. Like a sponge, they will resume their original shape if water is squeezed out. The spores, produced on the surfaces of the hollows of the sponge, are almond-shaped with rough surfaces, and measure 10‑12.5 μm by 6‑7 μm. The name of the fungus derives from the Nickelodeon cartoon character SpongeBob SquarePants from the show of the same name. S. squarepantsii is one of two species in Spongiforma; it differs from S. thailandica in its color, odour, and spore structure.

Sarawakian cuisine is a regional cuisine of Malaysia. Like the rest of Malaysian cuisine, Sarawak food is based on staples such as rice. There is also a great variety of other ingredients and food preparations due to the influence of the state's varied geography and indigenous cultures quite distinct from the regional cuisines of the Peninsular Malaysia. Sarawak is famous for its multi-ethnic population. As the homeland of many unique communities, Sarawak has a variety of cuisines rarely found elsewhere in Malaysia. The uniqueness of Sarawak well depends on its ethnic groups. Every native group in Sarawak has their own lifestyle, traditions, cultures and also foods. Sarawak cuisine is less spicy and has a subtle in taste. It uses fresh seafood and natural herbs like turmeric, lemongrass, ginger, lime and tapioca leaves. These ingredients are not only easily available, but also add a hint of aroma, texture and freshness to the delicacies. Food is one of the most cultural identities for native groups in Sarawak with each ethnic group having their own delicacies. Among the Iban, popular foods include tubu (stems), tuak and pansuh. The Malay have bubur pedas (porridge) and kek lapis Sarawak ; the Bidayuh have asam siok and sup ponas Bidayuh. The Melanau make tebaloi, sagu and umai and the Orang Ulu are known for garam barrio, kikid (broth), tengayen, and urum giruq (pudding).
Willughbeia angustifolia is a species of flowering plant, a woody monoecious vine in the dogbane family, that is native to Southeast Asia.


















