
Knautia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Caprifoliaceae. The common names are variants of "widow flower". Others are given the name "scabious", which properly belongs to the related genus (Scabiosa). The name Knautia comes from the 17th-century German botanists, Drs. Christoph and Christian Knaut.

Falconeria is a monotypic plant genus in the family Euphorbiaceae, first described as a genus in 1839. The genus is sometimes included within the genus Sapium. The sole species is Falconeria insignis. The plant is found from India, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka to Indochina, China, Thailand and Peninsular Malaysia.
Siegfried Jost Casper was a German biologist whose primary research was in limnology and the plant genus Pinguicula. Together with Heinz-Dieter Krausch he published a basic reference work on the freshwater flora of central Europe. For many years he studied the East German lake Stechlinsee as well as the river Saale. In 1966 he published a monograph of the genus Pinguicula, a work that is still in use today. He described at least 14 new species, most recently Pinguicula lippoldii and Pinguicula toldensis in 2007. He served as head of the Botanical Garden of the Friedrich Schiller University of Jena and from 1990 until his death was a member of the "Akademie Gemeinnütziger Wissenschaften" in Erfurt.

Hermagor-Pressegger See is a town in the Austrian state of Carinthia. It is the administrative centre of the Hermagor District.The town is named after Saint Hermagoras of Aquileia, the first bishop of Aquileia.

Franz Xaver Freiherr von Wulfen was an Austrian botanist, zoologist, mineralogist, alpinist, and Jesuit priest. He is credited with discovering the flowering plants Wulfenia carinthiaca, Saxifraga moschata, and Stellaria bulbosa. In 1845 the lead molybdate mineral wulfenite was named in his honor by Wilhelm Karl von Haidinger.
Davidiella carinthiaca is a fungal plant pathogen infecting red clover.
The Giardino Botanico Montano di Pratorondanino is a nature preserve and botanical garden located at 750 meters altitude in Pratorondanino, Campo Ligure, Province of Genoa, Liguria, Italy. It is open during the warmer months.
Pinguicula lippoldii is an insectivorous plant of the genus Pinguicula endemic to the Nipe-Sagua-Baracoa mountain region of eastern Cuba.
Pinguicula toldensis is an insectivorous plant of the genus Pinguicula endemic to the Nipe-Sagua-Baracoa mountain region of eastern Cuba.
The Giardino Botanico delle Alpi Orientali, also known as the Giardino Botanico di Monte Faverghera, is an alpine botanical garden located in the Corpo Forestale dello Stato die Belluno on Monte Faverghera, southeast of Nevegal, Province of Belluno, Veneto, Italy. It is open daily except Mondays in the warmer months; an admission fee is charged.

Wulfenia is a plant genus in the family Plantaginaceae. The genus was named after Franz Xaver von Wulfen (1728–1805), an Austrian botanist, zoologist, mineralogist, alpinist, and Jesuit priest. It was first described in 1781 by Nikolaus Joseph von Jacquin in. It is also in Tribe Veroniceae.

Sedella is a small genus of annual flowering plants in the family Crassulaceae. There are approximately 7 species, all native to California, United States, one with a distribution extending into Oregon. These are petite succulent plants growing a few centimeters tall and bearing tiny yellowish or brownish flowers. Mock stonecrop is a common name for these plants.

Árpád von Degen, was a Hungarian biologist and botanist whose activities were rooted in theoretical principles and scientific botany. Head of the royal Seed Testing Station in Budapest from 1896, Professor of Botany at the Budapest University from 1927 and member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, he died on 30 March 1934 in Budapest.

Galeopsis is a genus of annual herbaceous plants native to Europe and Asia. Members of this genus often have common names ending in hemp-nettle or hempnettle. Some species are naturalized in North America and New Zealand.

Wulfenia: Mitteilungen des Kärntner Botanikzentrums is a print-only peer-reviewed scientific journal of botany published by the Regional Museum of Carinthia. It was established in 1998 and the editor-in-chief is Roland K. Eberwein.

Allium nathaliae is a species of wild onion endemic to the Crimean Peninsula.

Astrantia major, the great masterwort, is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae, native to central and eastern Europe. Growing up to 90 cm (35 in) tall by 45 cm (18 in) broad, it is an herbaceous perennial, much used in gardens.

Gartnerkofel is a mountain of the Carnic Alps in Carinthia, Austria. It is located on the main chain of the Carnics above the Naßfeld Pass, near the border with Italy. The nearest town is Hermagor-Pressegger See. The mountain has two summits, and ravines fall down from its northern slopes, which are separated by rocky ridges. The normal route is from the northwest, from where it an easy climb across the ridge to the summit. The mountain is also a popular ski touring destination.

Kosovo is characterised by a diverse biodiversity and an abundance of different ecosystems and habitats determined by the climate along with the geology and hydrology. Predominantly mountainous, it is located at the center of the Balkan Peninsula bounded by Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the north and east, North Macedonia to the southeast, and Albania to the southwest.
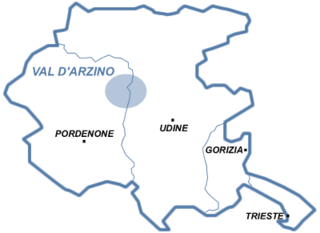
Pinguicula poldinii is a species of insectivorous plant endemic to Val d'Arzino, Italy, where it grows at elevations of 450–550 meters. It is restricted to steep rocks throughout a very small area in which it is threatened by over-collection. It was described in 2001.














