
The brolga, formerly known as the native companion, is a bird in the crane family. It has also been given the name Australian crane, a term coined in 1865 by well-known ornithologist John Gould in his Birds of Australia.

The wedge-tailed eagle also known as the eaglehawk, is the largest bird of prey in the continent of Australia. It is also found in southern New Guinea to the north and is distributed as far south as the state of Tasmania. Adults of the species have long, broad wings, fully feathered legs, an unmistakable wedge-shaped tail, an elongated upper mandible, a strong beak and powerful feet. The wedge-tailed eagle is one of 12 species of large, predominantly dark-coloured booted eagles in the genus Aquila found worldwide. Genetic research has clearly indicated that the wedge-tailed eagle is fairly closely related to other, generally large members of the Aquila genus. A large brown-to-black bird of prey, it has a maximum reported wingspan of 2.84 m and a length of up to 1.06 m.

The long-tailed planigale, also known as Ingram's planigale or the northern planigale, is the smallest of all marsupials, and one of the smallest of all mammals. It is rarely seen but is a quite common inhabitant of the blacksoil plains, clay-soiled woodlands, and seasonally flooded grasslands of Australia's Top End.

The Turbellaria are one of the traditional sub-divisions of the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms), and include all the sub-groups that are not exclusively parasitic. There are about 4,500 species, which range from 1 mm (0.039 in) to large freshwater forms more than 500 mm (20 in) long or terrestrial species like Bipalium kewense which can reach 600 mm (24 in) in length. All the larger forms are flat with ribbon-like or leaf-like shapes, since their lack of respiratory and circulatory systems means that they have to rely on diffusion for internal transport of metabolites. However, many of the smaller forms are round in cross section. Most are predators, and all live in water or in moist terrestrial environments. Most forms reproduce sexually and with few exceptions all are simultaneous hermaphrodites.

The frilled lizard, also known commonly as the frilled agama, the frillneck lizard, the frill-necked lizard, and the frilled dragon, is a species of lizard in the family Agamidae. The species is native to northern Australia and southern New Guinea and is the only member of the genus Chlamydosaurus. Its common names refer to the large frill around its neck, which usually stays folded against the lizard's body. The frilled lizard grows to 90 cm (35 in) from head to tail tip and can weigh 600 g (1.3 lb). Males are larger and more robust than females. The lizard's body is generally grey, brown, orangish-brown, or black in colour. The frills have red, orange, yellow, or white colours.
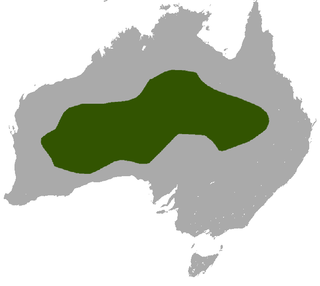
The Wongai ningaui is a tiny carnivorous marsupial native to the arid open grasslands of inland Australia. Their diet is mainly small insects, and occasionally larger prey such as spiders, grasshoppers and cockroaches, which they forage for at the ground and in clumps of spinifex. They have long and untidy fur, grey or gingery brown with longer black hairs, small ears, a narrow muzzle, and possess a partially prehensile tail and feet that allow them to climb. The population occurs sparsely across a wide area and common in favourable habitat, especially in years of good rainfall. Ningaui ridei was first described in 1975, one of two species of a new genus discovered amongst the poorly known mammals of the western regions of Australia.

The Australian flatback sea turtle is a species of sea turtle in the family Cheloniidae. The species is endemic to the sandy beaches and shallow coastal waters of the Australian continental shelf. This turtle gets its common name from the fact that its shell has a flattened or lower dome than the other sea turtles. It can be olive green to grey with a cream underside. It averages from 76 to 96 cm in carapace length and can weigh from 70 to 90 kg. The hatchlings, when emerging from nests, are larger than other sea turtle hatchlings when they hatch.
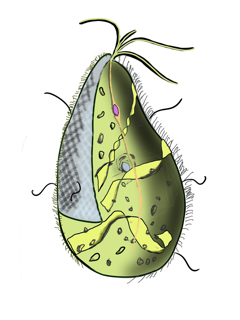
Mixotricha paradoxa is a species of protozoan that lives inside the gut of the Australian termite species Mastotermes darwiniensis.

Symsagittifera roscoffensis, also called the Roscoff worm, the mint-sauce worm, or the shilly-shally worm, is a marine acoel worm. The origin and nature of the green color of this worm stimulated the intrigued zoologists in the 1870's. It was discovered that the coloring resulted from the symbiosis between the animal and a green micro-algae, the species Tetraselmis convolutae, hosted under its epidermis. It is the photosynthetic activity of the micro-algae in hospite that provides the essential nutrients for the worm. This partnership is called photosymbiosis, from "photo", "light", and symbiosis "who lives with". These photosynthetic marine animals live in colonies on the tidal zone.
The narrow sawfish, also known as the pointed sawfish or knifetooth sawfish, is a species of sawfish in the family Pristidae, part of the Batoidea, a superorder of cartilaginous fish that include the rays and skates. Sawfish display a circumglobal distribution in warm marine and freshwater habitats. Their extant biodiversity is limited to five species belonging to two genera. The sawfishes are characterised by the long, narrow, flattened rostrum or extension on their snout. This is lined with sharp transverse teeth, arranged in a way that resembles the teeth of a saw and are used for killing prey. It is found in the shallow coastal waters and estuaries of the Indo-West Pacific, ranging from the Persian Gulf to southern Japan, Papua New Guinea and northern Australia. It is the only living member of the genus Anoxypristis, but was previously included in the genus Pristis. Compared to Pristis, Anoxypristis has a narrower rostral saw with numerous teeth on the distal part and no teeth on the basal one-quarter. It reaches a length of up to 3.5 m (11 ft).

The northern or sandy nail-tail wallaby is a species of macropod found across northern Australia on arid and sparsely wooded plains. The largest species of the genus Onychogalea, it is a solitary and nocturnal herbivorous browser that selects its food from a wide variety of grasses and succulent plant material. Distinguished by a slender and long-limbed form that resembles the typical and well known kangaroos, although their standing height is shorter, around half of one metre, and their weight is less than nine kilograms. As with some medium to large kangaroo species, such as Osphranter rufus, they have an unusual pentapedal motion at slow speeds by stiffening the tail for a fifth limb. When fleeing a disturbance, they hop rapidly with the tail curled back and repeatedly utter the sound "wuluhwuluh". Their exceptionally long tail has a broad fingernail-like protuberance beneath a dark crest of hair at its end, a peculiarity of the genus that is much broader than the other species. The name unguifera, meaning claw, is a reference to this extraordinary attribute, the purpose of which is unknown.

The star finch is a seed-eating bird species found in northern Australia. It has a distinctive red face and bill, and broad white spots down its flanks. One of its three subspecies may be extinct.
The Forrest's mouse, or desert short-tailed mouse, is a small species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is a widespread but sparsely distributed species found across arid and semi-arid inland Australia, commonly found in tussock grassland, chenopod shrubland, and mulga or savannah woodlands.

The northern hopping mouse is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is also known as woorrentinta, from Lardil, the language of Mornington Island.

The sandy inland mouse is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. Also known as the Hermannsburg (Mission) false-mouse or Hermannsburg mouse, it is endemic to Australia and found widely yet sparsely through arid and semi-arid areas.

The northern marsupial mole or kakarratul is a marsupial in the family Notoryctidae, an endemic animal of arid regions of Central Australia. It lives in the loose sand of dunes and river plains in the desert, spending nearly its entire life beneath ground. The facial features are reduced or absent; their small and strong bodies, weighing little more than 30 grams, are extremely specialised in moving through sand in search of prey. The species is elusive and it is one of the most poorly understood mammals of Australia.

Convolutriloba is a genus of marine acoels.
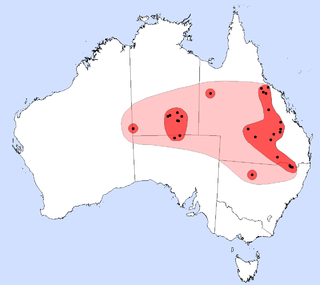
Setirostris eleryi is a species of small insectivorous bat found in inland eastern Australia. It is the sole species of the molossid genus Setirostris, a name that refers to the coarse bristles on their faces. Earlier common names have referred to this unique feature, and the 'free-tail' that is a common feature of its microchiropteran family, the Molossidae; no single common name emerged during the taxonomic revisions that identified what was referred to as the bristle-faced freetail.

The Eyre Basin beaked gecko is a gecko endemic to Australia in the family Diplodactylidae. It is found throughout parts of South Australia, Queensland and the Northern Territory and New South Wales.
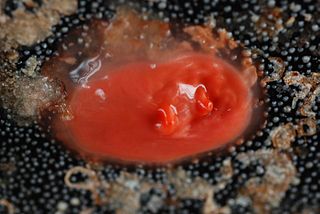
Cnemidocarpa finmarkiensis is a species of solitary ascidian tunicate in the family Styelidae. Common names include broad base sea squirt, orange sea squirt, red sea squirt, shiny orange sea squirt, shiny red tunicate and Finmark's tunicate. It is native to shallow waters in the northern and northeastern Pacific Ocean.

















