An allele, or allelomorph, is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or locus, on a DNA molecule.

An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA.

A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosome abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous.

Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic information of their parents. Through heredity, variations between individuals can accumulate and cause species to evolve by natural selection. The study of heredity in biology is genetics.

In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second is called recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child. Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance, such as incomplete dominance, in which a gene variant has a partial effect compared to when it is present on both chromosomes, and co-dominance, in which different variants on each chromosome both show their associated traits.

Oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy (OPMD) is a rare form of muscular dystrophy with symptoms generally starting when an individual is 40 to 50 years old. It can be autosomal dominant neuromuscular disease or autosomal recessive. The most common inheritance of OPMD is autosomal dominant, which means only one copy of the mutated gene needs to be present in each cell. Children of an affected parent have a 50% chance of inheriting the mutant gene.

X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be always expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation, see zygosity. Females with one copy of the mutated gene are carriers.

Sex linked describes the sex-specific reading patterns of inheritance and presentation when a gene mutation (allele) is present on a sex chromosome (allosome) rather than a non-sex chromosome (autosome). In humans, these are termed X-linked recessive, X-linked dominant and Y-linked. The inheritance and presentation of all three differ depending on the sex of both the parent and the child. This makes them characteristically different from autosomal dominance and recessiveness.

Non-Mendelian inheritance is any pattern in which traits do not segregate in accordance with Mendel's laws. These laws describe the inheritance of traits linked to single genes on chromosomes in the nucleus. In Mendelian inheritance, each parent contributes one of two possible alleles for a trait. If the genotypes of both parents in a genetic cross are known, Mendel's laws can be used to determine the distribution of phenotypes expected for the population of offspring. There are several situations in which the proportions of phenotypes observed in the progeny do not match the predicted values.
Human genetics is the study of inheritance as it occurs in human beings. Human genetics encompasses a variety of overlapping fields including: classical genetics, cytogenetics, molecular genetics, biochemical genetics, genomics, population genetics, developmental genetics, clinical genetics, and genetic counseling.
Genetics, a discipline of biology, is the science of heredity and variation in living organisms.

X-linked dominant inheritance, sometimes referred to as X-linked dominance, is a mode of genetic inheritance by which a dominant gene is carried on the X chromosome. As an inheritance pattern, it is less common than the X-linked recessive type. In medicine, X-linked dominant inheritance indicates that a gene responsible for a genetic disorder is located on the X chromosome, and only one copy of the allele is sufficient to cause the disorder when inherited from a parent who has the disorder. In this case, someone who expresses an X-linked dominant allele will exhibit the disorder and be considered affected. The pattern of inheritance is sometimes called criss-cross inheritance.

The genetic basis of coat colour in the Labrador Retriever has been found to depend on several distinct genes. The interplay among these genes is used as an example of epistasis.
Pseudodominance is the situation in which the inheritance of a recessive trait mimics a dominant pattern.

A hereditary carrier, is a person or other organism that has inherited a recessive allele for a genetic trait or mutation but usually does not display that trait or show symptoms of the disease. Carriers are, however, able to pass the allele onto their offspring, who may then express the genetic trait.
An obligate carrier is an individual who may be clinically unaffected but who must carry a gene mutation based on analysis of the family history; usually applies to disorders inherited in an autosomal recessive and X-linked recessive manner.
Glycerol kinase deficiency (GKD) is an X-linked recessive enzyme defect that is heterozygous in nature. Three clinically distinct forms of this deficiency have been proposed, namely infantile, juvenile, and adult. National Institutes of Health and its Office of Rare Diseases Research branch classifies GKD as a rare disease, known to affect fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States. The responsible gene lies in a region containing genes in which deletions can cause Duchenne muscular dystrophy and adrenal hypoplasia congenita. Combinations of these three genetic defects including GKD are addressed medically as Complex GKD.
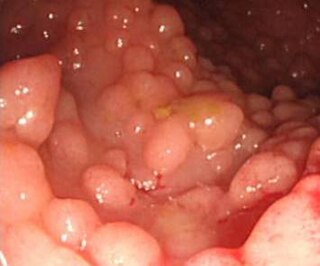
A hereditary cancer syndrome is a genetic disorder in which inherited genetic mutations in one or more genes predispose the affected individuals to the development of cancer and may also cause early onset of these cancers. Hereditary cancer syndromes often show not only a high lifetime risk of developing cancer, but also the development of multiple independent primary tumors.
This glossary of genetics and evolutionary biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in the study of genetics and evolutionary biology, as well as sub-disciplines and related fields, with an emphasis on classical genetics, quantitative genetics, population biology, phylogenetics, speciation, and systematics. It has been designed as a companion to Glossary of cellular and molecular biology, which contains many overlapping and related terms; other related glossaries include Glossary of biology and Glossary of ecology.













