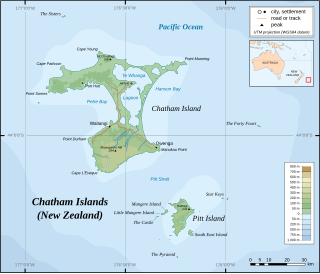
Hokorereoro, Rangatira, or South East Island is the third largest island in the Chatham Islands archipelago, and covers an area of 218 hectares. It lies 800 kilometres (497 mi) east of New Zealand's South Island off the south-east coast of Pitt Island, 55 kilometres (34 mi) south-east of the main settlement, Waitangi, on Chatham Island.
Hadramphus tuberculatus is a rare weevil endemic to Canterbury in the South Island of New Zealand. It was thought to be extinct in 1922 but was rediscovered in 2004.

Xylotoles is a genus of flat-faced longhorns in the beetle family Cerambycidae. There are more than 15 described species in Xylotoles found mainly in New Zealand, Australia, and surrounding islands.

Austrocidaria similata is a species of moth of the family Geometridae. It endemic to New Zealand.

Anagotus stephenensis, commonly known as the ngaio weevil, is a large flightless weevil that is only found on Stephens Island in New Zealand. The ngaio weevil was discovered in 1916 by A.C. O'Connor on Stephens Island. Thomas Broun described it in 1921 as Phaeophanus oconnori after its collector. The weevils were observed at the time to be 'feeding on tall fescue and the leaves of trees'.

Amychus granulatus, commonly known as the Cook Strait click beetle, is a large flightless click beetle in the family Elateridae.
Cerius otagensis is a species of flightless fungus weevil that is endemic to New Zealand. It has been found in only two locations in the Central Otago region.

Hadramphus spinipennis, commonly called the coxella weevil, is a large, nocturnal, flightless weevil only found on Mangere and Rangatira Islands in the Chatham Islands, New Zealand.

Geodorcus capito is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It is endemic to the Chatham Islands in New Zealand.

Geodorcus ithaginis, the Mokohinau stag beetle, is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It was described by Thomas Broun in 1893 after being discovered in the Mokohinau Islands by Andreas Stewart Sandager, a lighthouse keeper on the islands. The species survives only on the small unnamed island "Stack H", in a patch of vegetation the size of a living room, and is in extreme danger of extinction.

Geodorcus sororum is a large flightless species of stag beetle in the family Lucanidae. It was discovered in 1973 by Mr. A. Wright on an expedition to Middle Sister Island/Te Awanui, one of The Sisters Islands/Rangitatahi which are part of the Chatham Islands in New Zealand. This holotype specimen is held in the New Zealand Arthropod Collection. It was first described by Beverley Holloway in 2007. The name sororum is translated from Latin to mean "belonging to the sisters".

The Back Beach beetle is a small critically endangered species of ground beetle, found only in the intertidal sand of Back Beach, a small sandspit near Nelson, New Zealand.

Lyperobius huttoni is a New Zealand weevil found in alpine areas of the South Island and at sea level around the Wellington coast. It feeds only on speargrass (Aciphylla). Weevils from the endangered Wellington population have been translocated to predator-free Mana Island.
Creophilus rekohuensis is a beetle of the Staphylinidae family, subfamily Staphylininae. This species occurs only on some small predator-free islands in the Chatham Islands, New Zealand, where it lives in seabird burrows. Its name derives from Rekohu, the Moriori name for Chatham Island.

Amychus manawatawhi, commonly known as the Three Kings click beetle, is a large flightless click beetle in the family Elateridae, found only on the Three Kings Islands of New Zealand.

Coptomma marrisi is a species of longhorn beetle only known from Great Island in the Three Kings Islands, New Zealand.

The Lincoln University Entomology Research Collection is a collection of approximately 500,000 insect, spider, and other arthropod specimens housed in Lincoln University, New Zealand. One of New Zealand's largest insect research collections, it is the only one based in a university.

Horelophus walkeri is a small water scavenger beetle that is endemic to New Zealand. It is found in the South Island in the West Coast, Nelson, Buller and Marlborough regions. The preferred habitat of this species are the moss and crevices within the splash zone of waterfalls sourced from fast flowing, clear, cool waterways. The larvae of this species are carnivorous while the adults are herbivores or scavengers. In 2012 the Department of Conservation classified this beetle as Nationally Endangered.

Ichneutica thalassarche is a moth of the family Noctuidae. This species is endemic to New Zealand and is only found in the Chatham Islands. It has been collected at Chatham Island, Pitt Island and Rangatira Island. The life history of this species is unknown as are the host species of its larvae. The adults of this species are large with a pale grey thorax and forewing. A diagnostic feature is the pattern on its forewing which is a white subterminal line joined by black "teeth" markings. This species has been recorded as a winter flyer having been collected in June to August.

Creophilus oculatus or devil's coach horse is a species of large carrion-feeding rove beetle endemic to New Zealand.