
The ribbonfish are any lampriform fishes in the family Trachipteridae. These pelagic fish are named for their slim, ribbon-like appearance. They are rarely seen alive, as they typically live in deep waters, though are not bottom feeders. The perciform fish known as the red bandfish is sometimes referred to as ribbonfish, but it is unrelated to any ribbonfish in the Trachipteridae.

The gag grouper, also known as velvet rockfish, the gag, or charcoal belly, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It comes from warmer parts of the West Atlantic, including the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. It is a drab, mottled-gray fish lacking the distinguishing features of most other groupers. Its pattern of markings resemble the box-shaped spots of the black grouper. It lacks the streamer-points on the tail fin that scamp and yellowmouth grouper have and lacks yellow coloration around the mouth.

The giant oarfish is a species of oarfish of the family Regalecidae. It is an oceanodromous species with a worldwide distribution, excluding polar regions. Other common names include Pacific oarfish, king of herrings, ribbonfish, and streamer fish.
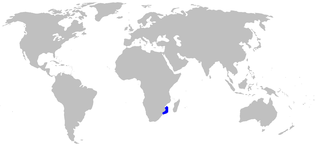
The balloon shark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to the southwestern Indian Ocean off South Africa and Mozambique. Benthic in nature, it is found over sandy and muddy flats at depths of 40–600 m (130–1,970 ft). This thick-bodied species has a broad, flattened head and a short tail; its distinguishing traits include narrow, lobe-like skin flaps in front of the nostrils, and a dorsal color pattern of faint darker saddles on a light grayish background.

The Gulf torpedo or variable electric ray, is a species of electric ray in the family Torpedinidae. It is found in the Indian Ocean, but may represent a species flock of several local endemic species. It is distinguishable from other Torpedo species in its range by its ornate dorsal coloration. Another common name, marbled electric ray, is not to be confused with Torpedo marmorata.

The smooth grouper is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is associated with reefs and is found in the western Indian Ocean.

The yellow grouper, also known as the banded grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in eastern Asian waters of the Western Pacific Ocean. Its natural habitats are shallow seas and rocky reefs.

The red grouper is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean.

Zebrasoma xanthurum, the purple tang or yellowtail tang, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae which includes the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. This species is endemic to the north western Indian Ocean.

Epinephelus flavocaeruleus, commonly called blue-and-yellow grouper, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is associated with reefs in the Indian Ocean.

The Chinese trumpetfish, Aulostomus chinensis, is a demersal marine fish belonging to the family Aulostomidae.
Figaro is a genus of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae. Until 2008, Figaro was generally considered to be a subgenus of Galeus. The two known species are found off Australia, inhabiting deep, offshore waters on or near the bottom. Figaro contains small, slender, firm-bodied sharks that bear distinctive crests of enlarged, spiny dermal denticles along the dorsal and ventral edges of their short caudal fins. The caudal peduncle is relatively long, such as that the anal and caudal fins are some distance apart. In adult males, the inner margins of the pelvic fins are fused together to form a subtle "apron" over the claspers. F. boardmani is a predator of fishes, crustaceans, and cephalopods, and is oviparous; less is known about the F. striatus. Both are harmless and are of no economic importance.

Cirrhibarbis capensis, the barbelled klipfish, is a species of clinid found in subtropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean around South Africa. This species can reach a maximum length of 36 centimetres (14 in) TL. This species preys primarily on benthic crustaceans, mostly amphipods and isopods. It is currently the only known member of its genus.
Cancelloxus elongatus, the whiteblotched klipfish, is a species of clinid found in subtropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean along the South African coast. It prefers sandy habitats with nearby rocks at depths of from 10 to 25 metres. It can reach a maximum length of 5 centimetres (2.0 in) TL. This species preys primarily on zoobenthos.

Clinus venustris, the speckled klipfish, is a species of clinid that occurs in subtropical waters of the Atlantic Ocean from Namibia to South Africa where it is found in the subtidal zone as well as being a denizen of tide pools. This species can reach a maximum length of 12 centimetres (4.7 in) TL. and feeds primarily on amphipods, isopods, mysids, and echinoderms.

Zu is a small genus of ribbonfishes with currently two recognized species:

The onefin electric ray or Cape numbfish is a common but little-known species of electric ray in the family Narkidae, native to South Africa and Namibia. It is a benthic fish found in shallow coastal bays over sandy or muddy bottoms. This small species reaches 38 cm (15 in) in length, and has a nearly circular pectoral fin disc and a short, muscular tail that supports a large caudal fin. It can be identified by its single dorsal fin, which is located over the large pelvic fins. Its dorsal coloration is yellowish to dusky brown.

Trachipterus arcticus is a species of ribbonfish found predominantly in the North Atlantic Ocean, with one report from the Mediterranean Sea. They are rarely encountered by humans due to their deep-sea habitat and the fact that they are of no commercial value. This species is commonly referred to as the dealfish to differentiate it from the nine other ribbonfish species in the family Trachipteridae.

The Spanish flag is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grouper from the subfamily Epinephelinae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the anthias and sea basses. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean. It is the only species in the genus Gonioplectrus.
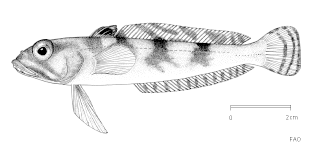
Lindbergichthys nudifrons, the yellowfin rockcod, also known as the yellow notie or the gaudy notothen, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Atlantic sector of the Southern Ocean.



















