
The Spanish manual alphabet is a fingerspelling system used in Spain. Different varieties are used in Madrid and Barcelona. [1]

The Spanish manual alphabet is a fingerspelling system used in Spain. Different varieties are used in Madrid and Barcelona. [1]
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is a, plural aes. It is similar in shape to the Ancient Greek letter Alpha, from which it derives. The uppercase version consists of the two slanting sides of a triangle, crossed in the middle by a horizontal bar. The lowercase version can be written in two forms: the double-storey a and single-storey ɑ. The latter is commonly used in handwriting and fonts based on it, especially fonts intended to be read by children, and is also found in italic type.

An alphabet is a standardized set of written letters that represent particular spoken sounds in a language. Specifically, letters correspond to phonemes, the categories of sounds that can distinguish one word from another in a given language. Not all writing systems represent language in this way: a syllabary assigns symbols to spoken syllables, while logographic systems assign symbols to spoken words, morphemes, or other semantic units.
E, or e, is the fifth letter and the second vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is e ; plural es, Es or E's. It is the most commonly used letter in many languages, including Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, French, German, Hungarian, Latin, Latvian, Norwegian, Spanish, and Swedish.
F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ef, and the plural is efs.

G, or g, is the seventh letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is gee, plural gees.
H, or h, is the eighth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, including the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is aitch, or regionally haitch.
N, or n, is the fourteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages, and others worldwide. Its name in English is en, plural ens.
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ess, plural esses.
V, or v, is the twenty-second letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is vee, plural vees.
Y, or y, is the twenty-fifth and penultimate letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. According to some authorities, it is the sixth vowel letter of the English alphabet. In the English writing system, it mostly represents a vowel and seldom a consonant, and in other orthographies it may represent a vowel or a consonant. Its name in English is wye, plural wyes.

Z, or z, is the twenty-sixth and last letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual names in English are zed and zee, with an occasional archaic variant izzard.

The (International) Radiotelephony Spelling Alphabet, commonly known as the NATO phonetic alphabet, is the most widely used set of clear code words for communicating the letters of the Roman alphabet. Technically a radiotelephonic spelling alphabet, it goes by various names, including NATO spelling alphabet, ICAO phonetic alphabet and ICAO spelling alphabet. The ITU phonetic alphabet and figure code is a rarely used variant that differs in the code words for digits.

Ç or ç (C-cedilla) is a Latin script letter used in the Albanian, Azerbaijani, Manx, Tatar, Turkish, Turkmen, Kurdish, Kazakh, and Romance alphabets. Romance languages that use this letter include Catalan, French, Portuguese, and Occitan, as a variant of the letter C with a cedilla. It is also occasionally used in Crimean Tatar and in Tajik to represent the sound. It is often retained in the spelling of loanwords from any of these languages in English, Basque, Dutch, Spanish and other languages using the Latin alphabet.

Á, á (a-acute) is a letter of the Chinese (Pinyin), Blackfoot, Czech, Dutch, Faroese, Filipino, Galician, Hungarian, Icelandic, Irish, Lakota, Navajo, Occitan, Portuguese, Sámi, Slovak, Spanish, Vietnamese, Welsh, Karakalpak and Western Apache languages as a variant of the letter a. It is sometimes confused with à; e.g. "5 pommes á $1", which is supposed to be written as "5 pommes à $1".
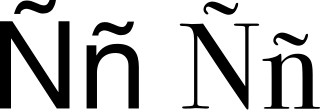
Ñ, or ñ, is a letter of the modern Latin alphabet, formed by placing a tilde on top of an upper- or lower-case ⟨n⟩. It became part of the Spanish alphabet in the eighteenth century when it was first formally defined, but it has subsequently been used in other languages, such as Galician, Asturian, the Aragonese Grafía de Uesca, Basque, Chavacano, some Philippine languages, Chamorro, Guarani, Quechua, Mapudungun, Mandinka, Papiamento, and Tetum alphabets, as well as in Latin transliteration of Tocharian and many Indian languages, where it represents or. It represents in Crimean Tatar, Kazakh, ALA-LC romanization for Turkic languages, the Common Turkic Alphabet, Nauruan and romanized Quenya. In Breton and in Rohingya, it denotes nasalization of the preceding vowel.

Ó, ó (o-acute) is a letter in the Czech, Emilian-Romagnol, Faroese, Hungarian, Icelandic, Kashubian, Polish, Slovak, Karakalpak, and Sorbian languages. This letter also appears in the Afrikaans, Catalan, Dutch, Irish, Nynorsk, Bokmål, Occitan, Portuguese, Spanish, Italian and Galician languages as a variant of letter "o". In some cases, the Letter "ó" is used in some languages as in a high rising tone. It is sometimes also used in English for loanwords.
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic and early Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BC, the Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard and it is this version that is still used for Greek writing today.
J, or j, is the tenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual name in English is jay, with a now-uncommon variant jy. When used in the International Phonetic Alphabet for the voiced palatal approximant it may be called yod or jod.
A Latin-script alphabet is an alphabet that uses letters of the Latin script. The 21-letter archaic Latin alphabet and the 23-letter classical Latin alphabet belong to the oldest of this group. The 26-letter modern Latin alphabet is the newest of this group.

Spanish Braille is the braille alphabet of Spanish and Galician. It is very close to French Braille, with the addition of a letter for ñ, slight modification of the accented letters and some differences in punctuation. Further conventions have been unified by the Latin American Blind Union, but differences with Spain remain.