Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C also known as MADS box transcription enhancer factor 2, polypeptide C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2C gene. [4] [5] MEF2C is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. [6] [7]
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C also known as MADS box transcription enhancer factor 2, polypeptide C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2C gene. [4] [5] MEF2C is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. [6] [7]
The gene is located at 5q14.3 on the minus (Crick) strand and is 200,723 bases in length. The encoded protein has 473 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 51.221 kilodaltons. Three isoforms have been identified. Several post translational modifications have been identified including phosphorylation on serine-59 and serine-396, sumoylation on lysine-391, acetylation on lysine-4 and proteolytic cleavage.
MEF2C has been shown to interact with:
This gene is involved in cardiac morphogenesis and myogenesis and vascular development. It may also be involved in neurogenesis and in the development of cortical architecture. Mice without a functional copy of the Mef2c gene die before birth and have abnormalities in the heart and vascular system. [15] It is one of the targets of an oncomiR, MIRN21.
In humans mutations of this gene result in autosomal dominant mental retardation 20 (MRD20), [16] characterised by severe psychomotor impairment, periodic tremor and an abnormal motor pattern with mirror movement of the upper limbs observed during infancy, hypotonia, abnormal EEG, epilepsy, absence of speech, autistic behavior, bruxism, and mild dysmorphic features, mild thinning of the corpus callosum and delay of white matter myelination in the occipital lobes [17]
MEF2C-binding site is associated with minor allele of SNP rs630923, associated with the risk of multiple sclerosis, and responsible for reduced CXCR5 gene promoter activity in B-cells during activation, that could lead to decreased autoimmune response [18]

MyoD, also known as myoblast determination protein 1, is a protein in animals that plays a major role in regulating muscle differentiation. MyoD, which was discovered in the laboratory of Harold M. Weintraub, belongs to a family of proteins known as myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs). These bHLH transcription factors act sequentially in myogenic differentiation. Vertebrate MRF family members include MyoD1, Myf5, myogenin, and MRF4 (Myf6). In non-vertebrate animals, a single MyoD protein is typically found.

Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes via chromatin remodeling by allowing histone proteins to wrap DNA less tightly. This enzyme plays an essential role in regulating cell growth and division, prompting cells to mature and assume specialized functions (differentiate), and preventing the growth of cancerous tumors. The p300 protein appears to be critical for normal development before and after birth.

Transcription factor Sp1, also known as specificity protein 1* is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SP1 gene.
The MADS box is a conserved sequence motif. The genes which contain this motif are called the MADS-box gene family. The MADS box encodes the DNA-binding MADS domain. The MADS domain binds to DNA sequences of high similarity to the motif CC[A/T]6GG termed the CArG-box. MADS-domain proteins are generally transcription factors. The length of the MADS-box reported by various researchers varies somewhat, but typical lengths are in the range of 168 to 180 base pairs, i.e. the encoded MADS domain has a length of 56 to 60 amino acids. There is evidence that the MADS domain evolved from a sequence stretch of a type II topoisomerase in a common ancestor of all extant eukaryotes.
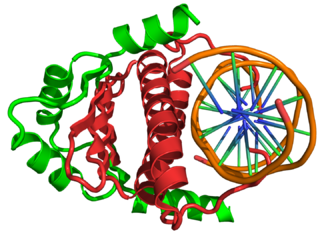
In the field of molecular biology, myocyte enhancer factor-2 (Mef2) proteins are a family of transcription factors which through control of gene expression are important regulators of cellular differentiation and consequently play a critical role in embryonic development. In adult organisms, Mef2 proteins mediate the stress response in some tissues. Mef2 proteins contain both MADS-box and Mef2 DNA-binding domains.
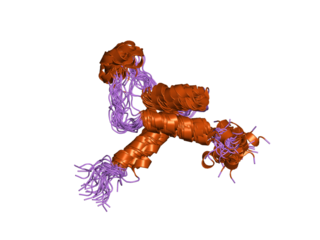
TEAD2, together with TEAD1, defines a novel family of transcription factors, the TEAD family, highly conserved through evolution. TEAD proteins were notably found in Drosophila (Scalloped), C. elegans, S. cerevisiae and A. nidulans. TEAD2 has been less studied than TEAD1 but a few studies revealed its role during development.
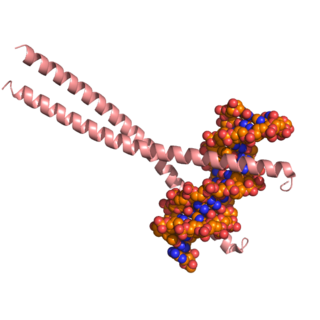
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPB gene.

Histone deacetylase 4, also known as HDAC4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HDAC4 gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase 7 also known as MAP kinase 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK7 gene.

Pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PBX1 gene. The homologous protein in Drosophila is known as extradenticle, and causes changes in embryonic development.
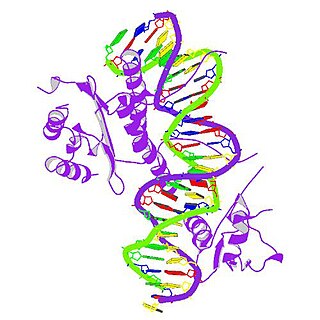
Serum response factor, also known as SRF, is a transcription factor protein.

Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2A gene. MEF2A is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. In humans it is located on chromosome 15q26. Certain mutations in MEF2A cause an autosomal dominant form of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction.

Histone deacetylase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC5 gene.

Histone deacetylase 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC9 gene.

Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2D gene.

Alpha-globin transcription factor CP2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFCP2 gene.

Transcriptional enhancer factor TEF-1 also known as TEA domain family member 1 (TEAD1) and transcription factor 13 (TCF-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TEAD1 gene. TEAD1 was the first member of the TEAD family of transcription factors to be identified.

Interferon-related developmental regulator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFRD1 gene. The gene is expressed mostly in neutrophils, skeletal and cardiac muscle, the brain, and the pancreas. The rat and the mouse homolog genes of interferon-related developmental regulator 1 gene are also known with the name PC4 and Tis21, respectively. IFRD1 is member of a gene family that comprises a second gene, IFRD2, also known as SKmc15.

Myocyte enhancer binding factor 2B (MEF2B) is a transcription factor part of the MEF2 gene family including MEF2A, MEF2C, and MEF2D. However, MEF2B is distant from the other three branches of MEF2 genes as it lacks the protein-coding Holliday junction recognition protein C-terminal (HJURP_C) region in vertebrates.
In molecular biology, the myogenic determination factor 5 proteins are a family of proteins found in eukaryotes. This family includes the Myf5 protein, which is responsible for directing cells to the skeletal myocyte lineage during development. Myf5 is likely to act in a similar way to the other MRF4 proteins such as MyoD which perform the same function. These are histone acetyltransferases and histone deacetylases which activate and repress genes involved in the myocyte lineage.