
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the other being the sympathetic nervous system. The enteric nervous system (ENS) is now usually referred to as separate from the autonomic nervous system since it has its own independent reflex activity. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed and breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after eating, including sexual arousal, salivation, lacrimation (tears), urination, digestion and defecation. Its action is described as being complementary to that of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for stimulating activities associated with the fight-or-flight response.

The facial nerve is the seventh cranial nerve, or simply CN VII. It emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerves typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI and anterior to cranial nerve VIII.
Articles related to anatomy include:

The glossopharyngeal nerve, known as the ninth cranial nerve, is a mixed nerve that carries afferent sensory and efferent motor information. It exits the brainstem out from the sides of the upper medulla, just anterior to the vagus nerve. The motor division of the glossopharyngeal nerve is derived from the basal plate of the embryonic medulla oblongata, while the sensory division originates from the cranial neural crest.

The otic ganglion is a small parasympathetic ganglion located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa and on the medial surface of the mandibular nerve. It is functionally associated with the glossopharyngeal nerve and innervates the parotid gland for salivation.

The pterygopalatine ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion found in the pterygopalatine fossa. It is largely innervated by the greater petrosal nerve ; and its axons project to the lacrimal glands and nasal mucosa. The flow of blood to the nasal mucosa, in particular the venous plexus of the conchae, is regulated by the pterygopalatine ganglion and heats or cools the air in the nose. It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck, the others being the submandibular ganglion, otic ganglion, and ciliary ganglion.
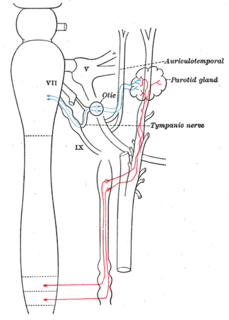
The auriculotemporal nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve (V3) that runs with the superficial temporal artery and vein, and provides sensory innervation to various regions on the side of the head.

A pseudounipolar neuron is a type of neuron which has one extension from its cell body. This type of neuron contains an axon that has split into two branches; one branch travels to the peripheral nervous system and the other to the central nervous system. A single process arises from the cell body and then divides into an axon and a dendrite. They develop embryologically as bipolar in shape and are thus termed pseudounipolar instead of unipolar.

The inferior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve is a sensory ganglion. It is larger than and below the superior ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve. It is located within the jugular foramen.

The superior ganglion of the vagus nerve, (jugular ganglion) is a sensory ganglion of the peripheral nervous system. It is located within the jugular foramen, where the vagus nerve exits the skull. It is smaller than and above the inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve.

The tympanic nerve is a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve found near the ear.

The lesser petrosal nerve is the general visceral efferent (GVE) component of the glossopharyngeal nerve, carrying parasympathetic preganglionic fibers from the tympanic plexus to the parotid gland. It synapses in the otic ganglion, from where the postganglionic fibers emerge.

The inferior ganglion of the vagus nerve, (nodose ganglion) is a sensory ganglion of the peripheral nervous system. It is located within the jugular foramen where the vagus nerve exits the skull. It is larger than and below the superior ganglion of the vagus nerve.

The intermediate nerve, nervus intermedius, nerve of Wrisberg or Glossopalatine nerve, is the part of the facial nerve located between the motor component of the facial nerve and the vestibulocochlear nerve. It contains the sensory and parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve. Upon reaching the facial canal, it joins with the motor root of the facial nerve at the geniculate ganglion. Alex Alfieri postulates, that the intermediate nerve should be considered as a separate cranial nerve and not a part of the facial nerve.

In the tympanic cavity, the tympanic nerve divides into branches which, along with sympathetic fibres from the carotid plexus, form the tympanic plexus. This plexus is located on the surface of the promontory.

The salivatory nuclei are the superior salivatory nucleus, and the inferior salivatory nucleus that innervate the salivary glands. They are located in the pontine tegmentum in the brainstem. They both are examples of cranial nerve nuclei.

The sympathetic root of ciliary ganglion is one of three roots of the ciliary ganglion, a tissue mass behind the eye. It contains postganglionic sympathetic fibers whose cell bodies are located in the superior cervical ganglion. Their axons ascend with the internal carotid artery as a plexus of nerves, the carotid plexus. Sympathetic fibers innervating the eye separate from the carotid plexus within the cavernous sinus. They run forward through the superior orbital fissure and merge with the long ciliary nerves and the short ciliary nerves. Sympathetic fibers in the short ciliary nerves pass through the ciliary ganglion without forming synapses.

The parasympathetic root of ciliary ganglion provides parasympathetic innervation to the ciliary ganglion.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the human nervous system:











