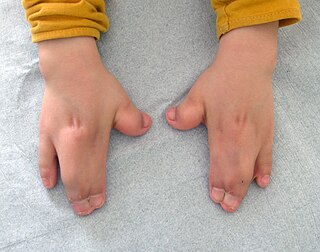
Polydactyly or polydactylism, also known as hyperdactyly, is an anomaly in humans and animals resulting in supernumerary fingers and/or toes. Polydactyly is the opposite of oligodactyly.
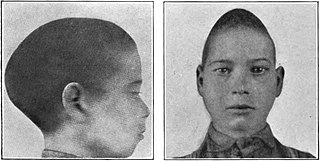
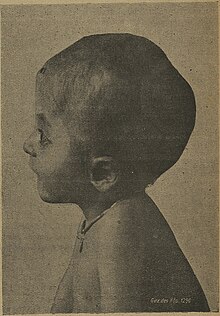
Scaphocephaly, or sagittal craniosynostosis, is a type of cephalic disorder which occurs when there is a premature fusion of the sagittal suture. Premature closure results in limited lateral expansion of the skull resulting in a characteristic long, narrow head. The skull base is typically spared.

Crouzon syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder known as a branchial arch syndrome. Specifically, this syndrome affects the first branchial arch, which is the precursor of the maxilla and mandible. Since the branchial arches are important developmental features in a growing embryo, disturbances in their development create lasting and widespread effects.

Apert syndrome is a form of acrocephalosyndactyly, a congenital disorder characterized by malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet. It is classified as a branchial arch syndrome, affecting the first branchial arch, the precursor of the maxilla and mandible. Disturbances in the development of the branchial arches in fetal development create lasting and widespread effects.

Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in a young infant's skull prematurely fuses by turning into bone (ossification), thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull. Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture, it compensates by growing more in the direction parallel to the closed sutures. Sometimes the resulting growth pattern provides the necessary space for the growing brain, but results in an abnormal head shape and abnormal facial features. In cases in which the compensation does not effectively provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure leading possibly to visual impairment, sleeping impairment, eating difficulties, or an impairment of mental development combined with a significant reduction in IQ.

Saethre–Chotzen syndrome (SCS), also known as acrocephalosyndactyly type III, is a rare congenital disorder associated with craniosynostosis. This affects the shape of the head and face, resulting in a cone-shaped head and an asymmetrical face. Individuals with SCS also have droopy eyelids (ptosis), widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism), and minor abnormalities of the hands and feet (syndactyly). Individuals with more severe cases of SCS may have mild to moderate intellectual or learning disabilities. Depending on the level of severity, some individuals with SCS may require some form of medical or surgical intervention. Most individuals with SCS live fairly normal lives, regardless of whether medical treatment is needed or not.

Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder, characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis), which affects the shape of the head and face. The syndrome includes abnormalities of the hands and feet, such as wide and deviated thumbs and big toes.

Greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome is a disorder that affects development of the limbs, head, and face. The features of this syndrome are highly variable, ranging from very mild to severe. People with this condition typically have one or more extra fingers or toes (polydactyly) or an abnormally wide thumb or big toe (hallux).

Duane-radial ray syndrome, also known as Okihiro Syndrome, is a rare autosomal dominant disorder that primarily affects the eyes and causes abnormalities of bones in the arms and hands. This disorder is considered to be a SALL4-related disorder due to the SALL4 gene mutations leading to these abnormalities. It is diagnosed by clinical findings on a physical exam as well as genetic testing and imaging. After being diagnosed, there are other evaluations that one may go through in order to determine the extent of the disease. There are various treatments for the symptoms of this disorder.
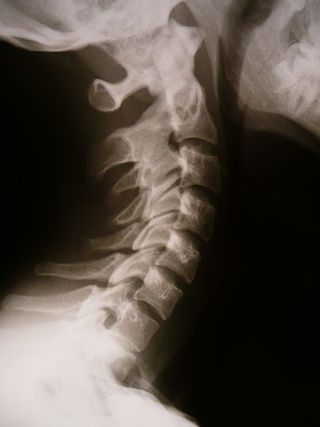
Synostosis is fusion of two or more bones. It can be normal in puberty, fusion of the epiphyseal plate to become the epiphyseal line, or abnormal. When synostosis is abnormal it is a type of dysostosis. Examples of synostoses include:
Acrocephalosyndactyly is a group of autosomal dominant congenital disorders characterized by craniofacial (craniosynostosis) and hand and foot (syndactyly) abnormalities. When polydactyly is present, the classification is acrocephalopolysyndactyly. Acrocephalosyndactyly is mainly diagnosed postnatally, although prenatal diagnosis is possible if the mutation is known to be within the family genome. Treatment often involves surgery in early childhood to correct for craniosynostosis and syndactyly.
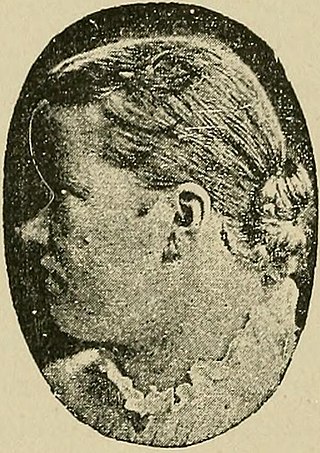
Muenke syndrome, also known as FGFR3-related craniosynostosis, is a human specific condition characterized by the premature closure of certain bones of the skull during development, which affects the shape of the head and face. First described by Maximilian Muenke, the syndrome occurs in about 1 in 30,000 newborns. This condition accounts for an estimated 8 percent of all cases of craniosynostosis.
Pediatric plastic surgery is plastic surgery performed on children. Its procedures are most often conducted for reconstructive or cosmetic purposes. In children, this line is often blurred, as many congenital deformities impair physical function as well as aesthetics.

Frontonasal dysplasia (FND) is a congenital malformation of the midface. For the diagnosis of FND, a patient should present at least two of the following characteristics: hypertelorism, a wide nasal root, vertical midline cleft of the nose and/or upper lip, cleft of the wings of the nose, malformed nasal tip, encephalocele or V-shaped hair pattern on the forehead. The cause of FND remains unknown. FND seems to be sporadic (random) and multiple environmental factors are suggested as possible causes for the syndrome. However, in some families multiple cases of FND were reported, which suggests a genetic cause of FND.

Roberts syndrome, or sometimes called pseudothalidomide syndrome, is an extremely rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder that is characterized by mild to severe prenatal retardation or disruption of cell division, leading to malformation of the bones in the skull, face, arms, and legs.

Ectrodactyly, split hand, or cleft hand involves the deficiency or absence of one or more central digits of the hand or foot and is also known as split hand/split foot malformation (SHFM). The hands and feet of people with ectrodactyly (ectrodactyls) are often described as "claw-like" and may include only the thumb and one finger with similar abnormalities of the feet.

McGillivray syndrome is a rare syndrome characterized mainly by heart defects, skull and facial abnormalities and ambiguous genitalia. The symptoms of this syndrome are ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, small jaw, undescended testes, and webbed fingers. Beside to these symptoms there are more symptoms which is related with bone structure and misshape.

Polysyndactyly is a congenital anomaly, combining polydactyly and syndactyly, in which affected individuals have an extra finger or toe that is connected, via fusing or webbing, to an adjacent digit.

Kleeblattschaedel is a rare malformation of the head where there is a protrusion of the skull and broadening of the face. This condition is a severe type of craniosynostosis.
Filippi syndrome, also known as Syndactyly Type I with Microcephaly and Mental Retardation, is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disease. Only a very limited number of cases have been reported to date. Filippi Syndrome is associated with diverse symptoms of varying severity across affected individuals, for example malformation of digits, craniofacial abnormalities, intellectual disability, and growth retardation. The diagnosis of Filippi Syndrome can be done through clinical observation, radiography, and genetic testing. Filippi Syndrome cannot be cured directly as of 2022, hence the main focus of treatments is on tackling the symptoms observed on affected individuals. It was first reported in 1985.