Related Research Articles

Trout Lake Township is located in north central Minnesota in Itasca County, United States. It is bordered by the City of Coleraine to the west and north, City of Bovey on the north, an unorganized township on the east, and Blackberry Township to the south. Town government was adopted on March 6, 1894. The population was 1,056 at the 2020 census.
The Indiana Department of Natural Resources (DNR) is the agency of the U.S. state of Indiana. There are many divisions within the DNR and each has a specific role. The DNR is not only responsible for maintaining resource areas but also manages Indiana's fish and wildlife, reclaims coal mine ground, manages forested areas, aids in the management of wildlife on private lands, enforces Indiana's conservation laws, and many other duties not named here. According to the department's website, their mission is "to protect, enhance, preserve, and wisely use natural, cultural, and recreational resources for the benefit of Indiana's citizens through professional leadership, management, and education".

Lake Vermilion is a shallow freshwater lake in northeastern Minnesota, United States. The Ojibwe originally called the lake Onamanii-zaaga'iganiing, which means “the evening sun tinting the water a reddish color”. French fur traders translated this to the Latin word Vermilion, which is a red pigment. Lake Vermilion is located between the towns of Tower on the east and Cook on the west, in the heart of Minnesota's Arrowhead Region at Vermilion Iron Range. The area was mined from the late 19th century until the 1960s, and the Soudan Mine operated just south of the lake.

Nerstrand-Big Woods State Park is a state park of Minnesota, US, northeast of Faribault just outside the small town of Nerstrand. The park derives its name from the Big Woods, a large, contiguous forested area covering much of southeast Minnesota prior to the 1840s, when European settlers began to establish farms in the territory, and from Nedstrand in Tysvær, Norway, of which Nerstrand is a namesake. The park and its forest were an outlying 'woods' typical of and similar to the Big Woods proper, which were historically found on the more recent glacier deposits located west of the Cannon River 10 miles (16 km) to the west. Aside from a small waterfall, the outstanding natural feature of the park is the forest itself.

The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, or Minnesota DNR, is the agency of the U.S. state of Minnesota charged with conserving and managing the state's natural resources. The agency maintains areas such as state parks, state forests, recreational trails, and recreation areas as well as managing minerals, wildlife, and forestry throughout the state. The agency is divided into six divisions - Ecological & Water Resources, Enforcement, Fish & Wildlife, Forestry, Lands & Minerals, and Parks & Trails.

The Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR) is a government agency of the U.S. state of Wisconsin charged with conserving and managing Wisconsin's natural resources. The Wisconsin Natural Resources Board has the authority to set policy for the WDNR. The WDNR is led by the Secretary, who is appointed by the Governor of Wisconsin. The WDNR develops regulations and guidance in accordance with laws passed by the Wisconsin Legislature. It administers wildlife, fish, forests, endangered resources, air, water, waste, and other issues related to natural resources. The central office of the WDNR is located in downtown Madison, near the state capitol.

The natural history of Minnesota covers many plant and animal species in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The continental climate and location of Minnesota at the physiographic intersection of the Laurentian and the Interior Plains influences its plant and animal life. Three of North America's biomes converge in Minnesota: prairie grasslands in the southwestern and western parts of the state, the eastern temperate deciduous forests in the east-central and the southeast, and the coniferous forest in the north-central and northeast.
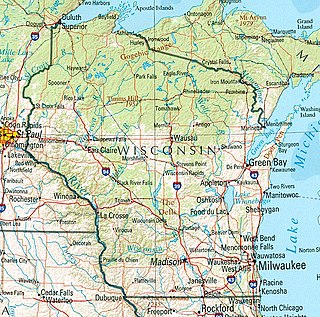
Wisconsin, a state in the Midwestern United States, has a vast and diverse geography famous for its landforms created by glaciers during the Wisconsin glaciation 17,000 years ago. The state can be generally divided into five geographic regions—Lake Superior Lowland, Northern Highland, Central Plain, Eastern Ridges & Lowlands, and Western Upland. The southwestern part of the state, which was not covered by glaciers during the most recent ice age, is known as the Driftless Area. The Wisconsin glaciation formed the Wisconsin Dells, Devil's Lake, and the Baraboo Range. A number of areas are protected in the state, including Devil's Lake State Park, the Apostle Islands National Lakeshore, and the Chequamegon–Nicolet National Forest.
The Little Isabella River is a 33.17 mi (53.38 km) stream in Superior National Forest, a United States National Forest in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The stream runs through Stony River Township, which is part of Lake County. The Little Isabella River Campground, which is operated by the United States Forest Service, is about 5 miles (8.0 km) north of Isabella, Minnesota, an unincorporated community. The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources has designated it as a trout stream and it is populated with Brook trout.
The Battleground State Forest is a state forest located near Gould Township in Cass County, Minnesota. It is managed by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. It lies entirely within the boundaries of the Chippewa National Forest, additionally, and a portion of the forest falls within the borders of the Leech Lake Indian Reservation.
The Blackduck State Forest is a state forest near the town of Blackduck, located in Beltrami and Itasca counties in Minnesota. It is adjacent to the Buena Vista State Forest and the federally managed Chippewa National Forest. It is managed primarily by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources and the counties.
The Bowstring State Forest is a state forest located in Itasca and Cass Counties in Minnesota. It is located entirely within the boundaries of the federally managed Chippewa National Forest, and is managed by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources.
The Buena Vista State Forest is a state forest located in Beltrami County, Minnesota. The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources manages 18,693 acres (7,565 ha) of state lands, with the majority of the forest split between private and other public ownership. The eastern half of the forest falls within the Chippewa National Forest, where Federal lands are managed by the United States Forest Service.
The General C. C. Andrew State Forest is a state forest located in Pine County, Minnesota. The forest is named in honor of major general Christopher Columbus Andrews, a Civil War veteran, and an early Minnesota state Forestry Commissioner and proponent for scientific forestry and forest management. The Minnesota Department of Natural Resources manages the majority of the forest.
The Insula Lake State Forest is a state forest located in Lake County, Minnesota. The forest is entirely within the limits of the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness of the Superior National Forest, and as such falls under the jurisdiction and management of the United States Forest Service.
The Jeanette State Forest is a state forest located in St. Louis County, Minnesota. The forest is within the limits of the Superior National Forest's Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness, and thus falls under the federal jurisdiction and management of the United States Forest Service.
The Lake Isabella State Forest is a state forest located in Lake County, Minnesota. The forest is located completely within the Superior National Forest and the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness, and is thus subject to the management of the United States Forest Service. At 638 acres (258 ha), it one of the smallest forests in the Minnesota state system.
The Nemadji State Forest is a state forest located primarily in Pine County, Minnesota. A small portion of the forest extends into neighboring Carlton County. The eastern perimeter of the forest borders the state of Wisconsin. It is managed by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Gray wolves, white-tailed deer, and eagles are present in the forest.
The Paul Bunyan State Forest is a state forest located in Hubbard and Cass counties in Minnesota. The forest borders the Chippewa National Forest and the Welsh Lake State Forest to the east, and the Mississippi Headwaters State Forest to the northwest. The forest is managed by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources and the land department for Hubbard County.

Crescent Lake is a lake located in Tofte Township and Lutsen Township, Cook County, Minnesota.
References
- ↑ "Division of Forestry - Minnesota DNR - MN Department of Natural Resources". Dnr.state.mn.us. 2018-09-24. Retrieved 2019-01-29.
- ↑ "State Forests - Minnesota DNR - MN Department of Natural Resources". Dnr.state.mn.us. 2018-09-24. Retrieved 2019-01-29.