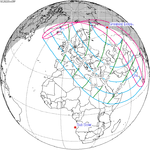
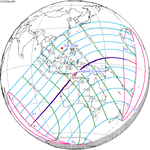
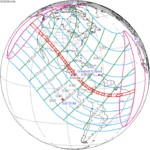
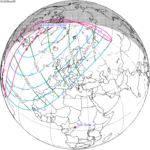
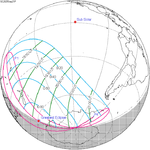
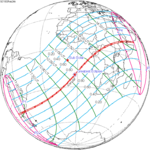
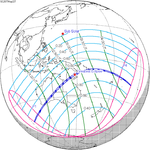
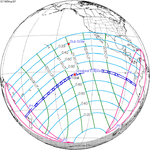
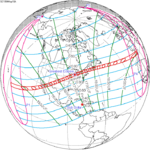
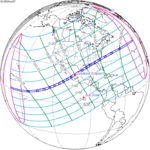
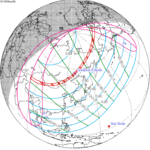
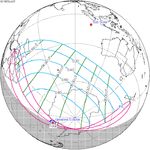
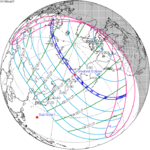
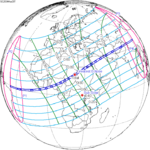
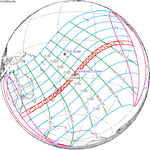
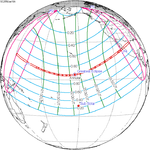
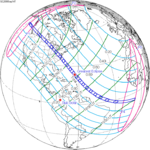
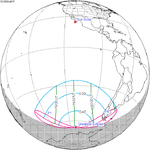
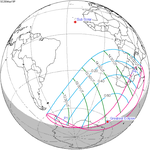
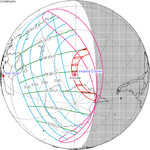
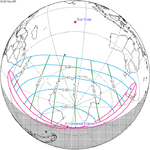
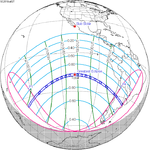
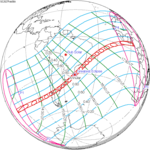
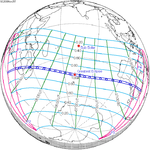
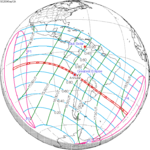
An annular solar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, April 29, 2014. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The center of the Moon's shadow missed the Earth's South Pole, but the partial eclipse was visible from parts of Antarctica and Australia, and an annular eclipse was visible from a small part of Antarctica.

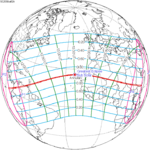
A total solar eclipse took place on 13–14 November 2012 (UTC). Because it crossed the International Date Line it began in local time on November 14 west of the date line over northern Australia, and ended in local time on November 13 east of the date line near the west coast of South America. Its greatest magnitude was 1.0500, occurring only 12 hours before perigee, with greatest eclipse totality lasting just over four minutes. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

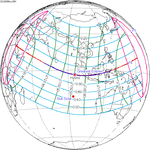
A total solar eclipse occurred at the ascending node of the Moon's orbit on Tuesday, July 2, 2019, with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0459. Totality was visible from the southern Pacific Ocean east of New Zealand to the Coquimbo Region in Chile and Central Argentina at sunset, with the maximum of 4 minutes 33 seconds visible from the Pacific Ocean. The Moon was only 2.4 days before perigee, making it fairly large.

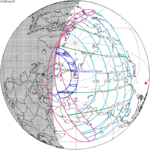
An annular solar eclipse took place at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on May 9–10 (UTC), 2013, with a magnitude of 0.9544. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 14, 2001. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. It was visible across the Pacific Ocean, southern Costa Rica, northern Nicaragua and San Andrés Island, Colombia. The central shadow passed just south of Hawaii in early morning and ended over Central America near sunset.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node on 3 November 2013. It was a hybrid eclipse of the Sun with a magnitude of 1.0159, with a small portion over the western Atlantic Ocean at sunrise as an annular eclipse, and the rest of the path as a narrow total solar eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's in sunrise and sunset, but at Greatest Eclipse the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's.

An annular solar eclipse took place on February 26, 2017. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 4.7 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. The moon's apparent diameter was just over 0.7% smaller than the Sun's.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Sunday, July 22, 1990. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southern Finland, the Soviet Union, and eastern Andreanof Islands and Amukta of Alaska.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on Wednesday, May 30, 1984. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in Mexico, the United States, Azores Islands, Morocco and Algeria. It was the first annular solar eclipse visible in the US in 33 years. The moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter because it occurred 6.7 days after apogee and 7.8 days before perigee.

A total solar eclipse occurred on November 22, 1984. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and southern Pacific Ocean. West of the International Date Line the eclipse took place on November 23, including all land in the path of totality. Occurring only 2.1 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was fairly larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred on September 9, 1904. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from German New Guinea on September 10 and Chile on September 9.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, June 30, 1992. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southeastern Uruguay and southern tip of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on Wednesday, October 12, 1977. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in the Pacific Ocean, Colombia and Venezuela.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on February 4–5, 1981. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. This annular solar eclipse was large because the Moon covered 99.4% of the Sun, with a path width of only 25 km . It was visible in Australia, crossing over Tasmania and southern Stewart Island of New Zealand near sunrise on February 5 (Thursday), and ended at sunset over western South America on February 4 (Wednesday). Occurring only 4 days before perigee, the moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred on July 20, 1963. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is at least the same size as the Sun's or larger, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with a partial solar eclipse visible over the surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Hokkaido in Japan and Kuril Islands in Soviet Union on July 21, and Alaska, and Maine in the United States and also Canada on July 20. Astronomer Charles H. Smiley observed the eclipse from a U.S. Air Force F-104D Starfighter supersonic aircraft that was "racing the Moon's shadow" at 1,300 mph (2,100 km/h) extending the duration of totality to 4 minutes 3 seconds. The Moon was 375,819 km from the Earth.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on April 8, 1959. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from Australia, southeastern tip of Milne Bay Province in the Territory of Papua New Guinea, British Solomon Islands, Gilbert and Ellice Islands, Tokelau, and Swains Island in American Samoa.
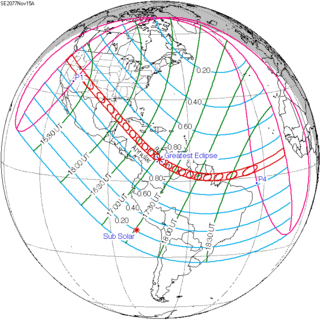
An annular solar eclipse will occur on Monday, November 15, 2077, with a magnitude of 0.9371. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partially obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The path of annularity will cross North America and South America. This will be the 47th solar eclipse of Saros cycle 134. A small annular eclipse will cover only 93.71% of the Sun in a very broad path, 262 km wide at maximum, and will last 7 minutes and 54 seconds. Occurring only 4 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller.
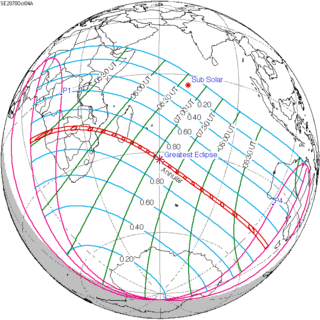
An annular solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, October 4, 2070. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse will occur on Sunday, September 22, 2052. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, May 22, 2077. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.