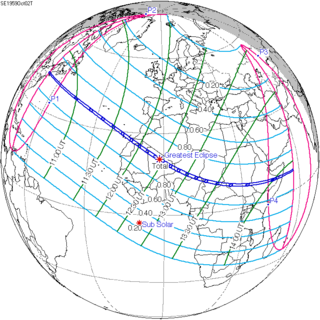
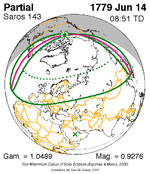
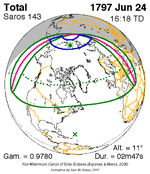
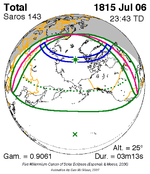
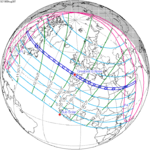
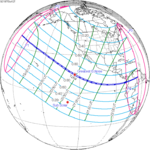
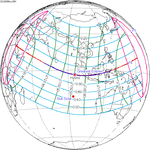
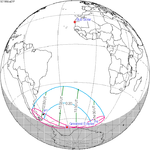
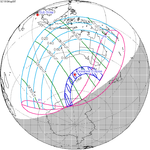
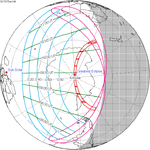
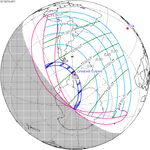
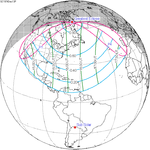
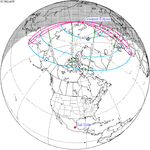
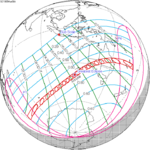
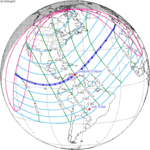
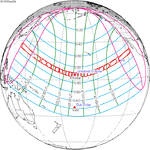
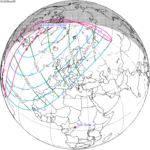
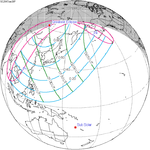
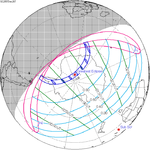
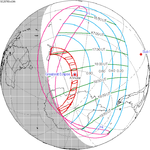
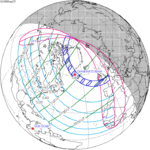
A total solar eclipse occurred on July 22, 1990. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southern Finland, the Soviet Union, and eastern Andreanof Islands and Amukta of Alaska.
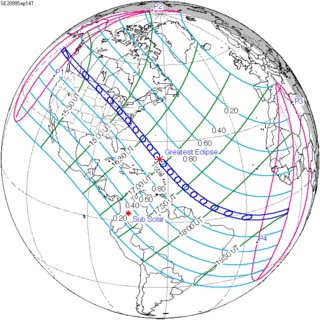
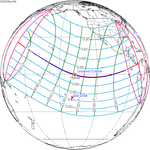
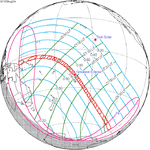
A total solar eclipse will occur on September 14, 2099. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Wednesday, May 11, 2078. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

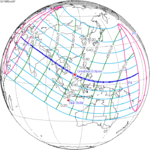
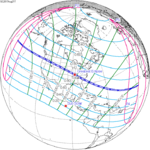
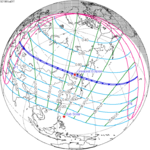
A total solar eclipse occurred on September 9, 1904. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from German New Guinea on September 10 and Chile on September 9.

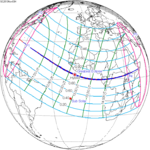
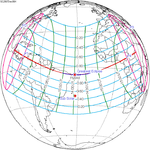
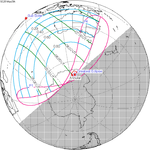
A total solar eclipse occurred on June 30, 1992. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southeastern Uruguay and southern tip of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.

One of the rarest Solar eclipses, a hybrid solar eclipse will occur on Thursday, April 20, 2023. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun] thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. A Hybrid solar eclipse is a rare type of solar eclipse that changes its appearance as the Moon's shadow moves across the earth's surface. Totality occurs in a narrow path across the surface of the Earth, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
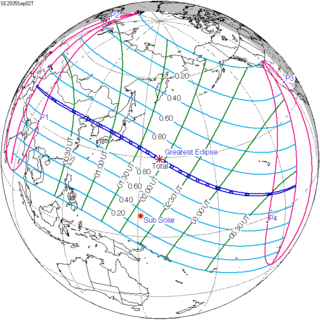
A total solar eclipse will occur on Sunday, September 2, 2035. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

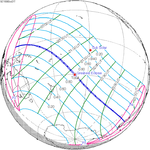
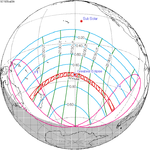
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node on June 19, 1936. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The path of totality crossed Europe and Asia. The full phase could be seen in Greece, Turkey, USSR, China and the Japanese island of Hokkaido. The maximum eclipse was near Bratsk and lasted about 2.5 minutes. The sun was 57 degrees above horizon, gamma had a value of 0.539, and the eclipse was part of Solar Saros 126.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on April 8, 1959. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from Australia, southeastern tip of Milne Bay Province in the Territory of Papua New Guinea, British Solomon Islands, Gilbert and Ellice Islands, Tokelau, and Swains Island in American Samoa.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Thursday, August 2, 2046. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is greater than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

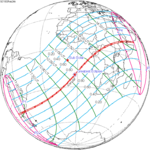
A total solar eclipse occurred on May 20, 1947. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Chile including the capital city Santiago, Argentina, Paraguay, Brazil, Liberia, French West Africa, British Gold Coast including capital Accra, French Togoland including capital Lomé, British Nigeria including capital Lagos, French Cameroons, French Equatorial Africa, Belgian Congo, British Uganda, British Tanganyika, and British Kenya. The southern part of Aconcagua, the highest mountain outside Asia, and Iguazu Falls, one of the largest waterfalls systems in the world, lie in the path of totality.

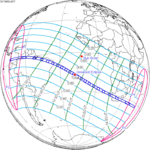
A total solar eclipse occurred on November 1, 1948. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Belgian Congo, Uganda Protectorate including the capital city Kampala, British Kenya including the capital city Nairobi, British Seychelles, and British Mauritius . During this eclipse, comet C/1948 V1, also known as the Eclipse Comet of 1948, was discovered shining near the sun.

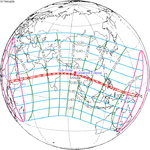
A total solar eclipse occurred on January 14, 1926. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from French Equatorial Africa, northeastern Belgian Congo, southwestern tip of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, British Uganda, British Kenya, southern tip of Italian Somaliland, British Seychelles, Dutch East Indies, North Borneo, and Philippines.

A total solar eclipse is forecast to occur on September 4, 2100. It will be the last solar eclipse of the 21st century. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Monday, May 1, 2079, with a maximum eclipse at 10:48:25.6 UTC. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The eclipse will be visible in Greenland, parts of eastern Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.

A total solar eclipse occurred on September 21, 1903. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on May 9, 1948. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from Car Nicobar, the northernmost of the Nicobar Islands, and Burma, Thailand including Bangkok, French Indochina, North Vietnam, China, South Korea, Rebun Island in Japan, Kuril Islands in the Soviet Union on May 9th, and Alaska on May 8th. It was the first central solar eclipse visible from Bangkok from 1948 to 1958, where it is rare for a large city to witness 4 central solar eclipses in just 9.945 years. The moon's apparent diameter was only 0.006% smaller than the Sun's, so this was an annular solar eclipse that occurred on May 9, 1948. Occurring 7.1 days after apogee and 6.6 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was near the average diameter.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on January 3, 1927. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from New Zealand on January 4th (Tuesday), and Chile, Argentina, Uruguay and southern Brazil on January 3rd (Monday).

An annular solar eclipse occurred on July 20, 1925. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from northern part of Northland Region and the whole Kermadec Islands in New Zealand on July 21st (Tuesday), and Rapa Iti in French Polynesia on July 20th (Monday).

An annular solar eclipse occurred on July 9, 1926. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from the islands of Pulo Anna and Merir in South Pacific Mandate in Japan and Wake Island on July 10th (Saturday), and Midway Atoll on July 9th (Friday).