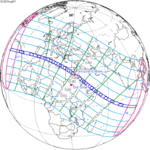
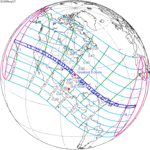
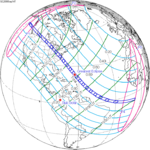
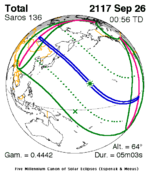
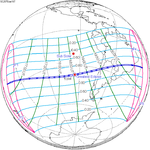
A total solar eclipse took place on 13–14 November 2012 (UTC). Because it crossed the International Date Line it began in local time on November 14 west of the date line over northern Australia, and ended in local time on November 13 east of the date line near the west coast of South America. Its greatest magnitude was 1.0500, occurring only 12 hours before perigee, with greatest eclipse totality lasting just over four minutes. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the ascending node of the Moon's orbit on Tuesday, July 2, 2019, with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0459. Totality was visible from the southern Pacific Ocean east of New Zealand to the Coquimbo Region in Chile and Central Argentina at sunset, with the maximum of 4 minutes 33 seconds visible from the Pacific Ocean. The Moon was only 2.4 days before perigee, making it fairly large.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node on 3 November 2013. It was a hybrid eclipse of the Sun with a magnitude of 1.0159, with a small portion over the western Atlantic Ocean at sunrise as an annular eclipse, and the rest of the path as a narrow total solar eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's in sunrise and sunset, but at Greatest Eclipse the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's.

A total solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on Saturday, March 30, 2052. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The path of totality will cross central Mexico and the southeastern states of the United States. Almost all of North America and the northern edge of South America will see a partial eclipse. It will be the 2nd total eclipse visible from the Florida Panhandle and southwest Georgia in 6.6 years. It will be the first total solar eclipse visible from Solar Saros 130 in 223 synodic months. It will be the last total solar eclipse visible in the United States until May 11, 2078.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Sunday, July 22, 1990. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southern Finland including its capital city Helsinki, the Soviet Union, and eastern Andreanof Islands and Amukta of Alaska.
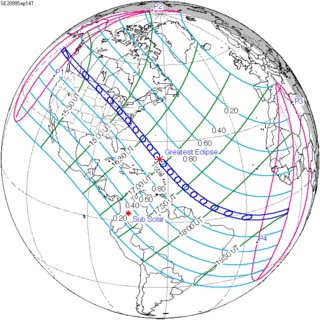
A total solar eclipse will occur on Monday, September 14, 2099. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Sunday, April 20, 2042. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It will be seen significantly in Western Indonesia, Eastern Malaysia, Brunei and the Philippines.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on June 11, 1983. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 48 hours before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred on September 9, 1904. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from German New Guinea on September 10 and Chile on September 9.
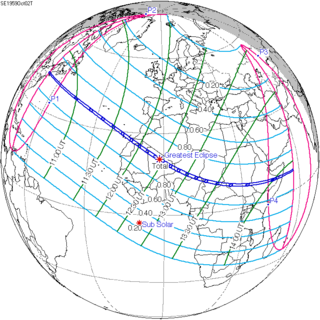
A total solar eclipse occurred on October 2, 1959. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from northeastern Massachusetts and the southern tip of New Hampshire in the United States, Canary Islands, Morocco, Spanish Sahara including the capital city Laayoune, French Mauritania, Mali Federation, French Niger, British Nigeria, British Cameroons and French Cameroons, French Chad including the capital city Fort-Lamy, French Central Africa, Sudan, Ethiopia, and the Trust Territory of Somaliland.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Tuesday, April 30, 2041. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
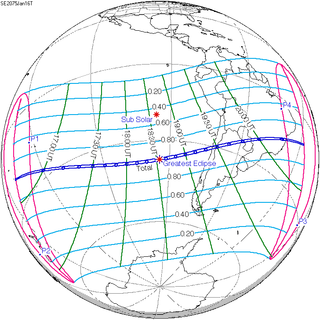
A total solar eclipse will occur on Wednesday, January 16, 2075. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
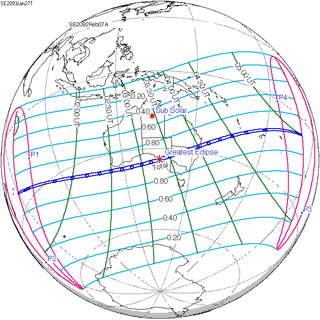
A total solar eclipse will occur on January 27, 2093. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred on October 21, 1930. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Niuafoʻou in Tonga, Chile, and a tiny part of Santa Cruz Province, Argentina.

A total solar eclipse occurred on January 14, 1926. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from French Equatorial Africa, northeastern Belgian Congo, southwestern tip of Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, British Uganda, British Kenya, southern tip of Italian Somaliland, British Seychelles, Dutch East Indies, North Borneo, and Philippines.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Thursday and Friday, April 10–11, 2070. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred on August 30, 1905. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Canada, Newfoundland Colony, Spain, French Algeria, French Tunisia, Ottoman Tripolitania include the capital Tripoli, Egypt, Ottoman Empire including Mecca, Emirate of Jabal Shammar, Aden Protectorate, and Muscat and Oman.
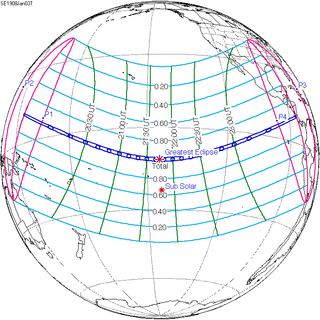
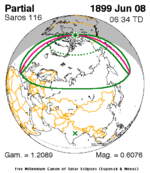
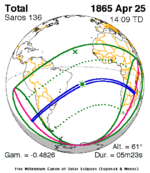
A total solar eclipse occurred on January 3, 1908. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Ebon Atoll in German New Guinea, British Western Pacific Territories, Line Islands, Phoenix Islands on January 4 (Saturday), and Costa Rica on January 3 (Friday). The green line means eclipse begins or ends at sunrise or sunset. The magenta line means mid eclipse at sunrise or sunset, or northern or southern penumbra limits. The green point means eclipse obscuration of 50%. The blue line means umbral northern and southern limits.

A total solar eclipse occurred on August 31, 1932. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Northwest Territories and Quebec in Canada, and northeastern Vermont, New Hampshire, southwestern Maine, northeastern tip of Massachusetts and northeastern Cape Cod in the United States.
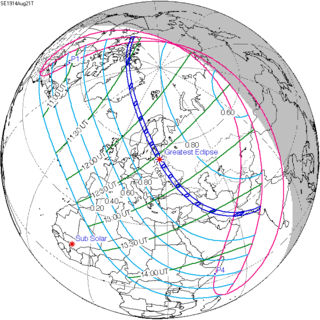
A total solar eclipse occurred on August 21, 1914. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The totality of this eclipse was visible from northern Canada, Greenland, Norway, Sweden, Russian Empire, Ottoman Empire, Persia and British Raj . It was the first of four total solar eclipses that would be seen from Sweden during the next 40 years. This total solar eclipse occurred in the same calendar date as 2017, but at the opposite node. The moon was just 2.7 days before perigee, making it fairly large.