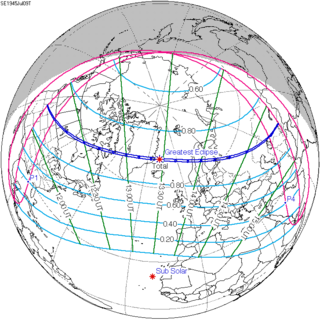
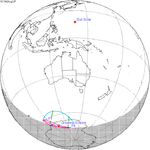
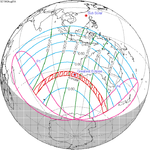
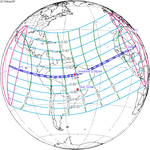
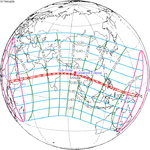
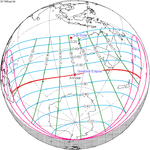
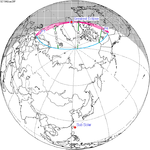
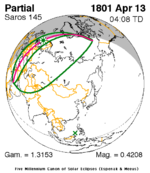
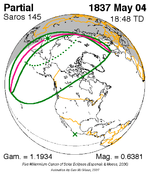
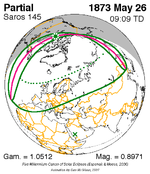
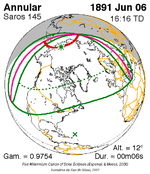
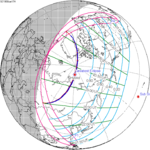
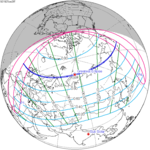
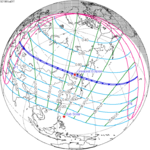
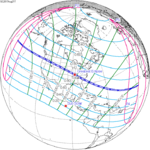
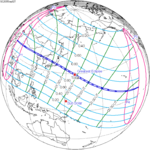
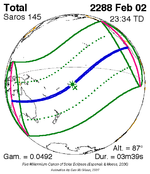
A total solar eclipse occurred on 11 August 1999 with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0286. A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between earth and the sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the sun for a viewer on earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the moon's apparent diameter is larger than the sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The path of the moon's shadow began in the Atlantic Ocean and, before noon, was traversing the southern United Kingdom, northern France, Belgium, Luxembourg, southern Germany, Austria, Slovenia, Croatia, Hungary, and northern FR Yugoslavia (Vojvodina). The eclipse's maximum was at 11:03 UTC at 45.1°N 24.3°E in Romania ; and it continued across Bulgaria, the Black Sea, Turkey, the northeastern tip of Syria, northern Iraq, Iran, southern Pakistan and Srikakulam in India and ended in the Bay of Bengal.

A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs approximately every six months, during the eclipse season in its new moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of Earth's orbit. In a total eclipse, the disk of the Sun is fully obscured by the Moon. In partial and annular eclipses, only part of the Sun is obscured. Unlike a lunar eclipse, which may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth, a solar eclipse can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world. As such, although total solar eclipses occur somewhere on Earth every 18 months on average, they recur at any given place only once every 360 to 410 years.

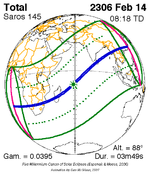
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on August 1, 2008. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It had a magnitude of 1.0394 that was visible from a narrow corridor through northern Canada (Nunavut), Greenland, central Russia, eastern Kazakhstan, western Mongolia and China. Visible north of the Arctic Circle, it belonged to the so-called midnight sun eclipses. The largest city in its path was Novosibirsk in Russia. The eclipse happened only 2+1⁄2 days after the perigee that occurred on July 29, 2008, and the Moon's apparent diameter was larger than average.

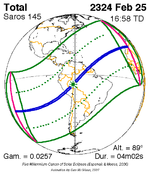
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of the orbit on Thursday, July 11, 1991. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality began over the Pacific Ocean and Hawaii moving across Mexico, down through Central America and across South America ending over Brazil. It lasted for 6 minutes and 53.08 seconds at the point of maximum eclipse. There will not be a longer total eclipse until June 13, 2132. This was the largest total solar eclipse of Solar Saros series 136, because eclipse magnitude was 1.07997.

A total solar eclipse occurred on March 20, 2015. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with a partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. This total solar eclipse is notable in that the path of totality passed over the North Pole. Totality was visible in the Faroe Islands and Svalbard.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the ascending node of the Moon's orbit on Tuesday, July 2, 2019, with an eclipse magnitude of 1.0459. Totality was visible from the southern Pacific Ocean east of New Zealand to the Coquimbo Region in Chile and Central Argentina at sunset, with the maximum of 4 minutes 33 seconds visible from the Pacific Ocean. The Moon was only 2.4 days before perigee, making it fairly large.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Sunday, March 9, 1997. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in eastern Russia, Northern Mongolia, northern tip of Xinjiang and Northeastern China and eastern tip of Kazakhstan.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Monday, July 10, 1972. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 2.9 days after perigee, the Moon's diameter was relatively large.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on Wednesday, June 30, 1954. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 3.1 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. Totality lasted 2 minutes and 34.93 seconds, but at sunrise 1 minute and 8.6 seconds and at sunset 1 minute and 5.3 seconds. The moon's apparent diameter was larger, 1930.2 arc-seconds.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Sunday, July 22, 1990. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in southern Finland including its capital city Helsinki, the Soviet Union, and eastern Andreanof Islands and Amukta of Alaska.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on June 11, 1983. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 48 hours before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, October 1, 1940. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Colombia, Brazil, Venezuela and South Africa.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on July 31, 1981. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The continental path of totality fell entirely within the Soviet Union, belonging to Georgia, Kazakhstan and Russia today. The southern part of Mount Elbrus, the highest mountain in Europe, also lies in the path of totality. Occurring only 3.8 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. With a path width of 107.8 km, this total solar eclipse had an average path.

A total solar eclipse occurred on June 29, 1927. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The path of totality crossed far northern Europe and Asia, including the United Kingdom, Norway, Sweden, Finland and Soviet Union on June 29 (Wednesday), and finally passed Amukta in Alaska on June 28 (Tuesday).
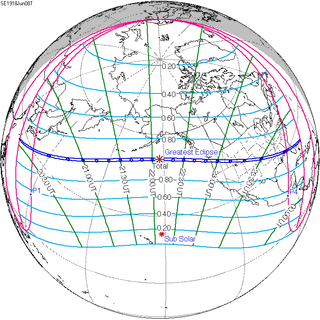
A total solar eclipse occurred on Saturday, June 8, 1918. The eclipse was viewable across the entire contiguous United States, an event which would not occur again until the solar eclipse of August 21, 2017.

A total solar eclipse occurred on September 22, 1968. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from the Soviet Union and Xinjiang in Northwestern China.
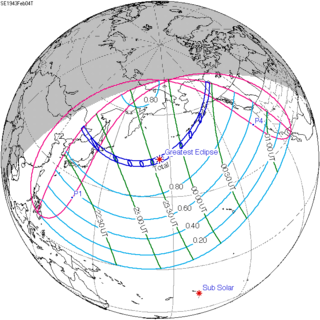
A total solar eclipse occurred between Thursday, February 4 and Friday, February 5, 1943. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It began on the morning on February 5 (Friday) over northeastern China, Primorsky Krai in the Soviet Union, Hokkaido and southern Kunashir Island in Japan and ended at sunset on February 4 (Thursday) over Alaska and Yukon in Canada.
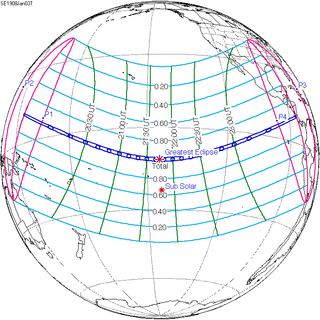
A total solar eclipse occurred on January 3, 1908. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Ebon Atoll in German New Guinea, British Western Pacific Territories, Line Islands, Phoenix Islands on January 4 (Saturday), and Costa Rica on January 3 (Friday). The green line means eclipse begins or ends at sunrise or sunset. The magenta line means mid eclipse at sunrise or sunset, or northern or southern penumbra limits. The green point means eclipse obscuration of 50%. The blue line means umbral northern and southern limits.

A total solar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, January 25, 1944. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible from Peru, Brazil, British Sierra Leone, and French West Africa. At greatest eclipse, the Sun was 78 degrees above horizon.
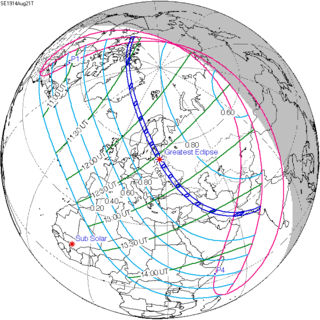
A total solar eclipse occurred on August 21, 1914. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The totality of this eclipse was visible from northern Canada, Greenland, Norway, Sweden, Russian Empire, Ottoman Empire, Persia and British Raj . It was the first of four total solar eclipses that would be seen from Sweden during the next 40 years. This total solar eclipse occurred in the same calendar date as 2017, but at the opposite node. The moon was just 2.7 days before perigee, making it fairly large.