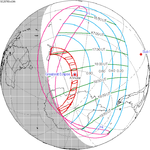
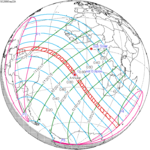
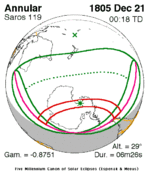
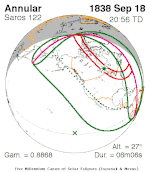
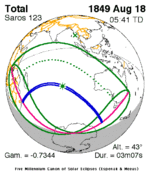
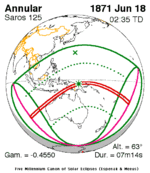
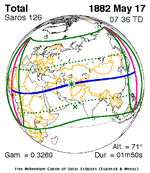
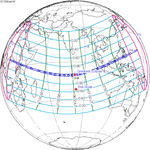
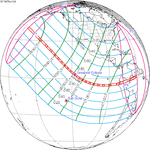
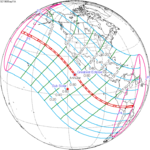
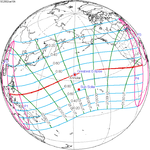
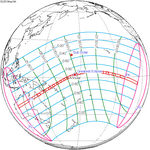
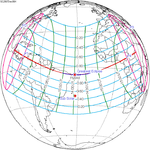
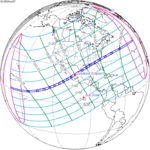
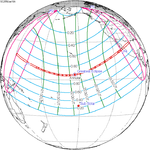
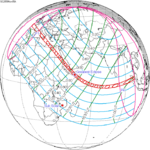
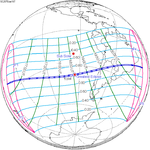
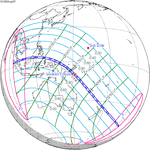
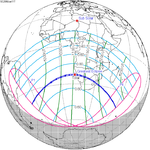
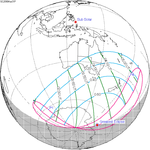
A total solar eclipse occurred on July 11, 1991. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality began over the Pacific Ocean and Hawaii moving across Mexico, down through Central America and across South America ending over Brazil. It lasted for 6 minutes and 53.08 seconds at the point of maximum eclipse. There will not be a longer total eclipse until June 13, 2132. This was the largest total solar eclipse of Solar Saros series 136, because eclipse magnitude was 1.07997.

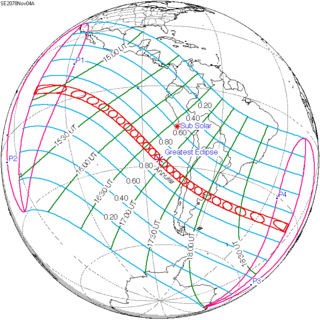
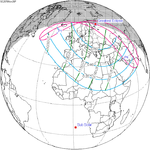
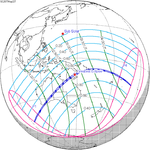
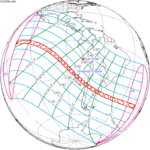
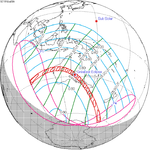
A total solar eclipse took place on 13–14 November 2012 (UTC). Because it crossed the International Date Line it began in local time on November 14 west of the date line over northern Australia, and ended in local time on November 13 east of the date line near the west coast of South America. Its greatest magnitude was 1.0500, occurring only 12 hours before perigee, with greatest eclipse totality lasting just over four minutes. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

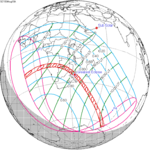
An annular solar eclipse took place at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on May 9–10 (UTC), 2013, with a magnitude of 0.9544. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

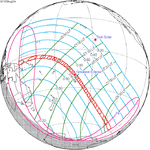
An annular solar eclipse occurred on June 10, 2002. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in Indonesia, Palau, Northern Mariana on June 11th (Tuesday), and the western tip of Jalisco, Mexico on June 10th (Monday). This eclipse was during the 2002 FIFA World Cup. The closest apogee occurred on June 4, 2002. It was the first annular solar eclipse visible in the Pacific in 6 months.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node on 3 November 2013. It was a hybrid eclipse of the Sun with a magnitude of 1.0159, with a small portion over the western Atlantic Ocean at sunrise as an annular eclipse, and the rest of the path as a narrow total solar eclipse. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A hybrid solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's in sunrise and sunset, but at Greatest Eclipse the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's.

An annular solar eclipse took place on February 26, 2017. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Occurring only 4.7 days before perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. The moon's apparent diameter was just over 0.7% smaller than the Sun's.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Wednesday, May 11, 2078. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total solar eclipse occurred on November 3, 1994. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. Totality was visible in Peru, northern Chile, Bolivia, northern Argentina, Paraguay including the northeastern part of its capital Asunción, Brazil and Gough Island of British overseas territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. The Iguazu Falls, one of the largest waterfalls systems in the world, also lies in the path of totality. Totality lasted about 4.4 minutes, so it was a relatively long total solar eclipse. Occurring only 10 hours and 2 minutes before perigee, the moon's apparent diameter was too larger.

A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on July 31, 1981. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The continental path of totality fell entirely within the Soviet Union, belonging to Georgia, Kazakhstan and Russia today. The southern part of Mount Elbrus, the highest mountain in Europe, also lies in the path of totality. Occurring only 3.8 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. With a path width of 107.8 km, this total solar eclipse had an average path.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Thursday, April 20, 2023. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across the surface of the Earth, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on January 4–5, 1992. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in the Federal States of Micronesia, Nauru, Kiribati, Baker Island, Palmyra Atoll, Kingman Reef, and southwestern California, including the southwestern part of Los Angeles.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on January 15–16, 1991. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in southwestern Western Australia, Tasmania, New Zealand and French Polynesia. It was visible over Australia as a partial solar eclipse at sunrise on January 16.

An annular solar eclipse will occur on Wednesday, October 2, 2024. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 14, 1955. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible from French Equatorial Africa, Libya, Anglo-Egyptian Sudan including the capital city Khartoum, French Somaliland including the capital Djibouti City, British Somaliland including the capital city Hargeisa, the Trust Territory of Somaliland, the Maldives, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Burma, Thailand including the capital city Bangkok, Cambodia, Laos, North Vietnam and South Vietnam, China, British Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Ryukyu Islands. It was the third central solar eclipse visible from Bangkok from 1948 to 1958, where it is rare for a large city to witness 4 central solar eclipses in just 9.945 years. This is the 20th member Solar Saros 141, and the last of first set of solar eclipses without a penumbral internal contact, the next event is the 1973 Dec 24 event, which is the first of 19 solar eclipses with a penumbral internal contact until 2298 Jul 09.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on February 4–5, 1981. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. This annular solar eclipse was large because the Moon covered 99.4% of the Sun, with a path width of only 25 km . It was visible in Australia, crossing over Tasmania and southern Stewart Island of New Zealand near sunrise on February 5th (Thursday), and ended at sunset over western South America on February 4th (Wednesday). Occurring only 4 days before perigee, the moon's apparent diameter was larger.

An annular solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on August 10, 1980 centred over the Pacific Ocean. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. Annularity was visible in Tabuaeran of Kiribati, Peru, Bolivia, northern Paraguay and Brazil. Occurring 5 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. At greatest eclipse, the Sun was 79 degrees above horizon.
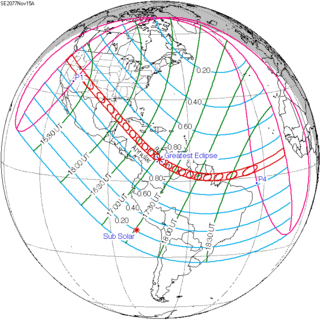
An annular solar eclipse will occur on Monday, November 15, 2077 with a magnitude of 0.9371. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partially obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. The path of annularity will cross North America and South America. This will be the 47th solar eclipse of Saros cycle 134. A small annular eclipse will cover only 94% of the Sun in a very broad path, 262 km wide at maximum, and will last 7 minutes and 54 seconds. Occurring only 4 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller.

A total solar eclipse will occur on Monday, May 1, 2079, with a maximum eclipse at 10:48:25.6 UTC. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The eclipse will be visible in Greenland, parts of eastern Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.

A total solar eclipse will occur on October 4, 2089. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. The tables below contain detailed predictions and additional information on the Total Solar Eclipse of 4 October 2089.

An annular solar eclipse occurred on December 25, 1935. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. This was the 5th solar eclipse in 1935, the maximum possible. The next time this will occur is 2206.