Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula Fe(C
5H
5)
2. The molecule consists of two cyclopentadienyl rings bound on opposite sides of a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor, that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation Fe(C
5H
5)+
2.

A thiol or thiol derivative is any organosulfur compound of the form R−SH, where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The –SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols, and the word is a portmanteau of "thio-" + "alcohol", with the first word deriving from Greek θεῖον (theion) meaning "sulfur".
Mesitylene or 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene is a derivative of benzene with three methyl substituents positioned symmetrically around the ring. The other two isomeric trimethylbenzenes are 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene (pseudocumene) and 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene (hemimellitene). All three compounds have the formula C6H3(CH3)3, which is commonly abbreviated C6H3Me3. Mesitylene is a colourless liquid with sweet aromatic odor. It is a component of coal tar, which is its traditional source. It is a precursor to diverse fine chemicals. The mesityl group (Mes) is a substituent with the formula C6H2Me3 and is found in various other compounds.

In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride (or acid chloride) is an organic compound with the functional group -COCl. Their formula is usually written RCOCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.
Cyclohexa-1,3-diene is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)2(CH)4. It is a colorless, flammable liquid. Its refractive index is 1.475 (20 °C, D). A naturally occurring derivative of 1,3-cyclohexadiene is terpinene, a component of pine oil.

Iron(II) chloride, also known as ferrous chloride, is the chemical compound of formula FeCl2. It is a paramagnetic solid with a high melting point. The compound is white, but typical samples are often off-white. FeCl2 crystallizes from water as the greenish tetrahydrate, which is the form that is most commonly encountered in commerce and the laboratory. There is also a dihydrate. The compound is highly soluble in water, giving pale green solutions.
An isocyanide is an organic compound with the functional group -N≡C. It is the isomer of the related nitrile (-C≡N), hence the prefix is isocyano. The organic fragment is connected to the isocyanide group through the nitrogen atom, not via the carbon. They are used as building blocks for the synthesis of other compounds.

DABCO (1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane) is an organic compound with the formula N2(C2H4)3. This colorless solid is a highly nucleophilic tertiary amine base, which is used as a catalyst and reagent in polymerization and organic synthesis.

n-Butyllithium is an organolithium reagent. It is widely used as a polymerization initiator in the production of elastomers such as polybutadiene or styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS). Also, it is broadly employed as a strong base (superbase) in the synthesis of organic compounds as in the pharmaceutical industry.
Umpolung or polarity inversion in organic chemistry is the chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of polarity of that group. This modification allows secondary reactions of this functional group that would otherwise not be possible. The concept was introduced by D. Seebach and E.J. Corey. Polarity analysis during retrosynthetic analysis tells a chemist when umpolung tactics are required to synthesize a target molecule.

A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the generic formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride Cl−Mg−CH
3 and phenylmagnesium bromide (C
6H
5)−Mg−Br. They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds

A dithiane is a heterocyclic compound composed of a cyclohexane core structure wherein two methylene bridges are replaced by sulfur centres. The three isomeric parent heterocycles are 1,2-dithiane, 1,3-dithiane and 1,4-dithiane.
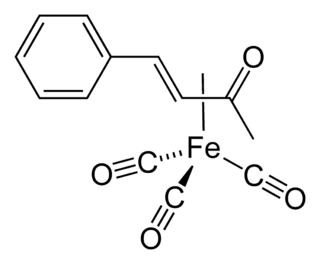
(Benzylideneacetone)iron tricarbonyl is the organoiron compound with the formula (C6H5CH=CHC(O)CH3)Fe(CO)3. It is a reagent for transferring the Fe(CO)3 unit. This red-colored compound is commonly abbreviated (bda)Fe(CO)3.

Disodium tetracarbonylferrate is the organoiron compound with the formula Na2[Fe(CO)4]. It is always used as a solvate, e.g., with tetrahydrofuran or dimethoxyethane,. which bind to the sodium cation. An oxygen-sensitive colourless solid, it is a reagent in organometallic and organic chemical research. The dioxane solvated sodium salt is known as Collman's reagent, in recognition of James P. Collman an early popularizer of its use.
Silylation is the introduction of a (usually) substituted silyl group (R3Si) to a molecule. The process is the basis of organosilicon chemistry.
Organoiron chemistry is the chemistry of iron compounds containing a carbon-to-iron chemical bond. Organoiron compounds are relevant in organic synthesis as reagents such as iron pentacarbonyl, diiron nonacarbonyl and disodium tetracarbonylferrate. Iron adopts oxidation states from Fe(−II) through to Fe(VII). Although iron is generally less active in many catalytic applications, it is less expensive and "greener" than other metals. Organoiron compounds feature a wide range of ligands that support the Fe-C bond; as with other organometals, these supporting ligands prominently include phosphines, carbon monoxide, and cyclopentadienyl, but hard ligands such as amines are employed as well.
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are commercially available and exhibit more convenient reactivity.

A dithiol is a type of organosulfur compound with two thiol functional groups. Their properties are generally similar to those of monothiols in terms of solubility, odor, and volatility. They can be classified according to the relative location of the two thiol group on the organic compound.
Metal acetylacetonates are coordination complexes derived from the acetylacetonate anion (CH
3COCHCOCH−
3) and metal ions, usually transition metals. The bidentate ligand acetylacetonate is often abbreviated acac. Typically both oxygen atoms bind to the metal to form a six-membered chelate ring. The simplest complexes have the formula M(acac)3 and M(acac)2. Mixed-ligand complexes, e.g. VO(acac)2, are also numerous. Variations of acetylacetonate have also been developed with myriad substituents in place of methyl (RCOCHCOR′−). Many such complexes are soluble in organic solvents, in contrast to the related metal halides. Because of these properties, acac complexes are sometimes used as catalyst precursors and reagents. Applications include their use as NMR "shift reagents" and as catalysts for organic synthesis, and precursors to industrial hydroformylation catalysts. C
5H
7O−
2 in some cases also binds to metals through the central carbon atom; this bonding mode is more common for the third-row transition metals such as platinum(II) and iridium(III).

Diiron propanedithiolate hexacarbonyl is the organoiron complex with the formula Fe2(S2C3H6)(CO)6. It is a red diamagnetic solid. It adopts a symmetrical structure with six terminal CO ligands. The complex is a precursor to hydrogenase mimics.












