
Inorganic chemistry deals with synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers chemical compounds that are not carbon-based, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture.

A metallocene is a compound typically consisting of two cyclopentadienyl anions (C
5H−
5, abbreviated Cp) bound to a metal center (M) in the oxidation state II, with the resulting general formula (C5H5)2M. Closely related to the metallocenes are the metallocene derivatives, e.g. titanocene dichloride, vanadocene dichloride. Certain metallocenes and their derivatives exhibit catalytic properties, although metallocenes are rarely used industrially. Cationic group 4 metallocene derivatives related to [Cp2ZrCH3]+ catalyze olefin polymerization.

In chemistry, hexol is a cation with formula {[Co(NH3)4(OH)2]3Co}6+ — a coordination complex consisting of four cobalt cations in oxidation state +3, twelve ammonia molecules NH
3, and six hydroxy anions HO−
, with a net charge of +6. The hydroxy groups act as bridges between the central cobalt atom and the other three, which carry the ammonia ligands.

Metal carbonyls are coordination complexes of transition metals with carbon monoxide ligands. Metal carbonyls are useful in organic synthesis and as catalysts or catalyst precursors in homogeneous catalysis, such as hydroformylation and Reppe chemistry. In the Mond process, nickel tetracarbonyl is used to produce pure nickel. In organometallic chemistry, metal carbonyls serve as precursors for the preparation of other organometallic complexes.

Cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) is a aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NH)4. It is a white solid.

Metal nitrosyl complexes are complexes that contain nitric oxide, NO, bonded to a transition metal. Many kinds of nitrosyl complexes are known, which vary both in structure and coligand.

1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane, also called 9-ane-S3, is the thia-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2S)3. This cyclic thioether is most often encountered as a tridentate ligand in coordination chemistry, where it forms transition metal thioether complexes.
Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005 is the 2005 version of Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry. It is a collection of rules for naming inorganic compounds, as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).

Tris(2-aminoethyl)amine is the organic compound with the formula N(CH2CH2NH2)3. This colourless liquid is soluble in water and is highly basic, consisting of a tertiary amine center and three pendant primary amine groups. Abbreviated tren or TREN it is a crosslinking agent in the synthesis of polyimine networks and a tripodal ligand in coordination chemistry.

PMDTA (N,N,N′,N′′,N′′-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine) is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)2NCH2CH2]2NCH3. PMDTA is a basic, bulky, and flexible, tridentate ligand that is a used in organolithium chemistry. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellowish.

Metal amides (systematic name metal azanides) are a class of coordination compounds composed of a metal center with amide ligands of the form NR2−. Amide ligands have two electron pairs available for bonding. In principle, they can be terminal or bridging. In these two examples, the dimethylamido ligands are both bridging and terminal:
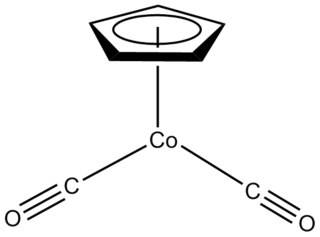
Half sandwich compounds, also known as piano stool complexes, are organometallic complexes that feature a cyclic polyhapto ligand bound to an MLn center, where L is a unidentate ligand. Thousands of such complexes are known. Well-known examples include cyclobutadieneiron tricarbonyl and (C5H5)TiCl3. Commercially useful examples include (C5H5)Co(CO)2, which is used in the synthesis of substituted pyridines, and methylcyclopentadienyl manganese tricarbonyl, an antiknock agent in petrol.

Transition metal nitrile complexes are coordination compounds containing nitrile ligands. Because nitriles are weakly basic, the nitrile ligands in these complexes are often labile.
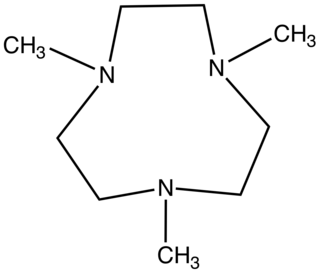
1,4,7-Trimethyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane is the aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NCH3)3. This colorless liquid is the N-methylated derivative of triazacyclononane (TACN), a face-capping tridentate ligand that is popular in coordination chemistry.
Karl Wieghardt is a German inorganic chemist and emeritus director of the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Energy Conversion in Mülheim. He was active in the preparation and detailed characterization of models for iron and manganese metalloenzymes, metal complexes of noninnocent ligands, and magnetic interactions in polynuclear metal complexes.
Transition metal amino acid complexes are a large family of coordination complexes containing the conjugate bases of the amino acids, the 2-aminocarboxylates. Amino acids are prevalent in nature, and all of them function as ligands toward the transition metals. Not included in this article are complexes of the amides and ester derivatives of amino acids. Also excluded are the polyamino acids including the chelating agents EDTA and NTA.

In chemistry, a transition metal chloride complex is a coordination complex that consists of a transition metal coordinated to one or more chloride ligand. The class of complexes is extensive.

Transition metal thioether complexes comprise coordination complexes of thioether (R2S) ligands. The inventory is extensive.

Transition metal oxalate complexes are coordination complexes with oxalate (C2O42−) ligands. Some are useful commercially, but the topic has attracted regular scholarly scrutiny. Oxalate (C2O42-) is a kind of dicarboxylate ligand. As a small, symmetrical dinegative ion, oxalate commonly forms five-membered MO2C2 chelate rings. Mixed ligand complexes are known, e.g., [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]κ+.

1,1,1-Tris(diphenylphosphinomethyl)ethane, also called Triphos, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH3C[CH2PPh2]3. An air-sensitive white solid, it is a tripodal ligand ("three-legged") of idealized C3v symmetry. It was originally prepared by the reaction of sodium diphenylphosphide and CH3C(CH2Cl)3:



















