This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2012) |
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in India Timeline of Indian history | ||||
Events from the year 1505 in India.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2012) |
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in India Timeline of Indian history | ||||
Events from the year 1505 in India.
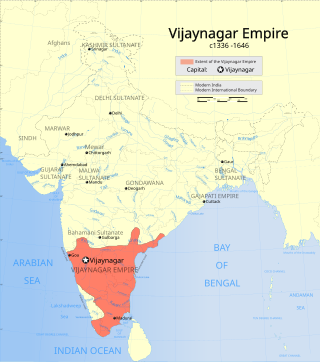
The Vijayanagara Empire was a late medieval Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, members of a pastoralist cowherd community that claimed Gadaria (Shepherd) lineage.

The history of southern India covers a span of over four thousand years during which the region saw the rise and fall of a number of dynasties and empires.

Krishnadevaraya was an emperor of the Vijayanagara Empire reigning from 1509 to 1529. He was the third monarch of the Tuluva dynasty, and is considered to be one of the greatest rulers in Indian history. He ruled the largest empire in India after the fall of the Islamic Delhi Sultanate. Presiding over the empire at its zenith, he is regarded as an icon by many Indians. Krishnadevaraya earned the titles Andhra Bhoja, Karnatakaratna Simhasanadeeshwara, Yavana Rajya Pratistapanacharya, Kannada Rajya Rama Ramana, Gaubrahmana Pratipalaka and Mooru Rayara Ganda. He became the dominant ruler of the peninsula by defeating the sultans of Bijapur, Golconda, the Bahmani Sultanate and the Gajapatis of Odisha, and was one of the most powerful Hindu rulers in India.

BukkaRaya I was an emperor of the Vijayanagara Empire from the Sangama Dynasty. He was a son of Bhavana Sangama, the chieftain of a cowherd pastoralist community, Yadava people of Golla (kuruba)descent. The first Bahmani-Vijayanagar War occurred during the reign of Bukka Raya I, in which he was besieged, and sued for peace.
The Saluva dynasty was the second dynasty to rule the Vijayanagara Empire and was created by the Saluvas, who by historical tradition were natives of the Kalyani region of northern Karnataka in modern India. The Gorantla inscription traces their origins to this region from the time of the Western Chalukyas and Kalachuris of Karnataka. The term "Saluva" is known to lexicographers as "hawk" used in hunting. They later spread into the east coast of modern Andhra Pradesh, perhaps by migration or during the Vijayanagara conquests during the 14th century.
Tuluva is the name of the third dynasty of the Vijayanagara Empire. The dynasty traces its patrilineal ancestry to Tuluva Narasa Nayaka, a powerful warlord from the westerly. His son Narasimha Nayaka arranged for the assassination of the weak Narasimha Raya II bringing an end to the rule of the Saluva dynasty. Narasimha Nayaka later assumed the Vijayangara throne as Viranarasimha Raya bringing the Tuluva dynasty to prominence. The dynasty was at its zenith during the rule of Krishnadevaraya, the second son of Tuluva Narasa Nayaka.

Vyāsatīrtha, also called Vyasaraja or Chandrikacharya, was a Hindu philosopher, scholar, polemicist, commentator and poet belonging to the Madhwacharya's Dvaita order of Vedanta. As the rajaguru of Vijayanagara Empire, Vyasatirtha was at the forefront of a golden age in Dvaita which saw new developments in dialectical thought, growth of the Haridasa literature under bards like Purandara Dasa and Kanaka Dasa and an increased spread of Dvaita across the subcontinent. He himself composed many kīrtanas in Kannada and Sanskrit.
Saluva Narasimha Deva Raya was an emperor of the Vijayanagara Empire from the Saluva Dynasty. A patron of the Madhwa saint Sripadaraya, he authored the Sanskrit work Rama Bhyudayam. He also patronised Kannada poet Kavi Linga.
Pemmasani Kamma Nayaks were a ruling clan in the south Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. They came into prominence during Vijayanagara Empire. After the Battle of Talikota in 1565 AD, the collapse of Vijayanagara Empire led to the emergence of Pemmasani Nayakas in the Rayalaseema region. They belonged to the Kamma social group.

Vijayanagara literature was produced in the Vijayanagara Empire during a golden age of literature in South India in general. The rulers patronised Kannada, Telugu, Sanskrit and Tamil scholars who wrote in the Jain, Virashaiva and Vaishnava traditions. The period produced hundreds of works on all aspects of Indian culture, religion, biographies, prabhandas (stories), music, grammar, poetics and medicine. An attempt is made in this section to list the various poets and saints and their most famous works.
Tuluva Narasa Nayaka was an Indian general a Bunt chieftain and later an Imperial Regent who founded the Tuluva dynasty of the Vijayanagara Empire. He was the father of the Emperors Viranarasimha Raya, Krishnadevaraya and Achyuta Deva Raya.
Vira Narasimha Raya became the Emperor of Vijayanagara after the death of his predecessor Narasimha Raya II. He was the older half-brother of Krishnadevaraya.
Thimma Bhupala was the elder son and heir-apparent of Saluva Narasimha Deva Raya, the Sovereign of the Vijayanagara Empire. During the reign of his father, he held the office of the Yuvaraja. Prince Thimma succeeded his father in 1491 but was soon assassinated by an army commander loyal to the Sangamas during a period of political unrest in Vijayanagara. He was succeeded by his younger brother Narasimha Raya II. The eldest son of his Saluva Narasimha Deva Raya's prime minister, Narasa Nayaka, had Narasimha Raya II assassinated and ascended to the throne himself in 1505, beginning the Tuluva dynasty, the third dynasty of the Vijayanagara empire.
Narasimha Raya II ( Narasimha II, Immadi Narasimha Raya or Dhamma Thimma Raya) was the third and last emperor from the Saluva dynasty, the second of the four dynasties to rule the Vijayanagara Empire.

The Battle of Raichur was fought between the Vijayanagara Empire and the Sultanate of Bijapur in 1520 in the town of Raichur, India. It resulted in a decisive victory for Vijayanagara forces, and the Bijapur ruler was defeated and pushed across the river Krishna.
Pemmasani Ramalinga Nayudu was an army commander of a Vijayanagara military unit. An inscription dated to 1544 CE, which was found in Tallaproddatu, states that Pemmasani Ramalinga enjoyed the nayankara of the village. Phillip B. Wagoner who analysed 17th century Telugu text Rayavachakamu noted that it is not known whether Ramalinga Nayudu served Krishnadeva Raya or some later ruler.
Events from the year 1509 in India.

Chandragiri Fort is an historical fort located in the Chandragiri suburb of Tirupati. It is situated in Tirupati district of Andhra Pradesh, India. It is mostly associated with the Vijayanagara Emperors. In 1460 CE Odra Gajapati Kapilendra Dev captured the Chandragiri Fort.
Chamarajara Wodeyar II was the fourth raja of the Kingdom of Mysore from 1478 until 1513.

The Deccani–Vijayanagar wars were a series of wars between 1495 to 1678 that pitted the rival powers of the Deccan Sultanates against the Vijayanagar Empire. Over the course of approximately 120 years, these two entities engaged in a series of wars and skirmishes that were marked by significant displays of military strength and strategic maneuvering.