| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in India Timeline of Indian history | ||||
Events in the year 1896 in India.
| |||||
| Centuries: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decades: | |||||
| See also: | List of years in India Timeline of Indian history | ||||
Events in the year 1896 in India.

Sree Narayana Guru was a philosopher, spiritual leader and social reformer in India. He led a reform movement against the injustice in the caste-ridden society of Kerala in order to promote spiritual enlightenment and social equality. A quote of his that defined his movement was "one caste, one religion, and one god for all human beings." He is the author of the Advaita poem Daiva Dasakam, which is one of the most used poem in Kerala for community prayer.

Bhikhaji Rustom Cama or simply as, Madam Cama, was one of the prominent figures in the Indian independence movement.

Govindan Parameswaran Pillai, also known as Barrister G. P. Pillai, was a freedom fighter, social reformer, barrister, journalist, and publisher. He established the first English language newspaper in South India, The Madras Standard. He drafted the Malayali Memorial in 1891. Pillai is the only Malayali whom Mahatma Gandhi has mentioned in his autobiography. He regularly wrote columns in various newspapers. Pillai stood against autocratic governance in Travancore and promoted civil rights and equal opportunity among all classes.

Padmanabhan Palpu was a physician from the Kingdom of Travancore who served as a chief medical officer of Mysore State.

The Ezhavas, also known as Thiyya or Tiyyar in the Malabar region, are a community with origins in the region of India presently known as Kerala, where in the 2010s they constituted about 23% of the population and were reported to be the largest Hindu community. The Malabar Ezhava group has claimed a higher rank in the Hindu caste system than the other Ezhava groups but was considered to be of a similar rank by colonial and subsequent administrations.

The Swaminarayan Sampradaya, also known as Swaminarayan Hinduism and Swaminarayan movement, is a Hindu Vaishnava sampradaya rooted in Ramanuja's Vishishtadvaita, characterized by the worship of its charismatic founder Sahajanand Swami, better known as Swaminarayan (1781–1830), as an avatar of Krishna or as the highest manifestation of Purushottam, the supreme God. According to the tradition's lore, both the religious group and Sahajanand Swami became known as Swaminarayan after the Swaminarayan mantra, which is a compound of two Sanskrit words, swami and Narayan.

The timeline of major famines in India during British rule covers major famines on the Indian subcontinent from 1765 to 1947. The famines included here occurred both in the princely states, British India and Indian territories independent of British rule such as the Maratha Empire.
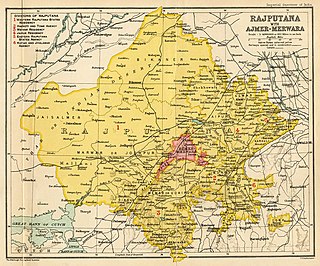
The Rajputana famine of 1869 affected an area of 296,000 square miles (770,000 km2) and a population of 44,500,000, primarily in the princely states of Rajputana, India, and the British territory of Ajmer. Other areas affected included Gujarat, the North Deccan districts, the Jubbalpore division of the Central Provinces and Berar, the Agra and Bundelkhand division of the United Provinces, and the Hissar division of the Punjab.

The Chalisa famine of 1783–1784 in the Indian subcontinent followed unusual El Niño events that began in 1780 and caused droughts throughout the region. Chalisa refers to the Vikram Samvat calendar year 1840 (1783). The famine affected many parts of North India, especially the Delhi territories, present-day Uttar Pradesh, Eastern Punjab, Rajputana, and Kashmir, then all ruled by different Indian rulers. The Chalisa was preceded by a famine in the previous year, 1782–1783, in South India, including Madras City and surrounding areas and in the extended Kingdom of Mysore.

The Great Famine of 1876–1878 was a famine in India under British Crown rule. It began in 1876 after an intense drought resulted in crop failure in the Deccan Plateau. It affected south and Southwestern India—the British-administered presidencies of Madras and Bombay, and the princely states of Mysore and Hyderabad—for a period of two years. In 1877, famine came to affect regions northward, including parts of the Central Provinces and the North-Western Provinces, and a small area in Punjab. The famine ultimately affected an area of 670,000 square kilometres (257,000 sq mi) and caused distress to a population totalling 58,500,000. The excess mortality in the famine has been estimated in a range whose low end is 5.6 million human fatalities, high end 9.6 million fatalities, and a careful modern demographic estimate 8.2 million fatalities. The famine is also known as the Southern India famine of 1876–1878 and the Madras famine of 1877.

The Indian famine of 1896–1897 was a famine that began in Bundelkhand, India, early in 1896 and spread to many parts of the country, including the United Provinces, the Central Provinces and Berar, Bihar, parts of the Bombay and Madras presidencies, and parts of the Punjab; in addition, the princely states of Rajputana, Central India Agency, and Hyderabad were affected. All in all, during the two years, the famine affected an area of 307,000 square miles (800,000 km2) and a population of 69.5 million. Although relief was offered throughout the famine-stricken regions in accordance with the Provisional Famine Code of 1883, the mortality, both from starvation and accompanying epidemics, was very high: approximately one million people are thought to have died.

The Agra famine of 1837–1838 was a famine in the newly established North-Western Provinces of Company-ruled India that affected an area of 25,000 square miles (65,000 km2) and a population of 8 million people. The central Doab in present-day Uttar Pradesh—the region of the districts of Kanpur, Etawah, Mainpuri, Agra and Kalpi—was the hardest hit; the trans-Jumna districts of Jalaun, Hamirpur, and Banda also suffered extreme distress.

The Indian famine of 1899–1900 began with the failure of the summer monsoons in 1899 over Western and Central India and, during the next year, affected an area of 476,000 square miles (1,230,000 km2) and a population of 59.5 million. The famine was acute in the Central Provinces and Berar, the Bombay Presidency, the minor province of Ajmer-Merwara, and the Hissar District of the Punjab; it also caused great distress in the princely states of the Rajputana Agency, the Central India Agency, Hyderabad and the Kathiawar Agency. In addition, small areas of the Bengal Presidency, the Madras Presidency and the North-Western Provinces were acutely afflicted by the famine.

Vaikom Satyagraha, from 30 March 1924 to 23 November 1925, was a nonviolent agitation for access to the prohibited public environs of the Vaikom Temple in the Kingdom of Travancore. Kingdom of Travancore was known for its rigid and oppressive caste system. The campaign was led by Congress leaders T. K. Madhavan, K. Kelappan, K. P. Kesava Menon. Other notable leaders who participated in the campaign include George Joseph, E. V. Ramasamy "Periyar" and it was noted for the active support and participation offered by different communities and a variety of activists.
Vivekodayam is a Malayalam literary journal established in 1904 to serve as a voice of the underprivileged communities in the Indian state of Kerala. It was founded by Kumaran Asan, a prominent poet of malayalam literature, social reformer, disciple of Narayana Guru and founder-secretary of the associated SNDP Yogam, who was inspired by the teachings of Swami Vivekananda.
Kishorlal Ghanshyamlal Mashruwala was an Indian independence activist as well as biographer, essayist and translator. Educated in Bombay and Agra, he completed BA and LLB. He was an associate of Mahatma Gandhi and was deeply influenced by him. He extensively wrote on education, religion and philosophy as well as translated some works in Gujarati.
The Travancore Legislative Council was the governing body of the Travancore princely state from 1888 to 1932. This legislature was the first opportunity in post-medieval India for non-royal natives to interfere, at least to some extent, with the sovereignty of princely states or imperial powers. Shri Moolam Tirunal Rama Varma, the Maharaja (King) of Travancore, is considered as the first Indian ruler to implement the concept of public participation in governance through the formation of this council. After passing through many stages of evolution, this assembly later became the basic framework of the Kerala Legislature and is considered to became the core of the legislative system of Kerala itself, which became a state in independent India.