Related Research Articles

Giordano Bruno was an Italian philosopher, poet, alchemist, astrologer, cosmological theorist, and esotericist. He is known for his cosmological theories, which conceptually extended to include the then-novel Copernican model. He practiced Hermeticism and gave a mystical stance to exploring the universe. He proposed that the stars were distant suns surrounded by their own planets (exoplanets), and he raised the possibility that these planets might foster life of their own, a cosmological position known as cosmic pluralism. He also insisted that the universe is infinite and could have no center.

Tycho Brahe, generally called Tycho for short, was a Danish astronomer of the Renaissance, known for his comprehensive and unprecedentedly accurate astronomical observations. He was known during his lifetime as an astronomer, astrologer, and alchemist. He was the last major astronomer before the invention of the telescope. Tycho Brahe has also been described as the greatest pre-telescopic astronomer.

1600 (MDC) was a century leap year starting on Saturday of the Gregorian calendar and a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 1600th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 600th year of the 2nd millennium, the 100th and last year of the 16th century, and the 1st year of the 1600s decade. As of the start of 1600, the Gregorian calendar was 10 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.
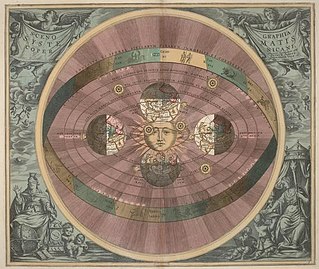
Heliocentrism is a superseded astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the centre of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at the center. The notion that the Earth revolves around the Sun had been proposed as early as the 3rd century BC by Aristarchus of Samos, who had been influenced by a concept presented by Philolaus of Croton. In the 5th century BC the Greek philosophers Philolaus and Hicetas had the thought on different occasions that the Earth was spherical and revolving around a "mystical" central fire, and that this fire regulated the universe. In medieval Europe, however, Aristarchus' heliocentrism attracted little attention—possibly because of the loss of scientific works of the Hellenistic period.
The year 1650 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1795 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1788 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1748 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1720 in science and technology involved some significant events.
Thomas Digges was an English mathematician and astronomer. He was the first to expound the Copernican system in English but discarded the notion of a fixed shell of immoveable stars to postulate infinitely many stars at varying distances. He was also first to postulate the "dark night sky paradox".

The Copernican Revolution was the paradigm shift from the Ptolemaic model of the heavens, which described the cosmos as having Earth stationary at the center of the universe, to the heliocentric model with the Sun at the center of the Solar System. This revolution consisted of two phases; the first being extremely mathematical in nature and the second phase starting in 1610 with the publication of a pamphlet by Galileo. Beginning with the 1543 publication of Nicolaus Copernicus’s De revolutionibus orbium coelestium, contributions to the “revolution” continued until finally ending with Isaac Newton’s work over a century later.

Renaissance magic was a resurgence in Hermeticism and Neo-Platonic varieties of the magical arts which arose along with Renaissance humanism in the 15th and 16th centuries CE. During the Renaissance period, magic and occult practices underwent significant changes that reflected shifts in cultural, intellectual, and religious perspectives. C. S. Lewis, in his work on English literature, highlighted the transformation in how magic was perceived and portrayed. In medieval stories, magic had a fantastical and fairy-like quality, while in the Renaissance, it became more complex and tied to the idea of hidden knowledge that could be explored through books and rituals. This change is evident in the works of authors like Spenser, Marlowe, Chapman, and Shakespeare, who treated magic as a serious and potentially dangerous pursuit.

The early Christians, like the early Jews, were vehemently opposed to astrology, even attributing it to demonic origin.

The Monument to Giordano Bruno, created by Ettore Ferrari, was erected in 1889 at Campo de' Fiori square in Rome, Italy, to commemorate the italian philosopher Giordano Bruno, who was burned there in 1600. Since its inception the idea of a monument dedicated to the executed heretic located in Rome, once the capital of the Papal States, has generated controversy between anti-clerical and those more aligned with the Roman Catholic church.
5148 Giordano, provisional designation 5557 P-L, is a background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 October 1960, by Dutch astronomer couple Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten on photographic plates taken by Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. It was named for Italian friar and heretic Giordano Bruno, who was burned at the stake in Rome in 1600. The presumably carbonaceous Themistian asteroid has a rotation period of 7.8 hours and possibly an elongated shape.
Philosophers throughout the history of philosophy have been held in courts and tribunals for various offenses, often as a result of their philosophical activity, and some have even been put to death. The most famous example of a philosopher being put on trial is the case of Socrates, who was tried for, amongst other charges, corrupting the youth and impiety.
The year 1546 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here.
The year 1548 in science and technology included a number of events, some of which are listed here.

Plaza Giordano Bruno is a public space in Colonia Juárez, Mexico City. Its namesake is Giordano Bruno (1548–1600), an Italian philosopher, poet, cosmological theorist and esotericist who was executed by the Papal States for heresy. A statue of Bruno adorns the plaza.
References
- ↑ Rothen, François (2009). Surprenante gravité. Focus science. Presses polytechniques et universitaires romandes. p. 61. ISBN 978-2-88074-774-9 . Retrieved 2011-08-05.
- 1 2 3 Grun, Bernard (1991). "1600" . The Timetables of History (3rd ed.). New York: Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-74919-6.
- ↑ "History of the museum". snm.ku.dk. Natural History Museum of Denmark. 2006-08-10. Retrieved 2020-12-23.
- ↑ "naturalist, n. and adj.". Oxford English Dictionary online version. Oxford University Press. December 2011. Retrieved 2011-12-20.(subscription or participating institution membership required)
- ↑ "1600 Eruption Caused Global Disruption". Geology Times. 2008-04-25. Archived from the original on 2011-02-15. Retrieved 2010-11-13.
- ↑ Witze, Alexandra (2008-04-11). "The volcano that changed the world". Nature.Com News. Nature Publishing Group. Archived from the original on 17 May 2008. Retrieved 2008-04-14.
- ↑ Morley, William F. E. (1979) [1966]. "Chauvin de Tonnetuit, Pierre de". In Brown, George Williams (ed.). Dictionary of Canadian Biography . Vol. I (1000–1700) (online ed.). University of Toronto Press . Retrieved 2011-06-22.
- ↑ Arturo Labriola, Giordano Bruno: Martyrs of free thought no. 1