Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthquakes are the planet's most powerful, with moment magnitudes (Mw) that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes.

An earthquake occurred on July 17, 2006, at along a subduction zone off the coast of west and central Java, a large and densely populated island in the Indonesian archipelago. The shock had a moment magnitude of 7.7 and a maximum perceived intensity of IV (Light) in Jakarta, the capital and largest city of Indonesia. There were no direct effects of the earthquake's shaking due to its low intensity, and the large loss of life from the event was due to the resulting tsunami, which inundated a 300 km (190 mi) portion of the Java coast that had been unaffected by the earlier 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami that was off the coast of Sumatra. The July 2006 earthquake was also centered in the Indian Ocean, 180 kilometers (110 mi) from the coast of Java, and had a duration of more than three minutes.
The 1877 Iquique earthquake occurred at 21:16 local time on 9 May. It had a magnitude of 8.5 on the surface-wave magnitude scale. Other estimates of its magnitude have been as high as 8.9 and 9.0 . It had a maximum intensity of XI (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale and triggered a devastating tsunami. A total of 2,385 people died, mainly in Fiji from the tsunami.

The 1944 Tōnankai earthquake occurred at 13:35 local time on 7 December. It had an estimated magnitude of 8.1 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum felt intensity of greater than 5 Shindo. It triggered a large tsunami that caused serious damage along the coast of Wakayama Prefecture and the Tōkai region. Together, the earthquake and tsunami caused 3,358 casualties.
The 1746 Lima–Callao earthquake occurred at on 28 October with a moment magnitude of 8.6–8.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme). The epicenter was located about 90 km (56 mi) north-northwest of the capital Lima, which was almost completely destroyed, and the subsequent tsunami devastated the port city of Callao. It was the deadliest earthquake in Peru's history prior to the 1970 earthquake.
The 1932 Jalisco earthquakes began on June 3 at 10:36 UTC with a megathrust event that registered 8.1 on the moment magnitude scale. With a maximum perceived intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale, at least 400 deaths were caused in Mexico and neighboring Guatemala. It was the first of a series of seismic events that affected parts of western Mexico during the month of June 1932, all reaching magnitude 7 or greater.
The 1931 Oaxaca earthquake affected portions of southern Mexico on January 14 at 18:50 MST. It registered a magnitude of 8.0 on the surface-wave magnitude scale and had a maximum perceived intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale.
The 1762 Arakan earthquake occurred at about 17:00 local time on 2 April, with an epicentre somewhere along the coast from Chittagong to Arakan in modern Myanmar. It had an estimated moment magnitude between 8.5 and 8.8 and a maximum estimated intensity of XI (Extreme). It triggered a local tsunami in the Bay of Bengal and caused at least 200 deaths. The earthquake was associated with major areas of both uplift and subsidence. It is also associated with a change in course of the Brahmaputra River to from east of Dhaka to 150 kilometres (93 mi) to the west via the Jamuna River.
The 1979 Tumaco earthquake occurred at on 12 December with a moment magnitude of 8.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). The epicenter was just offshore from the border between Ecuador and Colombia, near the port city of Tumaco. It triggered a major tsunami, which was responsible for most of the estimated 300–600 deaths. The hardest hit area was Colombia's Nariño Department.
The 1942 Peru earthquake occurred on August 24 at and was located near the border of the departments of Ica and Arequipa, Peru. It had a magnitude of 8.2 or 8.4.
The 1941 Andaman Islands earthquake struck the Andaman Islands on June 26 with a magnitude of 7.7 to 8.1. Details of this event are poorly known as much of Southeast Asia was in the turmoil of World War II. The quake caused severe damage in the Andaman Islands. The tsunami it triggered was reported along the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India and British Ceylon. There may have been damage and deaths in Bangladesh, Myanmar, and Thailand due to the tsunami.

The 1918 Celebes Sea earthquake occurred on August 15 at 12:18 UTC near the Moro Gulf coast of Mindanao. It had a magnitude of 8.3 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum perceived intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It triggered a tsunami of up to 7 m in height and the combined effects of the earthquake and tsunami led to the deaths of 52 people.
The 1999 Ambrym earthquake occurred on November 27 at with a moment magnitude of 7.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VII. The back arc thrust event occurred within the Vanuatu archipelago, just to the south of the volcanic island of Ambrym. Vanuatu, which was previously known as New Hebrides, is subject to volcanic and earthquake activity because it lies on an active and destructive plate boundary called the New Hebrides Subduction Zone. While the National Geophysical Data Center classified the total damage as moderate, a destructive local tsunami did result in some deaths, with at least five killed and up to 100 injured.
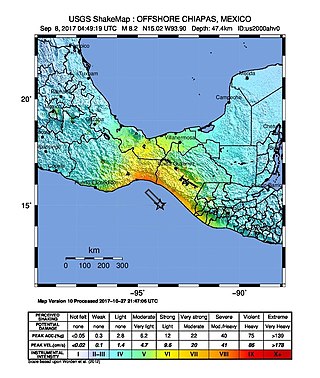
The 2017 Chiapas earthquake struck at 23:49 CDT on 7 September in the Gulf of Tehuantepec off the southern coast of Mexico near the state of Chiapas, approximately 87 kilometres (54 mi) southwest of Pijijiapan, with a Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent). The moment magnitude was estimated to be 8.2.
On January 30, 1973, at 15:01 (UTC–6), a magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck 35.3 km (21.9 mi) beneath the Sierra Madre del Sur range in the Mexican states of Colima, Jalisco and Michoacán. On the Mercalli intensity scale, the earthquake reached a maximum intensity of X (Extreme), causing serious damage in the region. At least 56 people were killed and about 390 were injured. The event is commonly referred to as the Colima earthquake.
The Nemuro-Oki earthquake in scientific literature, occurred on June 17 at 12:55 local time. It struck with an epicenter just off the Nemuro Peninsula in northern Hokkaidō, Japan. It measured 7.8–7.9 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ), 8.1 on the tsunami magnitude scale (Mt ) and 7.4 on the Japan Meteorological Agency magnitude scale (MJMA ).
During April 1819, the area around Copiapó in northern Chile was struck by a sequence of earthquakes over a period of several days. The largest of these earthquakes occurred on 11 April at about 15:00 local time, with an estimated magnitude of 8.5. The other two events, on 3 April between 08:00 and 09:00 local time and on 4 April at 16:00 local time, are interpreted as foreshocks to the mainshock on 11 April. The mainshock triggered a tsunami that affected 800 km of coastline and was also recorded at Hawaii. The city of Copiapó was devastated.

The Shōnai offshore earthquake occurred at around 14:00 on December 7, 1833. It struck with an epicenter in the Sea of Japan, off the coast of Yamagata Prefecture, Japan. A tsunami was triggered by the estimated MJMA 7.5–7.7 earthquake. One hundred and fifty people were killed and there was severe damage in the prefecture.

The southern margin of the Gulf of Corinth was struck by a major earthquake on 26 December 1861 at 08:28 a.m. local time. It had an estimated magnitude in the range 6.6–6.7 and a maximum felt intensity of IX (destructive) on the European macroseismic scale (EMS). It caused widespread damage on both sides of the Gulf and led to up to 20 deaths and a further 126 people being injured, 18 of them seriously. A series of tsunami waves were reported, with a maximum run-up of 2.1 m.






