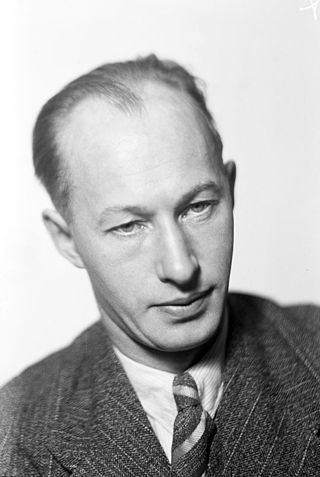Ivan Alekseyevich Bunin was the first Russian writer awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1933. He was noted for the strict artistry with which he carried on the classical Russian traditions in the writing of prose and poetry. The texture of his poems and stories, sometimes referred to as "Bunin brocade", is considered to be one of the richest in the language.

Mark Aldanov was a Russian and later French writer and critic, known for his historical novels.

The 1954 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the American author Ernest Hemingway (1899–1961) "for his mastery of the art of narrative, most recently demonstrated in The Old Man and the Sea, and for the influence that he has exerted on contemporary style."

The 1948 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to British-American poet Thomas Stearns Eliot (1888–1965) "for his outstanding, pioneer contribution to present-day poetry." Eliot is the fourth British recipient of the prize after John Galsworthy in 1932.

The 1956 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Spanish poet Juan Ramón Jiménez (1881–1958) "for his lyrical poetry, which in Spanish language constitutes an example of high spirit and artistical purity" He is the third Spanish recipient of the prize after the dramatist Jacinto Benavente in 1922.

The 1905 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Polish novelist Henryk Sienkiewicz (1846–1916) "because of his outstanding merits as an epic writer." He was given the prize on 10 December 1905. He is the first Polish author to win the Nobel Prize in the literary category and the second Polish citizen to win in general after the chemist Maria Skłodowska Curie in 1903. He was followed by Władysław Reymont in 1924.

The 1970 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Russian novelist Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn (1918–2008) "for the ethical force with which he has pursued the indispensable traditions of Russian literature." For political reasons he would not receive the prize until 1974. Solzhenitsyn is the fourth Russian recipient of the prize after Ivan Bunin in 1933, Boris Pasternak in 1958 and Mikhail Sholokhov in 1965.

The 1916 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Swedish poet and prose writer Verner von Heidenstam (1859–1940) "in recognition of his significance as the leading representative of a new era in our literature." Heidenstam was the second Swedish Nobel laureate in Literature after Selma Lagerlöf in 1909.

The 1909 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Swedish author Selma Lagerlöf (1858–1940) "in appreciation of the lofty idealism, vivid imagination and spiritual perception that characterize her writings." She became the first woman and first Swede to be awarded the prize.

The 1972 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the German author Heinrich Böll (1917–1985) "for his writing which through its combination of a broad perspective on his time and a sensitive skill in characterization has contributed to a renewal of German literature." Böll is the fifth German author to be recipient of the prize.

The 1931 Nobel Prize in Literature was posthumously awarded to the Swedish poet Erik Axel Karlfeldt (1864–1931) with the citation: "The poetry of Erik Axel Karlfeldt." He was the third Swede to win the prize and remains the only recipient to be posthumously awarded. Karlfeldt had been offered the award already in 1919 but refused to accept it, because of his position as permanent secretary to the Swedish Academy (1913–1931), which awards the prize.
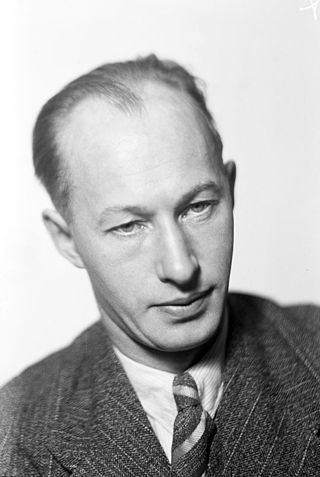
The 1974 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded jointly to Swedish authors Eyvind Johnson (1900–1976) "for a narrative art, farseeing in lands and ages, in the service of freedom" and Harry Martinson (1904–1978) "for writings that catch the dewdrop and reflect the cosmos." The winners were announced in October 1974 by Karl Ragnar Gierow, permanent secretary of the Swedish Academy, and later sparked heavy criticisms from the literary world.

The 1951 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded the Swedish author Pär Lagerkvist "for the artistic vigour and true independence of mind with which he endeavours in his poetry to find answers to the eternal questions confronting mankind." Lagerkvist is the fourth Swedish recipient of the Nobel Prize in Literature after Lagerlöf in 1909, Von Heidenstam in 1916, and Karlfeldt in 1931.

The 1955 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Icelandic writer Halldór Kiljan Laxness (1902–1998) "for his vivid epic power which has renewed the great narrative art of Iceland." He is the first and only Icelandic recipient of the Nobel prize in all categories. The literary critic Sveinn Hoskuldsson described him, saying:
"His chief literary works belong to the genre... [of] narrative prose fiction. In the history of our literature Laxness is mentioned beside Snorri Sturluson, the author of "Njals saga", and his place in world literature is among writers such as Cervantes, Zola, Tolstoy, and Hamsun... He is the most prolific and skillful essayist in Icelandic literature both old and new..."

The 1965 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded the Russian novelist Mikhail Sholokhov (1905–1984) "for the artistic power and integrity with which, in his epic of the Don, he has given expression to a historic phase in the life of the Russian people." He is the third Russian-speaking author to become the prize's recipient.

The 1915 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the French author Romain Rolland (1866–1944) "as a tribute to the lofty idealism of his literary production and to the sympathy and love of truth with which he has described different types of human beings." The prize was awarded the following year on November 9, 1916 and he is the third Frenchman who became a Nobel recipient for the literature category.

The 1930 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the American novelist Sinclair Lewis (1885–1951) "for his vigorous and graphic art of description and his ability to create, with wit and humour, new types of characters." He is the first American Nobel laureate in literature.

The 1932 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the British author John Galsworthy "for his distinguished art of narration which takes its highest form in The Forsyte Saga".

The 1923 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Irish poet and dramatist William Butler Yeats (1865–1939) "for his always inspired poetry, which in a highly artistic form gives expression to the spirit of a whole nation". He was the first Irish Nobel laureate in literature.