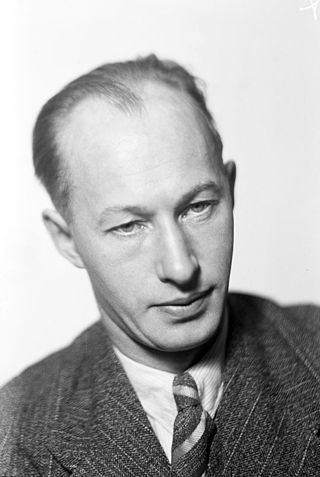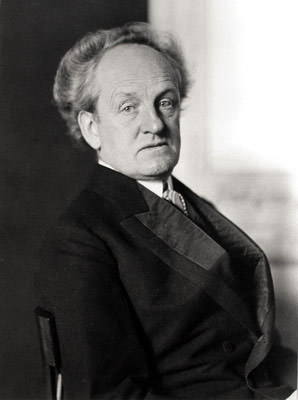Luigi Pirandello was an Italian dramatist, novelist, poet, and short story writer whose greatest contributions were his plays. He was awarded the 1934 Nobel Prize in Literature "for his bold and ingenious revival of dramatic and scenic art" Pirandello's works include novels, hundreds of short stories, and about 40 plays, some of which are written in Sicilian. Pirandello's tragic farces are often seen as forerunners of the Theatre of the Absurd.

The 1969 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Irish author Samuel Beckett (1906–1989) "for his writing, which - in new forms for the novel and drama - in the destitution of modern man acquires its elevation."

The 1954 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the American author Ernest Hemingway (1899–1961) "for his mastery of the art of narrative, most recently demonstrated in The Old Man and the Sea, and for the influence that he has exerted on contemporary style."

The 1948 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to British-American poet Thomas Stearns Eliot (1888–1965) "for his outstanding, pioneer contribution to present-day poetry." Eliot is the fourth British recipient of the prize after John Galsworthy in 1932.

The 1957 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded the French writer Albert Camus (1913–1960) "for his important literary production, which with clear-sighted earnestness illuminates the problems of the human conscience in our times." He is the ninth French author to become a recipient of the prize after Catholic novelist François Mauriac in 1952, and the fourth philosopher after British analytic philosopher Bertrand Russell in 1950.

The 1949 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded the American author William Faulkner (1897–1962) "for his powerful and artistically unique contribution to the modern American novel." The prize was awarded the following year on October 1950. The Nobel Committee for Literature had decided that none of the nominations for 1949 met the criteria as outlined in the will of Alfred Nobel, and the prize was reserved until the following year.

The 1966 Nobel Prize in Literature was divided equally between Shmuel Yosef Agnon (1888–1970) "for his profoundly characteristic narrative art with motifs from the life of the Jewish people" and Nelly Sachs (1891–1970) "for her outstanding lyrical and dramatic writing, which interprets Israel's destiny with touching strength."

The 1902 Nobel Prize in Literature was the second prestigious literary award based upon Alfred Nobel's will, which was given to German historian Theodor Mommsen (1817–1903) "the greatest living master of the art of historical writing, with special reference to his monumental work A History of Rome."

The 1938 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the American author Pearl S. Buck (1892–1973) "for her rich and truly epic descriptions of peasant life in China and for her biographical masterpieces." Buck was the first female American to be awarded the Nobel Prize and the third American recipient following Eugene O'Neill in 1936 and Sinclair Lewis in 1930. She was also the fourth woman to receive the prize.
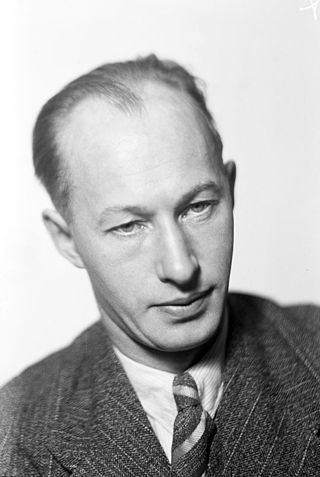
The 1974 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded jointly to Swedish authors Eyvind Johnson (1900–1976) "for a narrative art, farseeing in lands and ages, in the service of freedom" and Harry Martinson (1904–1978) "for writings that catch the dewdrop and reflect the cosmos." The winners were announced in October 1974 by Karl Ragnar Gierow, permanent secretary of the Swedish Academy, and later sparked heavy criticisms from the literary world.

The 1950 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded the British philosopher Bertrand Russell (1872–1970) "in recognition of his varied and significant writings in which he champions humanitarian ideals and freedom of thought." He is the fourth philosopher to become a recipient of the prize after the French analytic-continental philosopher Henri Bergson in 1927, and was followed by the French-Algerian existentialist Albert Camus in 1957. He is also the fifth British author to be awarded.

The 1953 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Sir Winston Churchill (1874–1965) "for his mastery of historical and biographical description as well as for brilliant oratory in defending exalted human values." He is the sixth British writer to receive the prize, coming after the philosopher Bertrand Russell in 1950.

The 1907 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the British writer Rudyard Kipling (1865–1936) "in consideration of the power of observation, originality of imagination, virility of ideas and remarkable talent for narration which characterize the creations of this world-famous author." He is the first English-language writer to receive the prize, and being aged 41, is its youngest recipient to date.

The 1911 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Belgian author Maurice Maeterlinck (1862–1949) "in appreciation of his many-sided literary activities, and especially of his dramatic works, which are distinguished by a wealth of imagination and by a poetic fancy, which reveals, sometimes in the guise of a fairy tale, a deep inspiration, while in a mysterious way they appeal to the readers' own feelings and stimulate their imaginations." He is the first and remains only the Belgian recipient of the prize.
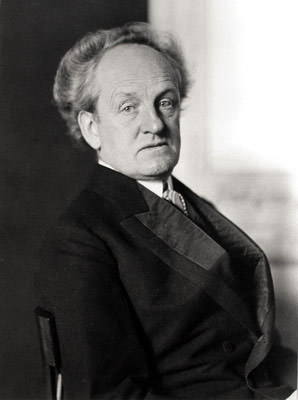
The 1912 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the German dramatist and novelist Gerhart Hauptmann (1862–1949) "primarily in recognition of his fruitful, varied and outstanding production in the realm of dramatic art." He is the fourth German author to become a recipient of the prize after Paul Heyse in 1910.

The 1951 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded the Swedish author Pär Lagerkvist "for the artistic vigour and true independence of mind with which he endeavours in his poetry to find answers to the eternal questions confronting mankind." Lagerkvist is the fourth Swedish recipient of the Nobel Prize in Literature after Lagerlöf in 1909, Von Heidenstam in 1916, and Karlfeldt in 1931.

The 1955 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the Icelandic writer Halldór Kiljan Laxness (1902–1998) "for his vivid epic power which has renewed the great narrative art of Iceland." He is the first and only Icelandic recipient of the Nobel prize in all categories. The literary critic Sveinn Hoskuldsson described him, saying:
"His chief literary works belong to the genre... [of] narrative prose fiction. In the history of our literature Laxness is mentioned beside Snorri Sturluson, the author of "Njals saga", and his place in world literature is among writers such as Cervantes, Zola, Tolstoy, and Hamsun... He is the most prolific and skillful essayist in Icelandic literature both old and new..."

The 1965 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded the Russian novelist Mikhail Sholokhov (1905–1984) "for the artistic power and integrity with which, in his epic of the Don, he has given expression to a historic phase in the life of the Russian people." He is the third Russian-speaking author to become the prize's recipient.

The 1915 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the French author Romain Rolland (1866–1944) "as a tribute to the lofty idealism of his literary production and to the sympathy and love of truth with which he has described different types of human beings." The prize was awarded the following year on November 9, 1916 and he is the third Frenchman who became a Nobel recipient for the literature category.

The 1936 Nobel Prize in Literature was awarded to the American playwright Eugene O'Neill "for the power, honesty and deep-felt emotions of his dramatic works, which embody an original concept of tragedy". The prize was awarded in 1937. He is the second American to become a literature laureate after Sinclair Lewis in 1930.