This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2010) |
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| +... |
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 1972.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(July 2010) |
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| +... |
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 1972.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) movements are social movements that advocate for LGBTQ people in society. Although there is not a primary or an overarching central organization that represents all LGBTQ people and their interests, numerous LGBT rights organizations are active worldwide. The first organization to promote LGBT rights was the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee, founded in 1897 in Berlin.
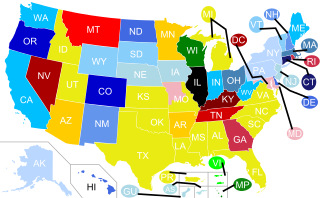
The United States has inherited sodomy laws which constitutionally outlawed a variety of sexual acts that are deemed to be illegal, illicit, unlawful, unnatural and/or immoral from the colonial-era based laws in the 17th century. While they often targeted sexual acts between persons of the same sex, many sodomy-related statutes employed definitions broad enough to outlaw certain sexual acts between persons of different sexes, in some cases even including acts between married persons.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 1976.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the 20th century before 1949.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan face severe challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Afghan members of the LGBT community are forced to keep their gender identity and sexual orientation secret, in fear of violence and the death penalty. The religious nature of the country has limited any opportunity for public discussion, with any mention of homosexuality and related terms deemed taboo.
The Society for Human Rights was an American gay-rights organization established in Chicago in 1924. Society founder Henry Gerber was inspired to create it by the work of German doctor Magnus Hirschfeld and the Scientific-Humanitarian Committee and by the organisation Bund für Menschenrecht by Friedrich Radszuweit and Karl Schulz in Berlin. It was the first recognized gay rights organization in the United States, having received a charter from the state of Illinois, and produced the first American publication for homosexuals, Friendship and Freedom. A few months after being chartered, the group ceased to exist in the wake of the arrest of several of the Society's members. Despite its short existence and small size, the Society has been recognized as a precursor to the modern gay liberation movement.
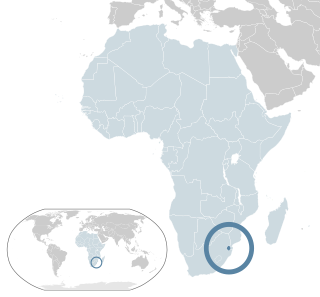
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Eswatini have limited legal rights. According to Rock of Hope, a Swati LGBT advocacy group, "there is no legislation recognising LGBTIs or protecting the right to a non-heterosexual orientation and gender identity and as a result [LGBT people] cannot be open about their orientation or gender identity for fear of rejection and discrimination." Homosexuality is illegal in Eswatini, though this law is in practice unenforced. According to the 2021 Human Rights Practices Report from the US Department of State, "there has never been an arrest or prosecution for consensual same-sex conduct."
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the 1960s.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the 1970s.

A sodomy law is a law that defines certain sexual acts as crimes. The precise sexual acts meant by the term sodomy are rarely spelled out in the law, but are typically understood and defined by many courts and jurisdictions to include any or all forms of sexual acts that are illegal, illicit, unlawful, unnatural and immoral. Sodomy typically includes anal sex, oral sex, manual sex, and bestiality. In practice, sodomy laws have rarely been enforced to target against sexual activities between individuals of the opposite sex, and have mostly been used to target against sexual activities between individuals of the same sex.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Mauritius have expanded in the 21st century, although LGBT Mauritians may still face legal difficulties not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Prior to 2023, sodomy was criminalized by Section 250 of the Criminal Code. However, Mauritius fully decriminalized homosexuality in October 2023. Although same-sex marriage is not recognized in Mauritius, LGBT people are broadly protected from discrimination in areas such as employment and the provision of goods and services, making it one of the few African countries to have such protections for LGBT people. The Constitution of Mauritius guarantees the right of individuals to a private life.
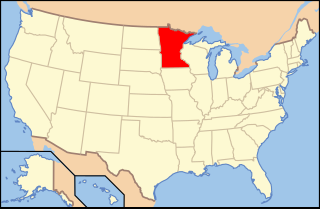
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of Minnesota have the same legal rights as non-LGBTQ people. Minnesota became the first U.S. state to outlaw discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity in 1993, protecting LGBTQ people from discrimination in the fields of employment, housing, and public accommodations. In 2013, the state legalized same-sex marriage, after a bill allowing such marriages was passed by the Minnesota Legislature and subsequently signed into law by Governor Mark Dayton. This followed a 2012 ballot measure in which voters rejected constitutionally banning same-sex marriage.
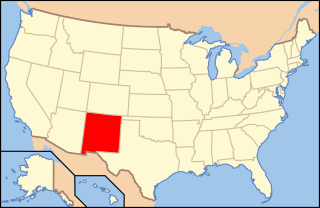
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of New Mexico enjoy the same rights as non-LGBTQ people. New Mexico has seen prominent advances in gay and lesbian rights in recent decades. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1975. Same-sex marriage is legal statewide in New Mexico, as is adoption and access to fertility treatments for lesbian couples. Same-sex couples have had the same rights as heterosexual married couples since 2013. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity is banned statewide in the areas of employment, housing and public accommodations. Additionally, conversion therapy on minors is prohibited in the state.
Lesbian, gay, bisexual transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of Idaho face some legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ people. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in Idaho, and same-sex marriage has been legal in the state since October 2014. State statutes do not address discrimination based on sexual orientation and gender identity; however, the U.S. Supreme Court's ruling in Bostock v. Clayton County established that employment discrimination against LGBTQ people is illegal under federal law. A number of cities and counties provide further protections, namely in housing and public accommodations. A 2019 Public Religion Research Institute opinion poll showed that 71% of Idahoans supported anti-discrimination legislation protecting LGBTQ people, and a 2016 survey by the same pollster found majority support for same-sex marriage.
The U.S. state of Illinois has an active LGBT history, centered on its largest city Chicago, where by the 1920s a gay village had emerged in the Old Town district. Chicago was also the base for the short-lived Society for Human Rights, an early LGBT rights advocacy organization (1924).

LGBTQ history in the United States spans the contributions and struggles of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people, as well as the LGBTQ social movements they have built.

Capital punishment as a criminal punishment for homosexuality has been implemented by a number of countries in their history. It is a legal punishment in several countries and regions, all of which have sharia-based criminal laws, except for Uganda.

The following is a timeline of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) history in the 20th century.

Some or all sexual acts between men, and less frequently between women, have been classified as a criminal offense in various regions. Most of the time, such laws are unenforced with regard to consensual same-sex conduct, but they nevertheless contribute to police harassment, stigmatization, and violence against homosexual and bisexual people. Other effects include exacerbation of the HIV epidemic due to the criminalization of men who have sex with men, discouraging them from seeking preventative care or treatment for HIV infection.