Related Research Articles
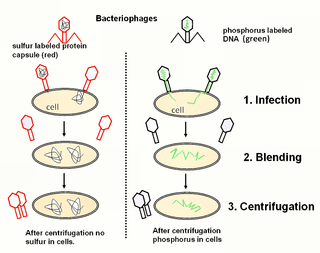
The Hershey–Chase experiments were a series of experiments conducted in 1952 by Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase that helped to confirm that DNA is genetic material.

James Ephraim Lovelock was an English independent scientist, environmentalist and futurist. He is best known for proposing the Gaia hypothesis, which postulates that the Earth functions as a self-regulating system.
The year 1911 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1914 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1916 involved a number of significant events in science and technology, some of which are listed below.

Brian David Josephson is a British theoretical physicist and professor emeritus of physics at the University of Cambridge. Best known for his pioneering work on superconductivity and quantum tunnelling, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1973 for his prediction of the Josephson effect, made in 1962 when he was a 22-year-old PhD student at Cambridge University. Josephson is the first Welshman to have won a Nobel Prize in Physics. He shared the prize with physicists Leo Esaki and Ivar Giaever, who jointly received half the award for their own work on quantum tunnelling.
The year 2004 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1923 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

The year 1945 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1997 in science and technology involved many significant events, listed below.
The year 1929 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1970 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, is a public research university located in Moscow Oblast, Russia. It prepares specialists in theoretical and applied physics, applied mathematics and related disciplines.

Robert Coleman Richardson was an American experimental physicist whose area of research included sub-millikelvin temperature studies of helium-3. Richardson, along with David Lee, as senior researchers, and then graduate student Douglas Osheroff, shared the 1996 Nobel Prize in Physics for their 1972 discovery of the property of superfluidity in helium-3 atoms in the Cornell University Laboratory of Atomic and Solid State Physics.
Stephen Robertson is a British computer scientist. He is known for his work on probabilistic information retrieval together with Karen Spärck Jones and the Okapi BM25 weighting model.

David Jeffery Wineland(born February 24, 1944) is an American Nobel-laureate physicist at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). His work has included advances in optics, specifically laser-cooling trapped ions and using ions for quantum-computing operations. He was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize in Physics, jointly with Serge Haroche, for "ground-breaking experimental methods that enable measuring and manipulation of individual quantum systems".

Richard Edward Taylor,, was a Canadian physicist and Stanford University professor. He shared the 1990 Nobel Prize in Physics with Jerome Friedman and Henry Kendall "for their pioneering investigations concerning deep inelastic scattering of electrons on protons and bound neutrons, which have been of essential importance for the development of the quark model in particle physics."

Purinergic signalling is a form of extracellular signalling mediated by purine nucleotides and nucleosides such as adenosine and ATP. It involves the activation of purinergic receptors in the cell and/or in nearby cells, thereby regulating cellular functions.
References
- ↑ Singer, S. J.; Nicolson, G. L. (1972). "The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes". Science . 175 (4023): 720–31. doi:10.1126/science.175.4023.720. PMID 4333397. S2CID 83851531.
- ↑ G., Burnstock (1972). "Purinergic nerves". Pharmacological Reviews . 24 (3): 509–81. PMID 4404211.
- ↑ Jackson, David A.; Symons, Robert H; Berg, Paul (1972). "Biochemical Method for Inserting New Genetic Information into DNA of Simian Virus 40: Circular SV40 DNA Molecules Containing Lambda Phage Genes and the Galactose Operon of Escherichia coli". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 69 (10): 2904–2909. Bibcode:1972PNAS...69.2904J. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2904 . PMC 389671 . PMID 4342968.
- ↑ Eldredge, N.; Gould, S. J. (1972). "Punctuated equilibria: an alternative to phyletic gradualism". In Schopf, T. J. M. (ed.). Models in Paleobiology. San Francisco: Freeman, Cooper. pp. 82–115.
- ↑ "Cray Timeline" (PDF). Cray. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-03-31. Retrieved 2011-04-04.
- ↑ Moore, Michael E.; Novak, Jeannie (2010). Game Industry Career Guide. Delmar: Cengage Learning. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-4283-7647-2.
In 1966, Ralph H. Baer ... pitched an idea ... to create interactive games to be played on the television. Over the next two years, his team developed the first video game system—and in 1968, they demonstrated the "Brown Box," a device on which several games could be played and that used a light gun to shoot targets on the screen. After several more years of development, the system was licensed by Magnavox in 1970 and the first game console system, the Odyssey, was released in 1972 at the then high price of $100.
- ↑ Thompson, Ken; Ritchie, Dennis M. (June 12, 1972). UNIX Programmer's Manual, Second Edition (PDF). Bell Telephone Laboratories. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-10-06.
- ↑ Spärck Jones, K. (1972). "A Statistical Interpretation of Term Specificity and Its Application in Retrieval". Journal of Documentation. 28: 11–21. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.115.8343 . doi:10.1108/eb026526. S2CID 2996187.
- ↑ Pease, Bob. "The origin of the WOM – the "Write Only Memory"". National Semiconductor. Archived from the original on 2011-09-10. Retrieved 2012-11-11.
- ↑ Chlupáč, Ivo; Hladil, Jindrich (January 2000). "The global stratotype section and point of the Silurian-Devonian boundary". CFS Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg. Retrieved 2020-12-07.
- ↑ "About The Ecologist". The Ecologist . Retrieved 2012-02-10.
- ↑ Lovelock, J. E. (August 1972). "Gaia as seen through the atmosphere". Atmospheric Environment. 6 (8): 579–580. Bibcode:1972AtmEn...6..579L. doi:10.1016/0004-6981(72)90076-5. ISSN 0004-6981.
- ↑ Gorenstein, D. (1979). "The classification of finite simple groups. I. Simple groups and local analysis". Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society. New Series. 1 (1): 43–199. doi: 10.1090/S0273-0979-1979-14551-8 . ISSN 0002-9904. MR 0513750. Appendix.
- ↑ Blair, Byron E., ed. (1974). Time and Frequency: Theory and Fundamentals (PDF). National Bureau of Standards. p. 32.
- ↑ Graterol, Javier (18 May 2009). "La astronomía es una ciencia apasionante". El Nacional.