Related Research Articles
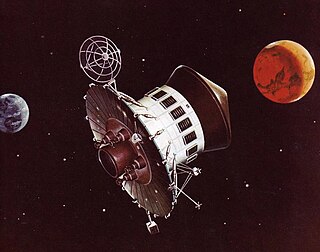
The Voyager Mars Program was a planned series of uncrewed NASA probes to the planet Mars. The missions were planned, as part of the Apollo Applications Program, between 1966 and 1968 and were scheduled for launch in 1974–75. The probes were conceived as precursors for a crewed Mars landing in the 1980s.
The year 1999 in science and technology involved some significant events.
The year 1920 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1998 in science and technology involved many events, some of which are included below.
The year 1922 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1969 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 2004 in science and technology involved some significant events.
Daniel Gray Quillen was an American mathematician. He is known for being the "prime architect" of higher algebraic K-theory, for which he was awarded the Cole Prize in 1975 and the Fields Medal in 1978.

The year 1945 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1928 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1976 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1975 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.
The year 1972 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below.

Wallach is a tiny lunar impact crater located in the eastern Mare Tranquillitatis. It was named after German chemist and Nobel laureate Otto Wallach in 1979. It is a circular, bowl-shaped feature with a negligible interior floor; the inner walls just slope down to the midpoint of the crater. Wallach is located to the northeast of the crater Maskelyne, near some low ridges in the lunar mare. It was previously identified as Maskelyne H before being given a name by the IAU.

Voyage is a 1996 hard science fiction novel by British author Stephen Baxter. The book depicts a crewed mission to Mars as it might have been in another timeline, one where John F. Kennedy survived the assassination attempt on him on 22 November 1963. Voyage won a Sidewise Award for Alternate History, and was nominated for the Arthur C. Clarke Award in 1997.

Albert Roach Hibbs was an American mathematician and physicist affiliated with the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). He was known as "The Voice of JPL" due to his gift for explaining advanced science in simple terms. He helped establish JPL's Space Science Division in 1960 and later served as its first chief. He was the systems designer for Explorer 1, the USA's first satellite, and helped establish the framework for exploration of the Solar System through the 1960s. Hibbs qualified as an astronaut in 1967 and was slated to be a crew member of Apollo 25, but he ultimately did not go to the Moon due to the Apollo program ending after the Apollo 17 mission in 1972.
The year 2006 in science and technology involved some significant events.

Martin Karplus is an Austrian and American theoretical chemist. He is the Director of the Biophysical Chemistry Laboratory, a joint laboratory between the French National Center for Scientific Research and the University of Strasbourg, France. He is also the Theodore William Richards Professor of Chemistry, emeritus at Harvard University. Karplus received the 2013 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, together with Michael Levitt and Arieh Warshel, for "the development of multiscale models for complex chemical systems".

Brian Todd O'Leary was an American scientist, author, and NASA astronaut candidate. He was part of NASA Astronaut Group 6, a group of scientist-astronauts chosen with the intention of training for the Apollo Applications Program.

The Starmus International Festival is an international gathering focused on celebrating astronomy, space exploration, music, art, and the natural sciences. It was founded by astronomer / amateur musician Garik Israelian and musician / astrophysicist Brian May. The festival has featured multiple well-known astronauts and astronomers.
References
- ↑ Howarth, Francis G. (1972-01-21). "Cavernicoles in Lava Tubes on the Island of Hawaii". Science . 175 (4019): 325–326. Bibcode:1972Sci...175..325H. doi:10.1126/science.175.4019.325. JSTOR 1733505. PMID 17814543. S2CID 36219772.
- ↑ O'Keefe, John; Dostrovsky, Jonathan (1971). "The hippocampus as a spatial map: preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat". Brain Research . 34 (1): 171–175. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(71)90358-1. PMID 5124915.
- ↑ Binder, Marc D (2009). Encyclopedia of Neuroscience . Springer. p. 3166. ISBN 978-3-540-23735-8.
- ↑ Hart, Michael (August 1992). "The History and Philosophy of Project Gutenberg". Project Gutenberg. Retrieved 2011-10-05..
- ↑ Tomlinson, Ray. "The First Network Email". Archived from the original on 2006-05-06. Retrieved 2011-10-05.
- ↑ Cook, Stephen (1971). "The complexity of theorem proving procedures". Proceedings of the Third Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing. pp. 151–158. doi:10.1145/800157.805047. ISBN 9781450374644. S2CID 7573663.
- ↑ Quillen, Daniel (1971). "The Adams Conjecture". Topology . 10: 67–80. doi: 10.1016/0040-9383(71)90018-8 . ISSN 0040-9383. MR 0279804.
- ↑ Takiff, S. J. (1971). "Rings of invariant polynomials for a class of Lie algebras". Transactions of the American Mathematical Society . 160: 249–262. doi: 10.2307/1995803 . ISSN 0002-9947. JSTOR 1995803. MR 0281839.
- ↑ Beckmann, E. C. (2006). "CT scanning: the early days". British Journal of Radiology. 79 (937): 5–8. doi:10.1259/bjr/29444122. PMID 16421398.
- ↑ Bywaters, E. G. L. (March 1971). "Still's disease in the adult". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases . 30 (2): 121–33. doi:10.1136/ard.30.2.121. PMC 1005739 . PMID 5315135.
- ↑ "Americas region is declared the world's first to eliminate rubella". WHO. 2015-04-30. Archived from the original on 2015-05-18. Retrieved 2015-04-30.
- ↑ Kielan-Jaworowska, Z.; Barsbold, R. (1972). "Narrative of the Polish-Mongolian Palaeontological Expeditions, 1967-1971" (PDF). Palaeontologia Polonica. 27: 1−12. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2024-05-20.
- ↑ Penrose, R.; Floyd, R. M. (1971). "Extraction of Rotational Energy from a Black Hole". Nature Physical Science. 229 (6): 177. Bibcode:1971NPhS..229..177P. doi:10.1038/physci229177a0.